Content
- What is atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries
- Symptoms
- Causes of the disease
- Disease classification
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries
- Drug treatment
- Surgery
- Possible complications and prognosis
- Video about BCA non-stenotic atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is characterized by impaired arterial patency as a result of the formation of fatty deposits inside them. Depending on how narrowed the lumen in the vessels, the disease is divided into non-stenosing and stenosing forms. The most dangerous is damage to the arteries supplying the brain (brachiocephalic or short BCA).
What is atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries
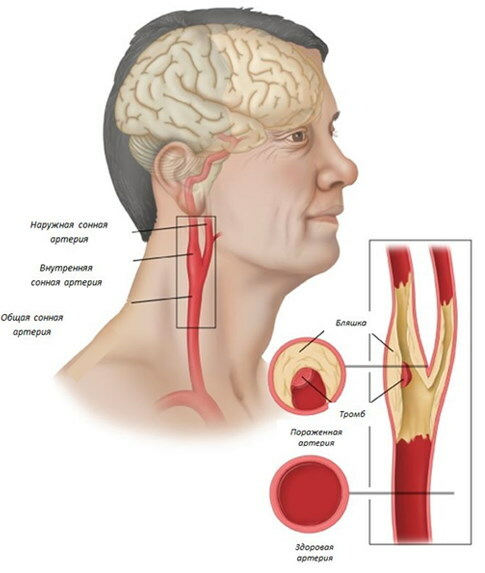
The brachiocephalic arteries are the vessels that carry blood to the brain, head and shoulder girdle tissues. They branch off from the main aorta and are divided into the vertebral, carotid, and subclavian arteries. In BCA atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques disrupt the patency of the listed vessels, as a result, the likelihood of developing cerebrovascular accident (stroke) is high.
The main reason for the development of BCA atherosclerosis is the gradual deposition of cholesterol plaques inside the arteries, as a result of which vascular patency worsens and blood flow is disturbed. In its advanced form, the disease can lead to a complete blockage of the artery. As a result, the pathology becomes the cause of the development of a stroke, and as a result, a person may die or remain disabled (in the absence of blood supply, vital parts of the brain die).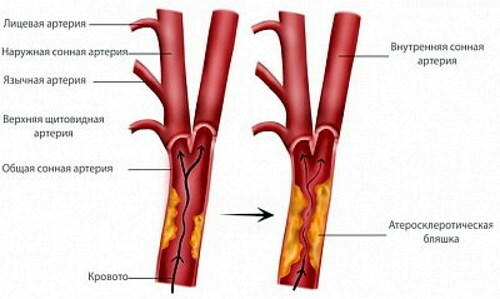
Interesting to know. It is believed that the disease begins to develop in people after 40 years, and after 55, the disease is detected in 90% of the population. In this regard, it is recommended after 40 years to regularly examine BCA, since it is easier to eliminate atherosclerosis than to deal with the consequences of a stroke.
Symptoms
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of BCA can be suspected if a person has symptoms:
- heaviness in the head;
- unreasonable dizziness and headaches, which are often worse with sudden movements or mental stress;
- instability of the emotional state. It can be manifested by increased mental excitability or vice versa by apathy and depression;
- a sharp and unreasonable change of mood from laughter to crying;
- a gradual decrease in concentration and memory. The development of memory gaps is not excluded;
- a person may feel light-headed and even faint;
- tinnitus or hum in the head;
- hearing impairment;
- temporary speech disorders, as well as voice changes;
- violation of the swallowing reflex;
- deterioration of vision. It can manifest itself in flashes before the eyes, a person can see "flies" or "stars";
- rapid fatigue, which leads to a decrease in performance;
- sensation of pulsation of blood vessels in the temples. To identify the symptom, it is enough to put your fingers on the temporal cavity;
- lack of coordination of movement or loss of balance;
- deterioration of the process of falling asleep and sleep;
- facial expressions become less pronounced;
- chest pain;
- the limbs are constantly cold, and a person can also feel their numbness.
In cases where a person does not have chronic pathologies that can cause the listed symptoms, then it is necessary to consult a doctor for an examination.
With an advanced form of BCA atherosclerosis, the symptomatology of the pathology is brighter:
- a person forgets old memories and may even not recognize relatives;
- acquired skills are lost, the patient can forget how to eat, dress, forgets words;
- a person gets lost in familiar places;
- pronounced violation of gait and gestures;
- frequent loss of consciousness;
- frequent and severe headaches;
- frequent nausea or vomiting.
Important. The brighter the listed signs appear, the more neglected the form of the disease, the less chances to completely restore the state of the damaged brain tissue.
Causes of the disease
BCA arthrosis is not a causeless disease.
The development of pathology is accompanied by the following provoking factors:
| List of causes of the disease | Description of factors |
| Smoking, alcohol, drugs | Bad habits impair metabolic processes, cause an increase in pressure, as well as a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels. |
| Regular pressure increase | Due to hypertension, the vessels wear out quickly. |
| High levels of bad cholesterol in the blood | The reason for the increase in the indicator may be unhealthy diet, a sedentary lifestyle. |
| Taking hormonal contraception | The drugs change the hormonal background, the process can be accompanied by pressure surges, metabolic disorders. All this provokes a deterioration in the state of blood vessels. |
| Menopause in women | During this period, a woman undergoes a strong hormonal change. |
| Diabetes | The disease proceeds with a pronounced violation of metabolic processes and the state of blood vessels. |
| Overweight | Overweight people have an increased number of fat cells in the body. |
| Age | The older the person, the more the fabrics are worn out. In addition, older people often have chronic pathologies that increase the likelihood of developing the disease. |
| Regular stress | Stress is accompanied by an increase in pressure, a deterioration in metabolic processes and a decrease in vascular tone. |
| Heredity | In this case, in the absence of other provoking factors, the likelihood of developing the disease is unlikely. |
| Presence of intrauterine abnormalities in the state of the vessels of the head or neck | The reason for the development of the deviation may be the mother's bad habits during pregnancy, the use of dangerous medications, as well as the mother's illness in severe form in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. |
If a person has several reasons for the development of atherosclerosis, then the likelihood of developing the disease increases.
It's important to know. The most important reason for the development of atherosclerosis is a violation of fat metabolism in the body.
Disease classification
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of BCA is one of the forms of pathology. Depending on the localization of the damaged area of the artery and the degree of neglect, the disease has the following divisions.
Classification of atherosclerosis by localization:
- damage to the arteries of the extracranial departments. The state of the vessels branching into the vertebral and subclavian zone is disturbed;
- damage to the arteries of the brain. The disease develops in the carotid arteries and in the vessels of the brain.
The latter type is more dangerous, since impaired vascular patency directly affects the nutrition of brain tissues and can lead to their rapid death.
Classification of atherosclerosis according to the degree of neglect:
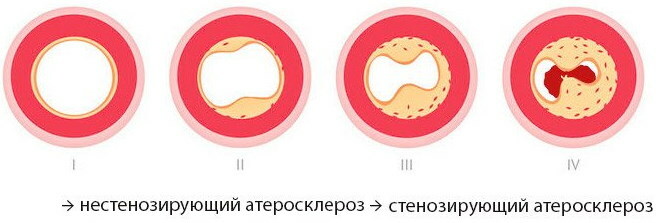
- non-senosing. Cholesterol plaques cover approximately 30-45% of the vessel diameter. In this case, the brain tissue receives less nutrients and oxygen, but they are sufficient to nourish the brain tissue;
- stenosing. The diameter of the arteries is blocked by approximately 50-90%. The brain tissues are severely deficient in oxygen and nutrients. Additionally, cholesterol plaques often break off, moving into the capillaries and clogging them. As a result, tissue nutrition in this area of the brain stops.
The last form of severity is dangerous by the development of disability and even death.
Diagnostics
BCA atherosclerosis is difficult to detect without a complete examination. If the development of the disease is suspected, a complete diagnosis of the vessels is required in order to identify the area of the affected arteries (brain, subclavian zone, spine) and the severity of the pathology (non-stenosing or stenosing atherosclerosis).
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries is performed according to the following algorithm:
- The doctor asks the patient about the presence of symptoms characteristic of BCA atherosclerosis, and also finds out the presence of factors that provoke the development of pathology.
- The specialist studies the hereditary factor that affects the development of atherosclerosis.
- Further, an external examination of the patient is carried out, and the doctor must also exclude diseases with similar symptoms.
- Listening to the patient's heart to exclude possible organ diseases. It is possible to precisely exclude heart pathologies with the help of hardware examinations.
- Using a phonendoscope, the doctor listens to the carotid arteries in the neck. The presence of noise allows one to suspect the development of BCA atherosclerosis.
- Laboratory examinations are prescribed. Blood and urine tests help determine the level of cholesterol, glucose and platelets, as well as assess the general condition of the patient.
- At the end, a hardware inspection is performed. It allows you to identify the affected artery and the degree of blockage of the vessel lumen.
From the methods of instrumental examination, the following can be assigned:
- electrocardiogram. ECG allows you to assess the condition and work of the heart;
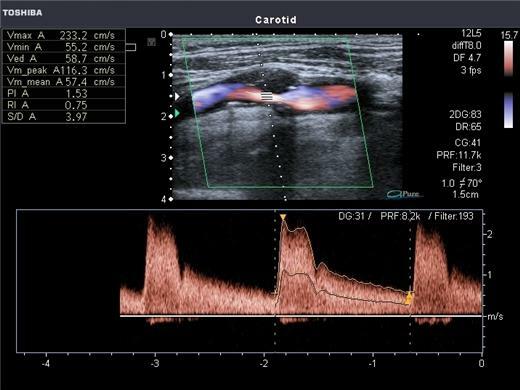
- ultrasound examination of BCA. With the help of ultrasound waves, it is possible to detect the presence of cholesterol plaques, blood clots in the vessels, as well as the percentage of narrowing of the arteries;
- Doppler ultrasound. The method allows you to determine the speed of blood flow through the vessels, as well as the state of the vessel walls;
- magnetic resonance angiography. With the help of a special magnet, the doctor determines the activity of the tissues of the brain and arteries. In addition, the procedure allows you to identify even small cholesterol formations in the arteries and determine the places affected by a stroke;
- computed tomography in angio mode. The method is more popular than radiography, since the radiation dose is less. CTA allows you to study the lumens of the vessels of the carotid and cerebral arteries, it also helps to detect even small cholesterol plaques, thrombosis and brain sites affected by cerebral impairment blood circulation;
-
cerebral angiography. The procedure is considered the best for examining the carotid arteries (their condition, patency and degree of damage). The process consists in the introduction of a special catheter and contrast agent into the carotid artery (through a puncture).
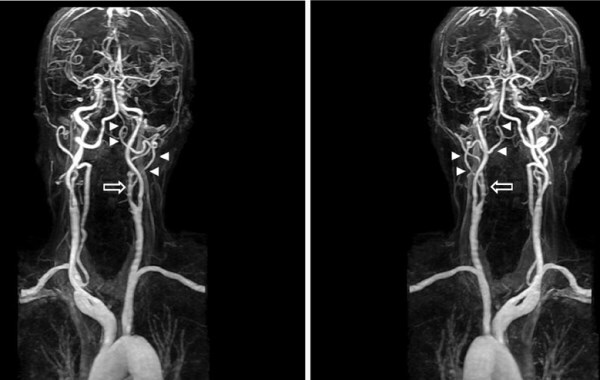
The listed hardware examinations allow:
- determine the percentage of narrowing of the lumen of the arteries;
- assess the rate of blood circulation through the arteries;
- identify the affected area in the artery;
- assess the condition of the intracerebral arteries;
- to study the state of brain tissues and the degree of their damage;
- assess the functioning of the brain;
- determine the method of treatment and how dangerous the operation can be if therapy is possible only by surgery.
Hardware examination allows you to assess the possible prognosis of the selected treatment.
After receiving the results of the examination, the doctor can refer the patient to a narrow specialist:
| List of specialists | What the doctor does |
| Angioneurologist | Treats carotid atherosclerosis. |
| Vascular surgeon | Specializes in the study of the condition of the veins and arteries. |
| Cardiologist | Evaluates the state of the heart, if the patient suspects acute coronary syndrome. |
| Angiosurgeon | The patient is referred to a specialist for stenosing lesions of the arteries of the neck. |
| Neurosurgeon | The doctor specializes in the study of lesions and the treatment of intracranial arteries. |
| Hematologist | A specialist is needed if blood clotting problems are identified. |
| Endocrinologist | The patient is sent to a specialist in diabetes mellitus. |
In addition, the patient may be referred to a psychiatrist to rule out the presence of mental illness.
Treatment of atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of BCA, depending on the neglect and the site of the lesion, can be eliminated medically or surgically.
But regardless of the prescribed method of therapy, the patient must, in addition, observe dietary nutrition, which is as follows:
- exclude from the diet fatty foods / products (meat, milk, cheeses), fast foods (they most often provoke an increase in blood cholesterol), meat products (kebabs, sausages, smoked meats) and canned food;
- increase the amount of fresh vegetables and fruits in the menu, lean meat and fish should also be present in the diet. It is recommended to replace coffee with herbal teas;
- quit smoking, reduce the amount of alcohol.
When following a diet for atherosclerosis, it is important to exclude or greatly reduce the amount of fat and salt in the menu, which are the main provocateurs of the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the arteries. In addition, you should try to avoid stress and maintain physical activity.
Important. The diet is prescribed for life, even after recovery, in order to avoid re-deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the arteries.
Drug treatment
If the disease is not started and cholesterol plaques block less than 50% of the lumen, then the doctor may prescribe drug therapy.
For treatment, the following can be prescribed:
-
anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. The funds help thin the blood, preventing the development of thrombosis. The group of these drugs includes: acetylsalicylic acid, warfarin, clopidogrel. Taking blood thinners can be lifelong;
Clopidogrel - medicines that activate blood flow and dilate blood vessels. Funds are prescribed, but only after excluding the likelihood of thrombosis, since due to increased blood flow, a thrombus can break off and clog the capillaries. The group of drugs that activate blood flow include: Cavinton, Actovegin;
- medicines that eliminate vascular spasms. Spasms, in addition to plaques of cholesterol, constrict the lumen of the arteries, disrupting blood flow. The list of funds includes: Barvobal, Galidor, Krategus;
- statins and fibrates. The drugs normalize blood cholesterol levels. But due to the large list of side effects, the funds cannot be used without a doctor's prescription. The group of these medicines includes: ezetrol, rosuvastin, alirocumab;
- medicines to lower blood pressure (atherosclerosis is often accompanied by increased blood pressure). The group of medicines includes: Enalapril, Lisinopril, Vero-drotaverin;
- drugs that affect the production of bile. Means prevent the absorption of large amounts of cholesterol.
Important. All the drugs described should be prescribed by a doctor, self-medication can not only not give improvements, but also provoke a deterioration in well-being.
Surgery
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of BCA in advanced form (cholesterol plaques block more than 70% of the lumen of the arteries) can only be eliminated by surgery.
Depending on the general condition of the patient, the location of the cholesterol plaque may be prescribed one of the following interventions:
-
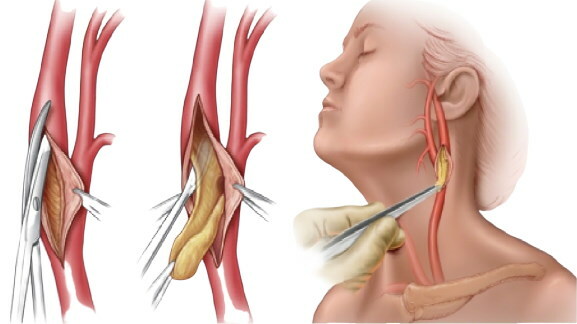
open operation. The surgeon makes an open incision at the site of the plaque formation. Next, the specialist cuts out the damaged area, after which the removed area is replaced or the artery is sutured. The operation is distinguished by its high efficiency, but also by the presence of a high risk of complications;
-
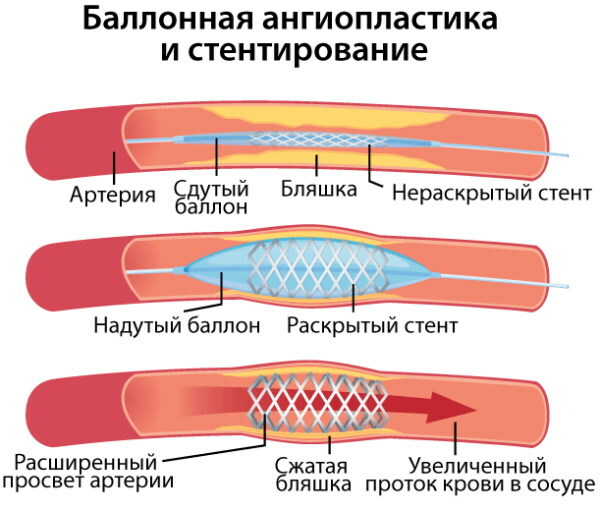
stenting. With the help of a catheter and an X-ray machine, a metal frame is installed in the affected area. The advantage of the operation is the low trauma, but at the same time the frame is gradually overgrown with cholesterol plaques, as a result, a second operation may be required;
- carotid endarterectomy. Under local anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision in the skin and arteries, and removes the cholesterol plaque with a special device. After that, the artery and the incision in the skin are sutured. The operation is distinguished by its high efficiency, but due to open intervention, there is a high risk of complications;
- extra-intracranial vascular microanastomosis. During surgery, the surgeon installs a shunt (it is usually made from an artery taken from the patient's arm or leg) and sutures it above and below the affected area of the vessel. As a result, blood enters the brain bypassing the affected area. The operation is considered to be as efficient as possible.
The choice of the type of operation is determined by the surgeon. The doctor selects the most accessible and safe method.
Possible complications and prognosis
Before prescribing treatment (medical or surgical), the doctor should warn the patient about the development of possible complications, and also voices what results can be achieved by the chosen method therapy.
With the correct administration of medicines, or as a result of a successful operation, the patient's blood flow is restored. As a result, the risk of developing a stroke is reduced, and as a result, the likelihood of brain tissue dying off decreases.
But even the correct intake of medications and a successfully performed surgical intervention is dangerous for the possible development of complications:
- due to taking blood thinning medications, internal bleeding may develop;
- some medications can cause disruption of the digestive tract, especially a heavy load on the liver;
- with surgical intervention, the likelihood of infection is not excluded.
One of the main complications after therapy (especially with surgery) is the likelihood of re-clogging of the artery with cholesterol plaques. In this case, another area of the vessel (not the one on which the operation was performed) may be affected.
It's important to know. The effectiveness of therapy depends on the following factors:
- the patient's age. The younger the patient, the higher the chance of a complete recovery;
- neglect of the disease. The earlier treatment is started, the less the likelihood of complications after therapy, and the greater the likelihood of complete restoration of blood supply in the damaged artery;
- timeliness and modernity of the treatment used. In some cases, after learning about the disease, patients postpone treatment or save on medicines;
- complete elimination of contraindications before starting therapy;
- the presence of chronic diseases.
In this regard, doctors recommend that you regularly undergo an examination of the arteries after 40 years or if there is a predisposition to this pathology.
Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries is one of the most dangerous diseases. Since, due to a violation of the patency of blood vessels, the nutrition of the brain tissues worsens. And with a complete blockage of the BCA, the death of brain tissue is noted, which often ends in disability or death. The least safe and treatable form of the disease is non-stenotic.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Video about BCA non-stenotic atherosclerosis
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries:



