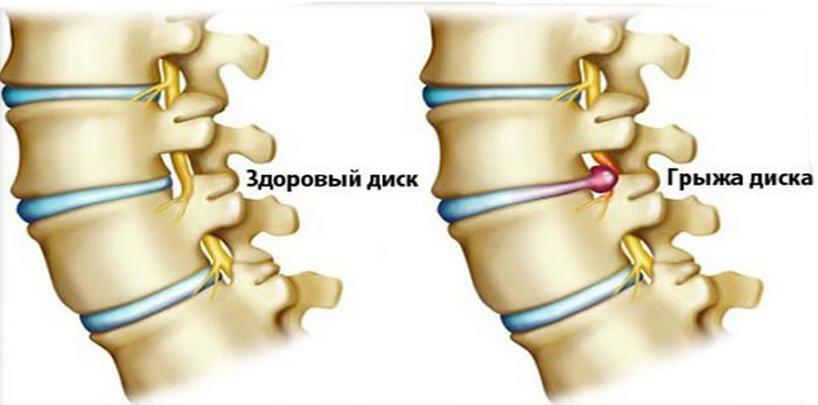
An intervertebral hernia is a displacement of one of the discs that has undergone deformation due to any negative factors. This defect can develop in any part of the spinal column( thoracic, cervical), but more often it is localized in the region of the waist.
Most often, this ailment is diagnosed in the stronger sex at the age of thirty to fifty years, but it can also occur in younger people, including women, and is a rather dangerous condition that requires prompt treatment.
Lumbar disc herniation: treatment, symptoms
Content of material
- 1 What is a herniated intervertebral disc?
- 2 Why develop a lumbar hernia?
- 2.1 Video - Everything you wanted to know about herniated
- 3 symptoms
- 3.1 Pain
- 3.2 spinal
- 3.3 syndrome Radicular
- 4 syndrome diagnosis of lumbar hernia
- 5 therapy lumbar hernia
- 5.1 Video - How to treat intervertebral hernia withoutoperations
- 5.2 Surgical treatment
- 6 Rehabilitation and life of patients with lumbar hernia
What is a herniated intervertebral disc?
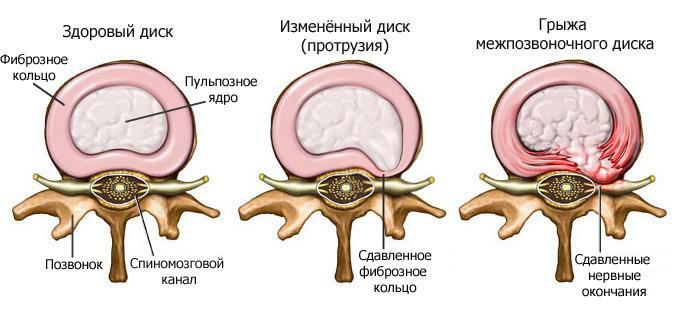
The spine is the core that supports the body of a person throughout life, with most of the body weight and load falls on the lower back. The vertebral column consists of 33 vertebrae, five of which are located in the lumbar region. They are divided among themselves by disks consisting of fibrous rings with a gelatinous substance in the center. The intervertebral disks function as a kind of shock absorbers, which soften the load on adjacent vertebrae.
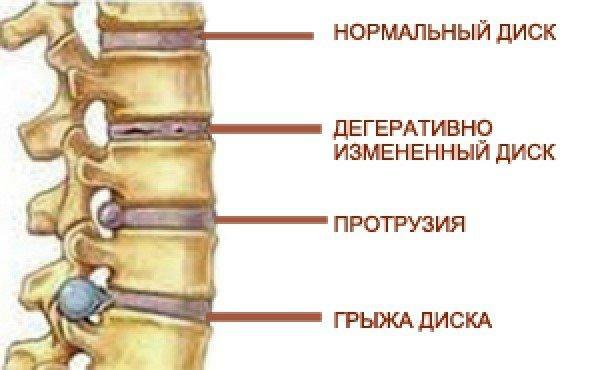
With age, as a result of improper lifestyle or injuries, the surface of the discs deforms, dries and cracks. In the first stage, these microtraumas do not bring much discomfort, but at some point the fibrous tissue breaks and the substance that is inside pours out and squeezes the nerve roots, as well as the brain stem. This is how the intervertebral hernia develops, which initially also does not cause a person special problems, but later the situation can become very complicated.
Herniated disc
Why develop a lumbar hernia?
There are several reasons that can cause deformation of the intervertebral disc, and subsequently a hernia.
- Great physical activity. This list includes not only weight lifting, but also sharp slopes, turns, etc. It is due to these factors that the intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region is diagnosed in people who are actively involved in sports.
- Diseases of the spine. This list includes scoliosis, osteochondrosis and other similar diseases that lead to the curvature of the spinal column and affect the cartilaginous and fibrous tissue of the spine.
- Congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system. The key cause of hernia is dysplasia of the hip joints - the disease leads to an incorrect distribution of the load on the vertebral column, as a result of which the discs begin to deform.
- Injury of the spine. Quite often the hernia of the vertebral column develops due to falls and bumps, as well as from car accident victims, who often get very serious and complex injuries of the spine.
- Metabolic disorders. As with any other organ, the health of the spine depends largely on the correct metabolism and the sufficient number of essential trace elements.
Intervertebral hernia can occur due to large physical exertion
In addition, there are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of the disease:
- obesity, overweight;
- wrong lifestyle( poor nutrition, smoking);
- inactivity( insufficient physical activity);
- some kinds of professional activity( movers, office workers, drivers);
- old age;
- genetic predisposition;
- frequent infection and hypothermia of the body.
Unfortunately, some of the above risk factors can not be completely excluded, therefore, one should pay special attention to the health of the spine and the musculoskeletal system as a whole.
Video - Everything you wanted to know about the intervertebral hernia
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar region are progressive, increasing in nature and conditionally divided into three stages.
Pain sensations
Pain is the primary and key symptom of a disease that accompanies the patient all the time. Pain syndrome can increase or decrease, change the nature and location, and also go in combination with other symptoms. In the initial stages, when the lesion is still small, a person feels pain in the lumbar region - where the deformed disk is located. They wear noisy, dull character, intensify with loads and excessive activity, with prolonged sitting in one position and weaken in a horizontal position. Such a course of the disease can last several months or years, periodically exacerbating and subside.
It should be noted that at this stage the disease does not require any special treatment - it is enough for a person to simply change the way of life, do light gymnastics and avoid bad habits.
Pain is the primary and key symptom of the intervertebral hernia
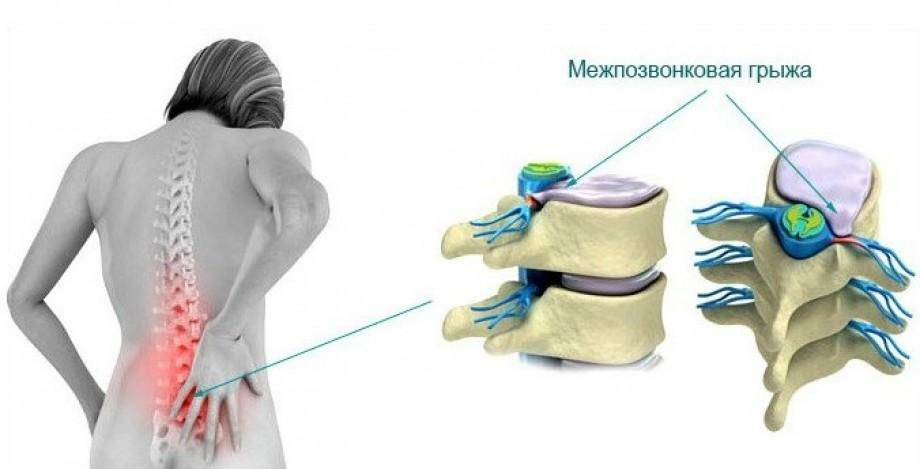
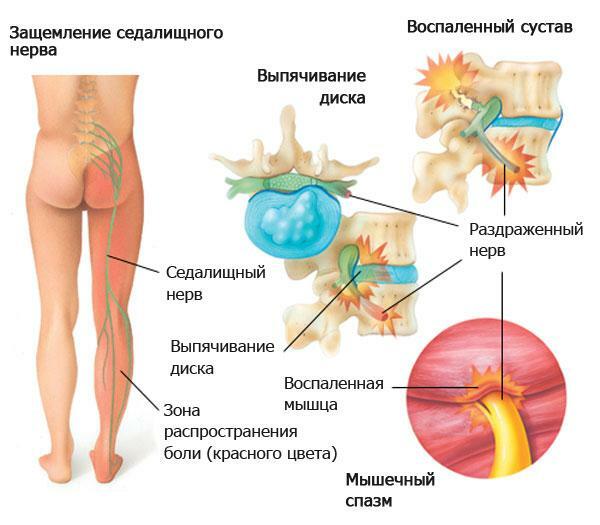
. As the area of the disc lesion increases, the roots and spinal cord are infringed, and the pain syndrome begins to increase. The pain is felt during the movements of the neck, raising the legs, palpation of certain areas. The nature of it also changes - the sensations become aching, piercing, and their localization depends on which parts of the spinal column have undergone deformation: discomfort can be seen in the buttocks, hips, legs, different parts of the feet or even in the thumbs. Increases discomfort in all movements, including coughing, sneezing, hiccough.
Vertebral Syndrome
The second stage of hernia development is characterized by a permanent spasm of the dorsal and lumbar muscles, which causes the pain syndrome to increase. The movements of the patient become chained, the person can not fully unbend his back, starts to stoop, he has a characteristic gait with a torso of the torso on the healthy side. Coordination of movements and resistance to walking is disrupted.
Radicular syndrome
If a person does not receive adequate treatment, manifestations of the disease lead to squeezing the roots of the spinal cord, so that they die, and the nutrition and blood circulation of tissues deteriorates. At this stage, there are specific signs, characteristic of the lumbar hernia.
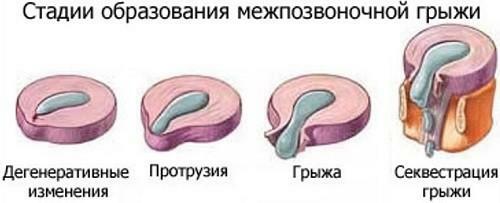
Stages of formation of the intervertebral hernia
- There is weakness and hypotension of the muscles of the lower limbs. A person is not able to sit down, it is difficult for him to walk on stairs, get up on socks and jump.
- Muscles of the leg atrophy, and eventually it becomes noticeable - the limb becomes thin, weakens and very poorly performs its functions. The gluteal fold disappears, and the figure acquires asymmetry.
- In the place of the lesion there is a violation of the sensitivity of the skin and soft tissues - the patient feels tingling, "goose bumps", numbness, a feeling of chilliness, the skin is dry and flaky or, conversely, often and too much sweats.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs - in patients urinary incontinence and feces are noted, in male patients potency decreases, and in a woman begin to suffer from gynecological diseases.
- In neglected cases, people become trapped in movements, partial or complete paralysis is possible, and sometimes complete disability and even conditions that are incompatible with life.
A visual image of a herniated intervertebral disc of the lumbar spine
Often, other pathological conditions are attached to the intervertebral hernia - for example, lumbago lumbago. They are characterized by acute, sharp pain, intensifying with the slightest movements, and subsequently disrupting the work of the hip and knee joints.
In general, the symptoms of the intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region depend on which of the five vertebrae has undergone deformation - experts designate them in Latin letters and numerals( L1, L2, L3, L4, L5).
| Disk designation | Zone of pain and sensitivity disorders | Zone of numbness | Zone of weakness of muscles and partial paralysis | Reflex reflexes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L3-L4 | Thigh front, back part of lower leg | Inner surface of thigh and areas near it, inside of lower leg and foot | Four-headed thigh muscle | Knee reflex |
| L4-L5 | Pain syndrome passes over the outer thigh and lower leg, to the rear surface of the foot towards the big finger | NThe upper part of the leg, the big toe | The most common is the big toe( the flex function is lost), more rarely the stop | The reflexes are fully preserved |
| L5-S1( the lumbosacral transition) | The pain passes over the back of the thigh and lower legfoot and fingers | Outer leg, feet, toes | Calf muscle, sometimes foot muscles | Achilles reflex |
Diagnosis of lumbar hernia
Diagnostic measures for this disease include examination of a neurologist and a specialistnye studies, including X-rays, CT and MRI.It should be noted that the usual X-ray in the diagnosis of a hernia is almost uninformative, since it does not allow you to see soft tissue.
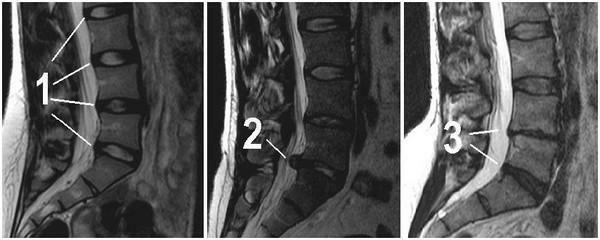
Herniated disc of the lumbar spine on the pictures
- Neurologist examination. The doctor checks the tendon reflexes, the tone of the muscles, the sensitivity of the skin. This is done through a variety of physiological tests: for example, the patient may be asked to look like a socks, raise a straightened leg, and also check the knee reflex with a hammer.
- Electromyography and neurography. Studies provide an opportunity to assess the state of nerves and muscles.
- CT and MRI.The most informative methods that allow layered visualization of all tissues and parts of the spine, including discs and nerve roots.
Lumbar hernia therapy
In most cases( when the situation is not yet too much started), the patient has enough conservative therapy - in this case the symptoms disappear for 6-8 weeks.
Treatment of a hernia is complex, and includes several activities.
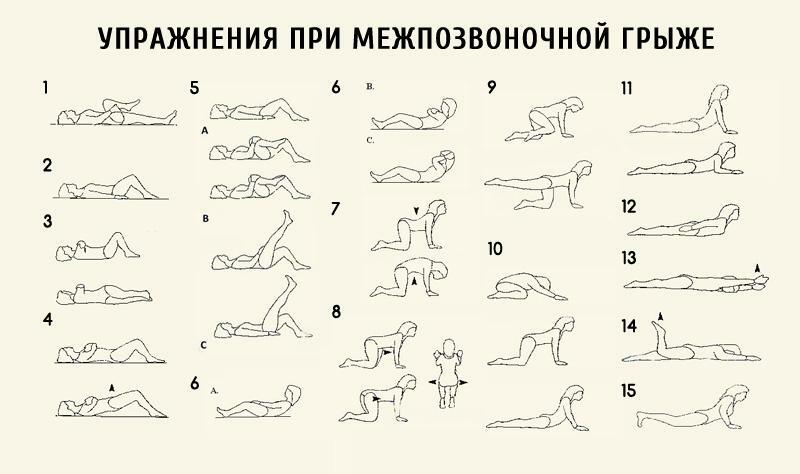
Gymnastics with lumbar hernia
- Gentle mode. The patient should stay in bed for at least 1-2 days until the pain syndrome decreases. All movements should be cautious and slow, and any loads must be limited.
- Medication therapy. In the treatment of herniated intervertebral discs, non-steroidal and steroid medications can be used. The first are taken orally and help relieve pain and inflammation in the area of the affected nerve root. Steroid drugs are more effective and are injected directly into the area where the nerve roots are located.
- Therapeutic gymnastics. Patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures in order to improve the blood circulation of the affected tissues, as well as gymnastic exercises in order to strengthen the muscles.
If conservative methods do not give the desired result for a long time( more than 6 months), doctors sometimes raise the question of surgical intervention.
Video - How to treat an intervertebral hernia without surgery
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment may be required when conservative methods have no effect, as well as with pronounced neurologic symptoms and horse tail syndrome( a pathology in which immobility and even paralysis of the legs take place).Surgery is performed only in extreme cases, since sometimes medication and physiotherapy give much better results, but surgical therapy of the dystrophy eliminates neurological symptoms: muscle weakness, numbness, etc.
Most often, with a lumbar hernia, an intervention called discectomy is performed, that is, removal of the damaged disc. This is a rather complicated procedure, which is prescribed exclusively for medical reasons - in particular, simple back pain is not the reason for the operation.
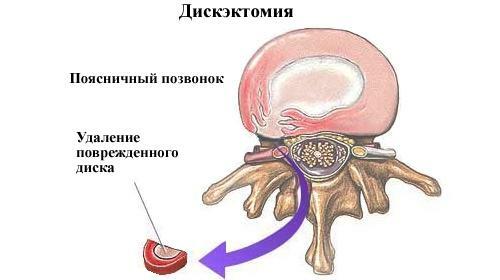
Disketctomy of the lumbar department of
In addition, recently minimally invasive techniques, in particular microdiscectomy, have become very popular, when not only the entire disc is removed, but only its affected area. This intervention, as well as the postoperative period, is much easier for patients. It should be noted that, regardless of the type of treatment performed, approximately 5% of patients experience a relapse of the disease.
Rehabilitation and life of patients with lumbar hernia
After the course of treatment( including surgical operation), no specific rehabilitation measures are required. The patient is recommended to walk daily for 30 minutes, as well as perform simple exercises to strengthen the muscles of the legs and back.
If patients with a diagnosis of a herniated lumbar intervertebral disc give adequate treatment in a timely manner, the disease has virtually no effect on quality of life. In cases where drug therapy gives the desired effect, a person can return to a normal existence immediately after the pain syndrome is eliminated. With the intervention of surgeons, about 95% of patients recover almost immediately and can lead their old life in 1-2 weeks.