Content
- What does acute left ventricular failure (LVVF) mean?
- Causes of occurrence
- Risk factors
- Types of acute left ventricular heart failure
- By flow type
- By origin
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Symptoms at the onset of an attack
- Instrumental and hardware diagnostics
- How pathology is displayed on the ECG
- First aid for acute heart failure
- Treatment at different stages
- Forecast
- Video about left ventricular failure
Acute left ventricular failure is a disorder resulting from cardiac decompensation. Pathology is extremely dangerous and requires immediate medical attention.
What does acute left ventricular failure (LVVF) mean?
The disease is one of the types of heart failure and is characterized by a sudden violation of the contractile ability of the heart. This leads to a violation of the blood supply to the organ, which is accompanied by the development of severe symptoms.
When a disease occurs, stagnant processes are observed in the pulmonary circulation (in the lungs).
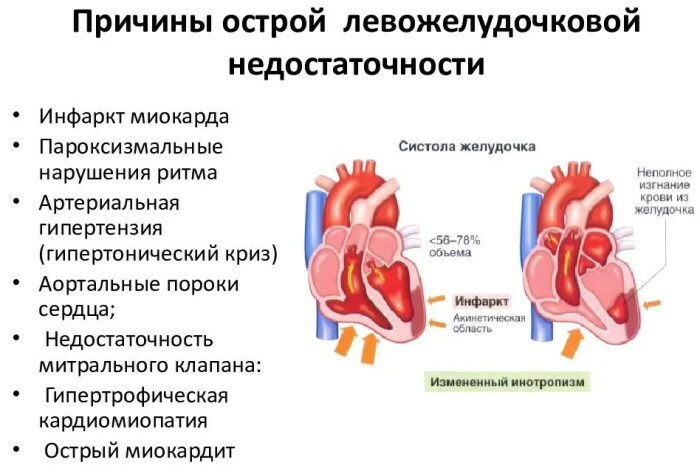
Causes of occurrence
There are 2 main reasons for the development of the disorder. The first has a cardinal (cardinal) nature of origin, the second is non-cardinal.
Cardinal reasons:
- heart failure, occurring in a chronic form in the stage of decompensation;
- myocardial infarction;
- hypertonic disease;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- severe course of the acute form of myocarditis;
- cardiac tamponade;
- frequent attacks of irregular heart rhythms;
- the development of infections in the area of the cardiovascular system.
Noncardinal reasons:
- abuse or misuse of medicines;
- a previous stroke;
- septic damage to the body;
- kidney failure;
- severe course of anemia;
- alcohol abuse;
- the presence of pheochromocytoma;
- severe lung disease;
- excessive administration of medicinal solutions.
The development of the disease can be affected by hyperthyroidism, which causes an increase in cardiac output and, as a result, leads to disruption of the left ventricle.
Risk factors
The cause of the development of the disorder is an increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
Risk factors:
- infectious diseases;
- ischemic disorders;
- previous surgical interventions;
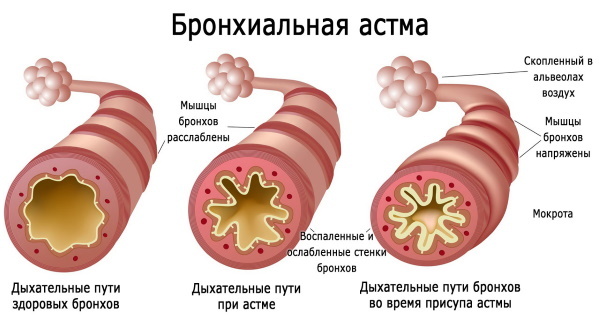
- bronchial asthma;
- circulatory disorders;
- severe kidney disease;
- the use of drugs;
- endocrine disorders;
- age over 60;
- myocardial infarction (re-development);
- overweight;
- hereditary diseases of the cardiovascular system.
As a result of provoking factors, there is a reverse flow and an increase in the amount of blood in the left atrium and in the area of the pulmonary vascular bed.
As a result of this, edema is formed in the intercellular space, which, in turn, leads to a narrowing of the lumens in the bronchi. In this case, foaming of the fluid flowing in the pulmonary alveoli occurs.
Against the background of such processes, cardiac asthma develops, edema in the lungs is formed.
Types of acute left ventricular heart failure
Acute left ventricular failure is a disease that is classified into several types, depending on the nature of the course and the nature of the origin. This classification allows you to assess the risks to the patient and prescribe the most appropriate therapy.
By flow type
According to the type of course, the disease is divided into acute and chronic. In the first case, the pathology develops rapidly with pronounced symptoms. This condition is very dangerous and requires immediate treatment.
The chronic form manifests itself periodically with alternating remission and exacerbation of symptoms. At the same time, the disease in humans is constantly present and monitored with the help of drugs and systematic research.
Cardiological classification:
- acute decompensated form (developed for the first time or as a result of a chronic form of the disease);
- hypertensive - signs of pathology occur in conjunction with arterial hypertension;
- swelling of the lungs;
- cardiogenic shock;
- a disease accompanied by large cardiac emissions (observed with an infectious lesion).
In all cases, the pathology requires monitoring by the attending specialist or the appointment of suitable therapy.
According to the duration of the course, the disorder is of several types:
- lightning fast - causes the death of the patient within a few minutes;
- acute (up to 4 hours) - the symptomatology is pronounced, develops rapidly, and even during resuscitation, it is not always possible to save the patient;
- subacute - signs of damage occur with alternating frequency;
- protracted - lasts from 12 to several days, the condition develops in the presence of a chronic form of the disease.
The pathology itself is dangerous not only for health, but also for the patient's life, since it can lead to a sudden death.
By origin
By the nature of its origin, the disease is subdivided into cardinal and non-cardinal forms. In the first case, the disease occurs as a result of any internal disturbances in the work of the heart and cardiovascular system, including an infectious lesion.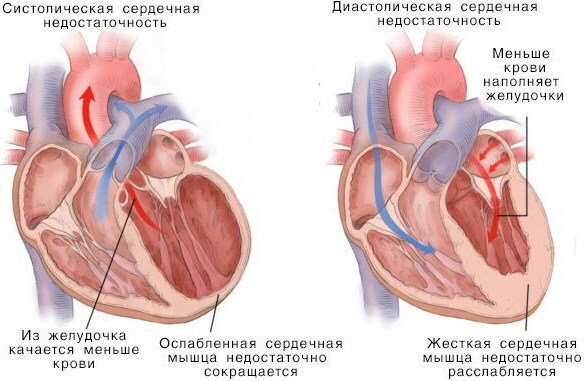
In the non-cardinal type of disorder, signs develop against the background of other external and internal factors that are not interrelated with work or heart disease.
Symptoms
Acute left ventricular failure is a disorder that has characteristic and pronounced symptoms, which allows time suspect the development of the disease and take all necessary measures to prevent the occurrence of those that are dangerous to health and life complications.
The symptomatology of the disease depends on the stage of its course and the presence of additional complicating factors.
At the initial stages, the following signs develop:
- dyspnea;
- increased blood pressure;
- the condition improves with a certain position of the body;
- discomfort in the sternum;
- wheezing in the lower part of the lungs;
- increased sweating;
- anxiety and agitation;
- increased heart rate;
- signs of tachycardia;
- cyanosis;
- cough (especially when changing body position).
In the absence or ineffectiveness of treatment, edema in the lung area occurs, which leads to more pronounced main symptoms.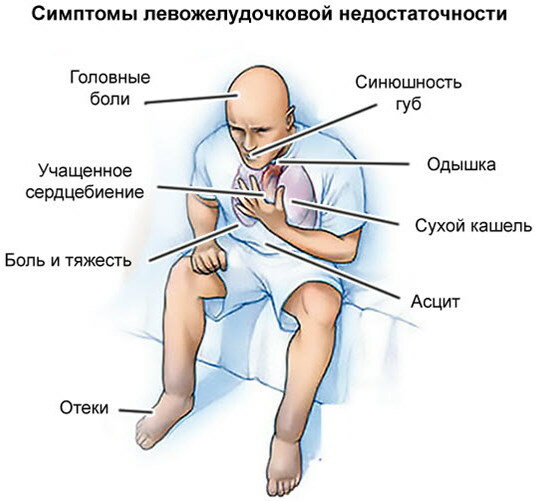
In this case, the following signs develop:
- inhibited state;
- fear of death;
- wheezing breathing (shallow or gurgling breathing);
- instability of blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness;
- coma;
- death.
The patient's death occurs against the background of asphyxiation (asphyxiation).
Diagnostics
Acute development of left ventricular failure can be determined both using special hardware or instrumental techniques, and by visual examination (based on patient complaints).
Diagnostics allows you to identify the cause of the violation, the severity of its course, and also helps to choose the most effective treatment.
Symptoms at the onset of an attack
First of all, a visual examination of the patient is carried out. The condition of the skin is assessed for signs of cyanosis. Then the specialist conducts listening to the lungs with a stethoscope - the presence of wheezing and noises is examined.
After that, the patient's blood pressure is measured using a tonometer.
Additionally, chest tapping may be performed to determine the accumulation of fluid in the lungs or edema.
Based on the data obtained, a preliminary diagnosis is made, after which the patient is referred for additional laboratory diagnostics.
Laboratory research methods:
- General analysis of blood and urine.
- Blood sugar test.
- Blood chemistry.
- Coagulogram - an assessment of blood clotting. Diagnostics is used when pulmonary edema is suspected.
- Diagnostics to determine the concentration of gases in arterial blood.
After passing the laboratory test, hardware methods for examining the patient are assigned.
Instrumental and hardware diagnostics
To determine the cause of the disease and the nature of its course, several main types of instrumental diagnostics are used.
Research:
-
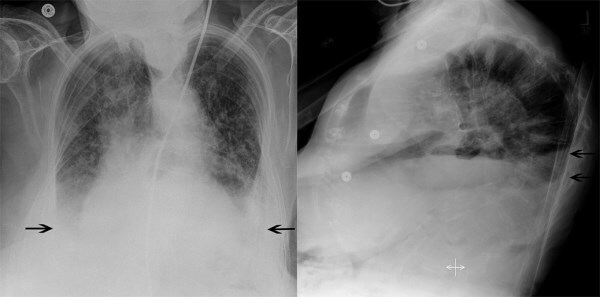
Chest (lung) X-ray. Direct and lateral projection is performed. Diagnostics allows you to detect pulmonary edema.
- Pulse Oximetry - determination of the amount of oxygen in the blood (less than 90%) and shows the level of oxygen binding with hemoglobin.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). Diagnostics allows you to detect violations of the cardiovascular system, including edema in the lungs.
- Transthoracic echocardiography. It is prescribed to assess the work of the heart muscle and valves. The study is often used to establish the cause of swelling in the lung tissue.
- Measurement of central venous pressure. Also used to determine the cause of the formation of swelling in the lungs.
- Pulmonary artery catheterization. The examination helps to identify the cause of pulmonary edema.
In most cases, these studies are sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis.
How pathology is displayed on the ECG
With the help of an ECG, it is possible to determine the development of the disease, taking into account deviations in certain leads of the isolines.
Signs of pathology:
- Increased amplitude indicators in the P wave in leads 1, 2, aVL, M5-6.
- The negative 2nd phase of the P wave also increases the duration of the amplitude.
- Formation of a negative P wave in leads V
- The P3 wave becomes negative or 2-phase.
- The width of the P wave also increases by more than 0.1 s.
At the same time, a general disturbance of rhythms and conduction is also noted, hypertrophic changes and overload develop in the region of the left heart.
First aid for acute heart failure
Acute left ventricular failure is a pathology that requires immediate and rapid treatment measures, since the condition can worsen in a few minutes and lead to lethal outcome.
With an attack of acute development of the disease, you should first call the medical team. Before the arrival of an ambulance, it is necessary to provide the patient with the correct body position and medication.
First aid:
- Arrange the patient half-sitting.
- Provide the room where the patient is with an inflow of fresh air (open the window).
- Unbutton the top buttons on the shirt and loosen or remove the belt.
- Give a tablet of Valocardin or Corvalol (the dosage should be checked with a specialist in advance).
- Take blood pressure measurements and determine the heart rate. These measurements must be taken every 5-10 minutes.
- In case of high blood pressure (systole values more than 100 mm Hg), it is necessary to give the patient a nitroglycerin tablet (sublingually).
- If the patient has lost consciousness, he should be laid on his side to prevent accidental swallowing of the tongue.
- If the patient does not have breathing or heartbeat, direct cardiac massage or artificial respiration should be performed.
These measures will help to avoid death and save the patient's life. When performing them, it is necessary to strictly observe all the rules prescribed by a specialist, otherwise the effectiveness of such measures may not bring the desired result.
Treatment at different stages
Treatment tactics depend on the form and severity of the pathological process.
In case of development of edema in the lungs, the following complex treatment is carried out:
- Place the patient in a sitting position and give 1-2 tablets of Nitroglycerin.
- Then a 1% solution of morphine hydrochloride (1 ml) is injected intravenously.
- A catheter is inserted through the nasal cavity and defoaming is performed. In this case, alcohol vapors or alcohol infusion of antifomsilan are used.
- Then, tourniquets are applied to the legs.
Also, non-invasive ventilation of the lungs is performed through special catheters that are inserted into the nasal passages.
Medical treatment is mandatory and is prescribed to patients regardless of the stage and severity of the disorder.
| Group of drugs | Application / Recommendations |
| Pain relievers (analgesics) | Intravenous morphine is most commonly prescribed. The dosage is 3 mg. Reuse is possible on the advice of a specialist. The remedy has contraindications, including pulmonary edema |
| Diuretics | They are used only if absolutely necessary and only when a large amount of fluid accumulates in the body. Often used in conjunction with nitrates. Administered intravenously (Furosemide at a dosage of 20 to 40 mg). This group of funds does not apply to medications that must be taken. |
| Vasodilators | It is recommended to start therapy with sublingual forms of Nitroglycerin or isosorbide dinitrate. In the absence of efficiency after 10 minutes. one of the drugs (preferably Nitroglycerin) can be taken repeatedly. Further dosage is calculated according to blood pressure. |
| Nootropic drugs | Applied only according to the testimony of a doctor with great care. Funds are prescribed to patients with reduced pressure, as well as in case of impaired renal function. The most commonly used infusion is dopamine |
| Cardiac glycosides | The drugs are prescribed to patients in whom the disease was caused by tachycardia. The drugs have various contraindications, including AV block and bradycardia. Funds are used only on the advice of the attending physician |
Acute left ventricular failure is a disease that has several stages of its course and developmental stages. This feature must be taken into account when choosing a treatment regimen.
Treatment of the acute form of the disease is determined according to blood pressure.
Thus, under reduced pressure, the following tactics apply:
- Dopamine. It is used to eliminate signs of arrhythmias, lowers heart rate and increases blood pressure.
- At a pressure below 80 mm Hg. Art. additionally norepinephrine is prescribed.
- After the pressure has recovered (in the presence of edema in the lungs), intravenous administration of Furosemide and sodium nyroprusside (or Nitroglycerin) is used.
In the case of increased blood pressure or at its normal level, the following drugs are used:
- Furosemide (intravenously at the rate of 0.5-1 mg per kg of the patient's body weight).
- Nitroglycerin (0.5 mg sublingually every 5 minutes).
- Sodium nitroprusside. When using it, it is necessary to ensure that the pressure level does not drop below 90 mm Hg. Art.
- In the absence of effectiveness and preservation of negative symptoms, Dobutamine or Amrinon is used. The dosage of funds is determined individually in such a way that an increase in cardiac output occurs.
In the case of stabilization of the patient's condition, he is prescribed further intake of diuretics, nitrates and ACE inhibitors.
All patients who received first aid are subject to compulsory hospitalization in the cardiology or cardiac surgery departments of the hospital.
Forecast
With pathology, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable, since in the presence of pulmonary edema, in most cases, patients die.
Moreover, the forecast itself depends on many other factors:
- the nature of the origin of the violation;
- the affected area;
- the age of the patient;
- timely therapy;
- the presence of other diseases or complications from the cardiovascular system and lungs.
In order to avoid the development of the disease, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules that will reduce or completely eliminate the risks of other health problems.
Prevention:
- Refusal from tobacco products and taking alcoholic beverages.
- Compliance with the rules of nutrition or diet.
- Leading a healthy lifestyle - doing moderate physical activity.
- Avoiding physical overwork, psycho-emotional overload, stressful situations.
- Systematic passing of preventive examinations by a cardiologist.
If you develop any symptoms that indicate acute left ventricular failure, you should immediately consult a specialist for help. This will avoid the development of complications and prevent sudden death of the patient.
Video about left ventricular failure
Left ventricular failure: