Content
- The concept of especially dangerous infections, which diseases were included in the group initially
- Groups of especially dangerous infections
- Diseases with an unusual course of the disease that can affect health
- Smallpox
- Flu
- Polio
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
- Diseases that affect health and spread rapidly
- Cholera
- Pneumonic plague
- Yellow fever
- Hemorrhagic fevers
- Dengue fever
- Rift Valley Fever
- Meningococcal infection
- anthrax
- Tularemia
- ROI classification
- Quarantine infections
- Methods for diagnosing AOI
- Prophylaxis
- Video about especially dangerous infections
Infectious diseases are dangerous to thosethat are transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, and for the purpose of treatment, it is required to correctly identify the pathogen, otherwise the therapy will not be effective. In addition, there is a group of diseases that are under special control, since infection with them carries an epidemiological danger.
The concept of especially dangerous infections, which diseases were included in the group initially
Especially dangerous infections (in abbreviated form of OI) are diseases that are severe, spread quickly and Moreover, even the availability of treatment does not guarantee a complete recovery of the patient (the patient is more often disabled or dies). This group of diseases is conditional and carries an epidemiological hazard.
Initially, the group of these diseases, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) dated July 26, 1969, included only 5 diseases:
- plague. The pathogen most often affects the lymphatic and pulmonary systems, but other organs can also be infected;
- cholera. The disease is localized in the intestine;
- anthrax. The pathogen affects the skin, but infection can also develop in the lungs and intestines;
- typhus. This is a group of infectious diseases in which the disease affects the nervous and cardiovascular systems;
- relapsing fever. The pathogen enters the circulatory and nervous systems.
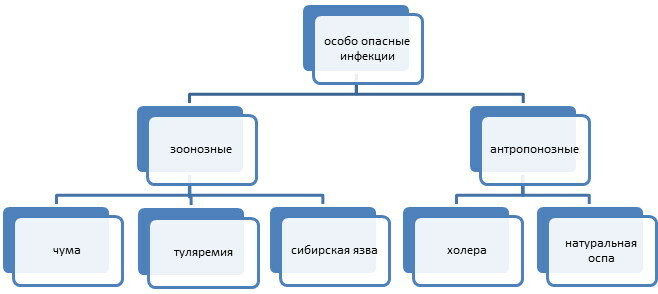 But in 1970 relapsing fever and typhus were removed from the OID list. As a result, in 1981, only 3 diseases were included in the list of especially dangerous infections. But gradually the list of diseases was replenished, and by 2021 the All-World Health Organization includes more than 100 diseases in this list. At the same time, in each region, the list of OIs can be supplemented with diseases that are characteristic of this region.
But in 1970 relapsing fever and typhus were removed from the OID list. As a result, in 1981, only 3 diseases were included in the list of especially dangerous infections. But gradually the list of diseases was replenished, and by 2021 the All-World Health Organization includes more than 100 diseases in this list. At the same time, in each region, the list of OIs can be supplemented with diseases that are characteristic of this region.
Groups of especially dangerous infections
The general group of especially dangerous infections is conditionally divided into 2 subgroups:
| List of subgroups | Subgroup description |
| The first | Diseases that are seriously harmful to health and occur with specific symptoms. |
| The second | Diseases that are severe and spreading rapidly. |
Below are the most common and dangerous diseases from these groups, with a brief description.
Diseases with an unusual course of the disease that can affect health
Highly dangerous infections are diseases that are difficult to identify by symptoms, as they can occur with unusual symptoms. For an accurate diagnosis, laboratory tests are required to identify the pathogen.
Smallpox
Smallpox (smallpox) is believed to be eradicated, but there is a possibility that the infection can be stored in classified laboratories, and used as a biological weapons. In this regard, the WHO did not exclude the disease from the OOI list.
The cause of the development of the disease is a virus, the type of which depends on the type of smallpox. The most dangerous causative agent of the disease is "Variola major". The virus is transmitted through airborne droplets, through household items (dishes, bedding, toys, etc.) so on) by penetration into the body through the skin, and also gets to the fetus (in pregnant women) through the placenta.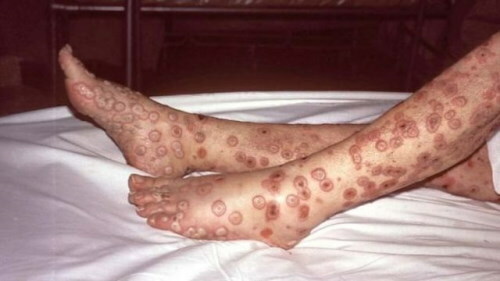
You can suspect an infection by the symptoms:
- severe general intoxication of the body (severe headaches and muscle pains, a rapid rise in temperature to 39-40 degrees, vomiting and other signs of body poisoning with toxins that the pathogen releases in the process life activity);
- severe pain arising in the region of the sacrum, as well as the lower back;
- specific rashes on the skin, mainly in the lower abdomen, on the thighs (inner part) and mucous membranes.
After the virus enters the body, symptoms may appear after 8-15 days, including rashes that appear within two days (then the rash begins to fester and dry out). The ripening period of the rash is most dangerous in smallpox. The patient is contagious for about 30-40 days.
Smallpox is dangerous with a high probability of death (from 40 to 90%). In case of recovery, the patient has a partial or complete loss of vision, the formation of deep scars or ulcers on the skin and mucous membranes, at the site of the rash. The sick person acquires lifelong immunity to the disease.
Flu
The AOI list includes influenza caused by a new subtype of the virus (avian influenza). The pathogen is transmitted mainly from migratory waterfowl. Human infection occurs when hygiene rules are not followed during poultry care, as well as when eating poultry meat that has undergone an incomplete heat treatment.
The main signs of infection are:
- temperature reaching 39 degrees in revenge. At the same time, it is difficult to bring it down;
- severe inflammation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract;
- classic flu symptoms, accompanied by an intolerable headache;
- the development of pneumonia of a viral nature.
The period of manifestation of symptoms of infection can be from 1 to 7 days. At the same time, severe respiratory failure can manifest itself as early as 6-8 days, after the onset of the first symptoms of the disease (the infection can also affect the kidneys, brain, liver).
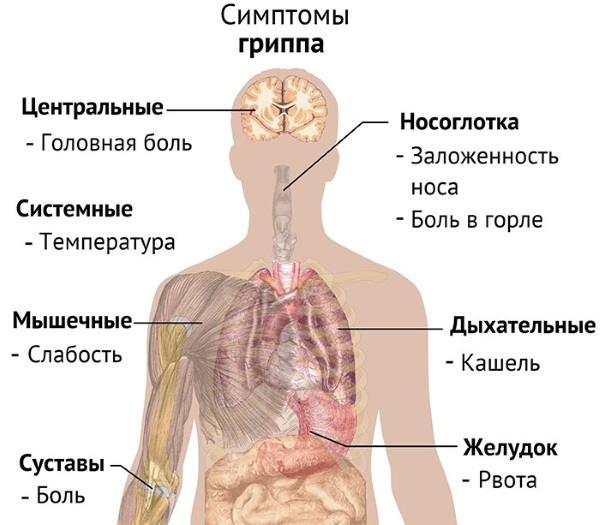
Avian influenza is included in the AOI group, since the probability of a fatal outcome is about 60-80% (especially in cases where the disease has penetrated the lungs).
Polio
The AOI list includes a type of poliomyelitis caused by wild poliovirus. The pathogen enters the body mainly from dirty hands, through dirty water or food, and can also penetrate from an infected person to a healthy person by airborne droplets.
The main signs of the disease are:
- temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- abdominal pain and indigestion;
- temporary (can gradually turn into permanent) muscle paralysis. Moreover, paralysis can be not only of the extremities, it is possible to violate the act of swallowing, speech, but the most dangerous is the paralysis of the muscles of the diaphragm, as a result, the patient cannot breathe himself;
- severe sore throat and headaches.
Symptoms of infection may appear within 2-35 days. The first signs of paralysis can be observed one day after the onset of the first signs of the disease. Also, poliomyelitis can be asymptomatic, while the patient will secrete an infection and infect healthy people.
Mortality from polio infection is approximately 20-30%. The disease is more dangerous with complete paralysis or limbs, which often remain lifelong, and can also cause the development of meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain).
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
SARS (SARS or coronavirus) is a viral disease caused by SARS-CoV is transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as through objects and products that have come into contact with infection.
You can suspect an infection by the symptoms:
- temperature rise to 38 degrees and above;
- intolerable headache that cannot be eliminated with drugs;
- unproductive severe cough and choking;
- severe muscle pain.
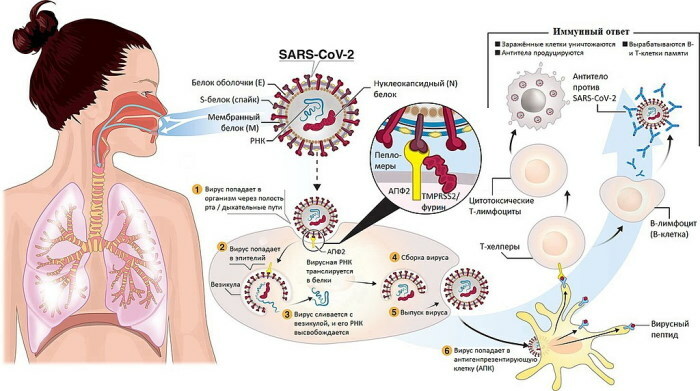
The first signs of infection appear within 2-10 days after infection. After the first signs appear, the disease progresses over a period of 10-20 days. Moreover, even after the symptoms of the disease disappear, a person can be contagious for about 30 more days.
The disease is dangerous with a high death rate (approximately 20-50%), as well as the fact that after recovery, the patient has violation of the activity of the cardiovascular system, memory impairment, in addition, chronic diseases are exacerbated, which can be suppressed hard.
Important. The disease bears the greatest danger to patients over 50 years old.
Diseases that affect health and spread rapidly
Particularly dangerous infections are diseases with a rapid spreading phase, affecting not only cities, but also entire regions at once, and sometimes countries. Therefore, it is important to have time to timely identify the disease before it turns into an epidemic.
Cholera
The cause of the development of the disease is the penetration of the bacteria "Vibrio cholerae" into the intestine. The entry of the pathogen into the body occurs mainly through infected waters, less often infection occurs through household items, dirty hands and food.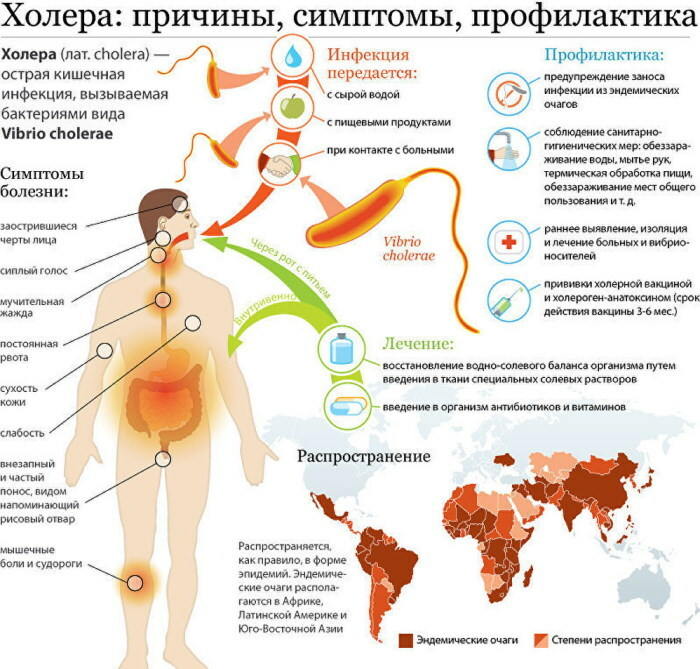
When infected with cholera, symptoms are more common:
- lowering the temperature;
- profuse vomiting and diarrhea, which lead to rapid dehydration;
- severe dryness of the mucous membranes;
- sinking eyes.
The first symptoms of cholera can appear both 5 hours after infection and 5 days later. After the infection begins to enter the body, the patient may die within 2 days, as the disease develops rapidly.
Cholera is dangerous due to the rapid development of dehydration, as a result of which the activity of the heart, kidneys and liver deteriorates. In the absence of therapy, the patient may die within 24 hours.
Pneumonic plague
The causative agent of the plague is the bacterium "Yersinia pestis". The disease is distinguished by a variety of forms, but only the pulmonary form of the disease is included in the OOI list, since the spread of this type of disease occurs with lightning speed. Infection with pneumonic plague occurs by airborne droplets, and the infection can also be transmitted through household items.
You can suspect an infection by the symptoms:
- severe headaches and joint pains;
- redness and swelling of the face;
- the temperature rises to 41 degrees;
- breathing is very difficult;
- the tongue is covered with a white coating;
- when coughing, blood is present in the sputum.
The incubation period of the plague can take from 3 to 10 days. Further, the disease develops rapidly, and in the absence of treatment, death can occur within 3 days, after the onset of symptoms.
Plague in the pulmonary form is dangerous in that it is difficult to identify it without tests, since changes in the lungs, as well as wheezing, are absent. And the probability of developing a fatal outcome, in the absence of therapy, is 100%.
Yellow fever
The disease develops after the penetration of a virus into the body, which is carried by mosquitoes, and the source of the disease is monkeys and rodents (less often an infected person). The danger of the disease lies in the difficulty of destroying the carrier of the infection. The disease is common in Africa and South America.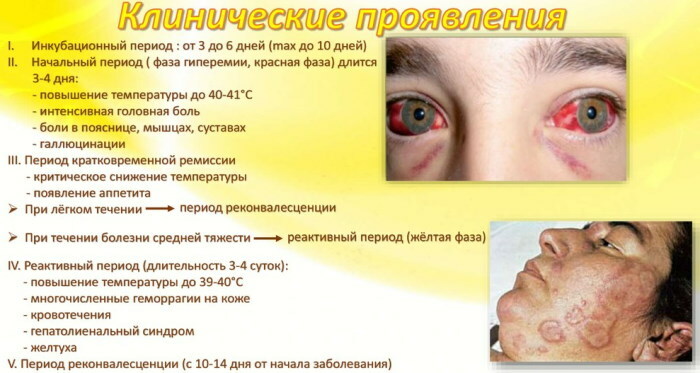
The main signs of infection are:
- a sharp change in the composition of the blood;
- heat up to 40 degrees;
- pronounced swelling of the lips and eyelids;
- the liver and spleen greatly increase in size;
- vomiting with blood in the vomit;
- severe disruption of the kidneys (manifested by swelling and a decrease in the amount of urine) and liver (manifested by yellowing of the skin, as well as protein in the eyes).
After the first signs of the disease appear (the incubation period can take about 6 days), the patient can die within 4 days. Yellow fever is dangerous due to the development of gangrene of muscle tissue and limbs, and the likelihood of death in 50% of cases of infection.
Hemorrhagic fevers
This group of diseases includes: Lassa, Ebola, Marburg, as well as West Nile fever. The causative agent of disease is a virus. Sources and routes of transmission of infection depend on the type of disease.
The main signs of infection are:
- heat;
- headaches and muscle pains;
- severe symptoms of intoxication, which affect the performance of all vital organs;
- the appearance of a hemorrhagic rash or subcutaneous hemorrhage;
- the skin is swollen red due to the rush of blood.
The incubation period and duration of the disease depend on its type. The danger of infection is the development of cardiovascular failure, which is fatal.
Dengue fever
The causative agent of the disease is a virus that is transmitted by mosquitoes from infected monkeys, humans or bats. In Europe, the disease develops extremely rarely.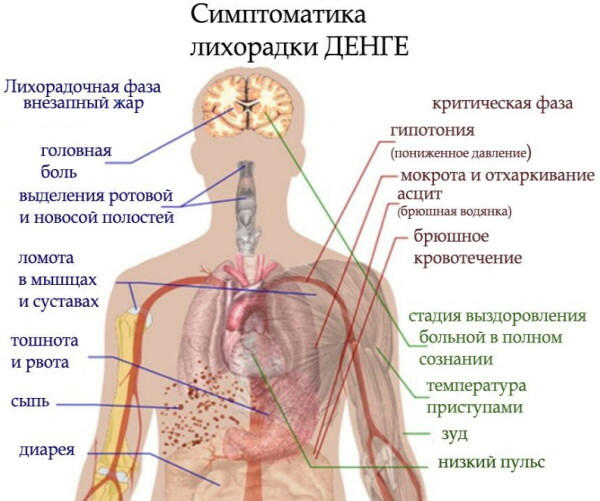
Dengue fever infection can be suspected by symptoms:
- change in gait;
- the temperature rises to 40 degrees;
- fever with severe aching joints, muscles and headache;
- an increase in the size of the lymph nodes;
- the presence of symptoms of severe poisoning of the body with toxins.
In the presence of treatment, recovery occurs after 1 week, and in the absence of therapy, the disease turns into hemorrhagic form, as a result, internal bleeding develops, followed by a sharp drop in pressure, which leads to fatal the outcome. The probability of developing a fatal outcome is 50%.
Rift Valley Fever
Rift Valley Fever is caused by a virus that is spread by mosquitoes and blood-sucking flies. Sources of disease can be infected animals, humans, and milk from infected livestock.
Signs of infection can be as follows:
- fever;
- loss of taste and lack of appetite. Blurred vision or memory impairment. Symptoms depend on which organ is affected by the virus;
- redness of the eyes;
- severe muscle and headaches.
The first symptoms of infection may appear 2-6 days after the infection has entered the body. The disease is dangerous with asymptomatic course, as a result, due to the lack of therapy, 50% of patients experience loss of vision, without subsequent recovery, as well as liver necrosis, as a result of which the patient may die 7-10 days after infection.
Meningococcal infection
The causative agent of the disease is meningococcus, which is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy, aerosol way (less often through household items). Moreover, the disease is common in Central Africa.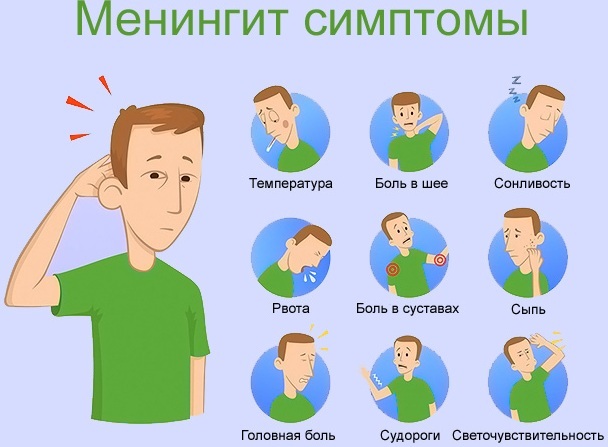
Signs of infection:
- severe intoxication;
- hearing impairment or loss;
- the appearance of a rash of purple color;
- disruption of the nervous and cardiovascular system;
- damage to the soft tissues of the brain. It is manifested by a refusal in the work of vital organs.
The incubation period of meningococcal infection is 1-10 days. In this case, an infected person can be a source of infection for up to 6 weeks. The probability of developing a fatal outcome is 50%.
anthrax
The disease is included in this subgroup only in Russia. The causative agent of the disease is a bacterium that is transmitted from an infected animal. The infection enters the human body through poorly processed meat or animal saliva.
The symptoms of infection are as follows:
- fever;
- severe intoxication;
- the appearance of skin ulcers;
- swollen lymph nodes.
The first signs of the disease can appear after 6 hours or 8 days. In severe cases of the disease, a person can die 2-3 days after infection. The likelihood of a lethal outcome, even with therapy, is 20-90% (depending on the form of the severity of the disease).
Tularemia
The disease is included in this subgroup only in Russia. The sources of bacterial infection are rats, hares, mice. Ways of transmission of infection is the entry of the pathogen into the bloodstream, upon contact with an infected animal, the use of poorly processed meat or water, if an infected animal has been in it. And also mosquitoes, horseflies, ticks can carry the disease.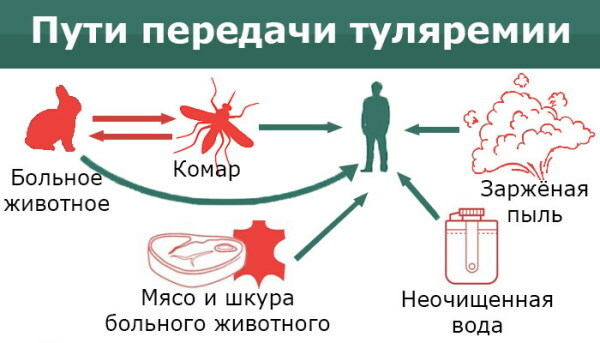
Signs of infection:
- severe bowel dysfunction;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the appearance of a kind of rash.
The incubation period after infection can last from 3 to 20 days. Further, in the absence of therapy, fever develops, which can last up to 1 month. The disease is dangerously fast spreading among the population, as well as the development of complications in the heart, impaired brain function and gangrene of the extremities. The likelihood of developing a fatal outcome is about 10%.
Important. People with tularemia do not spread the infection.
ROI classification
Dangerous diseases are under international control, since due to population migration and vacations abroad, there is a high probability of the spread of the disease outside the country. In this regard, when an infection is detected from the listed OOI list, the country is temporarily isolated from the entry and exit of people.
For the convenience of monitoring the epidemiological situation, the listed "special" diseases are divided into the following groups:
| List of groups | Characteristics of groups | Disease lists |
| Conventional (quarantine) diseases | The diseases are under international control. If a disease from this list is detected in the country, notification to WHO is required. Further, by the joint efforts of all countries, joint activities are being carried out to avoid the development of the epidemic around the world. |
|
| Diseases requiring international control, while joint activities are not carried out | Diseases from this list are also under international control, but at the same time, if they are detected, it is enough to carry out anti-epidemiological measures only in the "infected" country. |
|
| Diseases under regional control that do not require international surveillance | When AOIs from this group are identified, it is not necessary to notify WHO. The responsibility for eliminating the epidemiological danger lies with the regional authorities. |
|
This classification of AOI allows you to avoid the development of the epidemiological situation around the world, and at the same time, the development of WHO "overload" and panic among the population is not allowed.
Quarantine infections
Particularly dangerous infections are diseases that are further divided into a special subspecies - quarantine. When OOIs from this group are identified, quarantine is introduced. It can apply both to an entire country (full quarantine, upon detection of diseases from the conventional list of diseases), and to a settlement (partial quarantine).
In addition, only certain establishments in which a case of infection was recorded can be quarantined. The extent of the quarantine measures depends on the type of disease identified. So, for example, and if a patient with measles is identified, then it is enough to close the institution that the sick person visited.
Methods for diagnosing AOI
Due to the large list of especially dangerous infections, diagnostic methods depend on the type of suspected infection.
To confirm it, or exclude it, the patient can be assigned diagnostic procedures from the following list:
| Diagnostics type | List of procedures |
| Classical. Allows you to establish a diagnosis with an accuracy of 100%. |
|
| Accelerated. It is used if it is necessary to confirm the disease in a short time. |
|
In addition, standard blood, urine and feces donation tests are prescribed.
Prophylaxis
Especially dangerous infections are diseases that carry the risk of developing an epidemic not only in a small settlement, but can also affect an entire country.
In this regard, WHO has provided for a number of preventive measures:
- vaccination. They vaccinate people from the most dangerous and common diseases from birth. But some types of vaccines are used immediately before the need for a person to visit countries dangerous for contracting a disease from the OOI list;
- keeping records of cases. When a disease is detected from the OOI list, daily control over the number is carried out: infected, recovered and dead. If the number of cases is constantly growing, then the authorities introduce restrictive measures in order to prevent a further increase in the number of patients;
- isolation of patients. All patients with AOI (especially if their number is still minimal) are immediately isolated from healthy people in order to prevent further spread of the infection;
-
disinfection. They disinfect not only premises, but also people (for example, doctors) who have been in contact with patients.
The complex use of prevention methods can reduce the risk of an epidemic.
Dangerous diseases are specially allocated to a special group, since in case of infection with them, the infection spreads quickly and is dangerous with a high probability of death. If even one person is found in a locality, city or country who has contracted a disease from the POI list, the authorities must introduce special epidemiological measures.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Video about especially dangerous infections
Quarantine and especially dangerous infections: