Pituitary-mediated thyroid-stimulating hormone( TSH) is a catalyst for the reproduction of the free thyroid hormones triiodothyronine( T3) and thyroxine( T4) by the thyroid gland.
These substances are energy sources of the metabolism of fats, proteins and glucosides in the human body, and are also responsible for the full functioning of the genitourinary and cardiovascular system, the digestive tract. In addition, they affect the psyche of the individual. In this case, the stimulation of the production of T3 and T4 occurs on the principle of feedback - with an increase in the hormonal synthesis of the thyroid gland, suppression of the reproduction of the thyroid-stimulating hormone occurs. Therefore, in modern medicine, the definition of TSH is carried out in conjunction with the delivery of thyroid hormone assays.
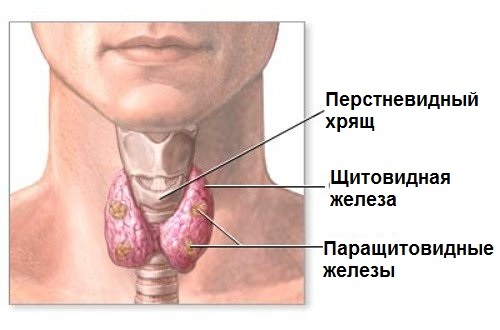
If the process of production of these three substances is unbalanced, the following morbid conditions are possible:
- under hypothyroidism means a lowered level of free hormones T3 and T4;
- an increased level of synthesis of thyroid hormones is called hyperthyroidism;
- thyrotoxicosis is called the excessive synthesis of thyroid hormones, which is the cause of the "intoxication" of the human body.
Preparation and conduct of TSG analysis
Control of the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone synthesis is mandatory for all patients suffering from thyroid diseases, as well as in the initial diagnosis of various endocrine diseases. As a result of the analysis, the TSH standard is established, or its deficiency and concentration excess. American doctors believe that women who have reached the age of fifty must necessarily take the TSH test, regardless of the presence of endocrine diseases.
Before carrying out a biological study, it is necessary to quit smoking, taking iodine preparations within one to two days, and to limit excessive physical overload. The patient should refrain from taking hormonal drugs. The blood test is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach. When determining the dynamics of the level of a hormone, analyzes that are stretched by the days of the week are taken at the same time of day.
Normal level of thyroid-stimulating hormone
According to various medical standards, the male and female TSH norm differ. Its normal concentration is determined by a doctor-endocrinologist and depends on the patient's age, individual characteristics of the organism and the presence of a variety of somatic diseases and psychoemotional defects. A healthy individual has the highest level of synthesis in the early morning.

When carrying out a blood test, hormone levels in women older than 40 years are very important, as well as those of the fair sex who are preparing to become mothers. Thus TTG-analysis is often spent at pregnant women in the absence of complaints on the state of health. Deviation of hormone levels from normal can harm the embryo and cause the child to have congenital diseases.
Elevated TSH level
TTG analysis allows to determine the dysfunction of the thyroid gland, when the concentration of free hormones T3 and T4 in blood serum are out of normal. Usually thyroid-stimulating hormone is increased if the following functional disorders in the human body are present:
- adrenal insufficiency,
- severe psychological traumas,
- malignant and benign neoplasms,
- severe gestosis,
- syndrome of atypical secretion of TSH.
In addition, thyroid stimulating hormone can be increased due to heavy physical exertion and drug therapy, conducted using:
- neuroleptics,
- iodine-containing drugs,
- beta-blockers.
TSH in the blood can be increased due to hemodialysis, intoxication with lead, and may also occur after surgical treatment of the gallbladder. If the blood test showed excess beyond the norm, then it is necessary to proceed to treatment as quickly as possible, otherwise the patient may develop hypothyroidism.
Often TTG is elevated in pregnancy, which is not always considered a pathology or a deviation from the norm.
Low level of TTG

The decrease in TSH concentration below the norm can be caused by:
- , pituitary dysfunction,
- self-medication hormonal preparations,
- stress,
- benign tumors in the thyroid,
- postpartum pituitary cell degradation in women( Shihan syndrome),
- by Plummer's disease.
Most often, hormone deficiency is caused by goitre of toxic etiology or excessive intake of medicinal hormonal drugs that affect thyroid function. Often, a deficiency of TSH leads to dietary fasting and a change in the psychoemotional state of the patient, caused by the transferred stress. In addition, lowering TSH below normal may be a consequence of cancer or acute inflammation of the thyroid gland, trauma to the pituitary, which reduces the normal production of hormones.
The level of TTG in pregnancy
During pregnancy, the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone can be in the range of 0.2-3.5 mU / l. Such a high run-up of indicators explains the different methods of analysis and different chemical reagents used in its conduct. Especially important is the control of the hormonal background to 10 weeks, the code of the thyroid gland of the embryo is not yet formed and all hormones necessary for the development of the fetus come from the organs of internal secretion of the mother.
The level of TTG of a pregnant woman can vary during the entire period of bearing of the child. At the same time, it depends on the physical condition of the woman and, in comparison with the norm, can be increased or slightly reduced. However, it should be noted that a significant deviation of the concentration from the norm can harm not only the fetus, but also complicate the course of immaturity in the woman herself. The lowest level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is at 10-12 weeks. However, cases when its level is lowered not only in the second, but also the third trimester are not uncommon.
Usually, a decrease in the level of TSH is observed in 25.0% -30.0% of pregnant women bearing one child and in 100.0% of cases of multiple pregnancies. About 10.0% of parturient women are suppressed the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone, however, the concentration of free T4 is increased. The norm is determined by the observing physician, who can decide whether to make additional studies using the method of ultrasound or fine needle biopsy of the thyroid gland.
In the case of an elevated level of TSH in the early stages of fetal development, drug therapy with L-thyroxine( L-Thyroxin) may be prescribed.
No less important is the control of the TSH level when planning pregnancy. If the hormonal balance is disturbed, this can lead to dysfunction of the thyroid gland, which has a very negative effect on the development of the fetus. With increased production of thyroid-stimulating hormone, the synthesis of the free hormone T4 is inhibited, which affects the intellectual development of the child. If the future mother is diagnosed with hypothyroidism, then the drug is treated with L-thyroxine. Moreover, the adjustment of the dosage of the drug is administered throughout the gestation period, after the delivery of the corresponding analyzes.
Symptoms of hormone level disruption
Both high and low levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone are accompanied by deterioration of the patient's physical condition and in some cases can cause serious harm to human health.

The high norm of TSH is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- decrease in physical activity, along with general weakness and fast fatigue,
- lethargy, increased irritability,
- mental retardation along with slow thinking,
- sleep disturbance, expressed by night insomnia and daytime drowsiness,
- skin blanchingand its edema,
- obesity, which is difficult enough to provide correction,
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract( nausea, constipation),
- in pregnant women observed thickening of the neck,
- decrease in body temperature,
- loss of appetite.
In case of TSH below normal, the following symptoms may appear:
- presence of headaches,
- increased blood pressure,
- tremor in hands and eyelids,
- emotional instability,
- frequent indigestion,
- increased appetite and lack of satiety,
- constantly elevated body temperature,
- increased heart rate.
Treatment of

Prophylaxis and treatment of both increased and decreased levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone should be performed only after the appointment of an endocrinologist, after carrying out all necessary medical examinations. Self-administration of hormonal medicines is unacceptable. Many patients with this disease use traditional medicine in the form of herbal medicines or herbs. However, this method of treatment should be used only after consulting a doctor.
In cases where the level of TSH is above the norm and exceeds 7.1 mU / l, this indicates the presence of hyperthyroidism. Drug therapy involves the use of a synthetic substitute for free thyroxine( T4).If before the treatment was applied specially treated thyroid of domestic animals, today synthetic medications are more effective and have a higher degree of purification.
Medical therapy begins with the introduction of minimal doses of synthetic hormonal drugs, which gradually increase until the level of TSH and free T4 is normalized. In this case only the endocrinologist appoints a specific treatment course for each patient, in which various synthetic T4 substitutes can be used. This is due to the fact that the synthesis of TSH and free thyroxine in each patient is individual, and the drug is administered only after the delivery of all necessary tests.
In addition, thyroid-stimulating hormone can cause the appearance and development of malignant tumors of the thyroid gland. To exclude the slightest likelihood of such phenomena, the course of treatment begins with minimal doses, which are adjusted, then as long as the TSH and free hormones T3 and T4 values do not return to normal.
After the course of treatment, patients who are susceptible to disruption of the hormonal level are examined once a year, confirming the absence of violations of hormonal norms.
At a low level of TSH( less than 0.01 mU / l), the restoration of its norm is performed using hormonal drugs, and the treatment itself is under the supervision of an endocrinologist.
If the levels of free hormones T3 and T4 are normal, and the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone exceeds the allowable value, then endocrinologists diagnose subclinical hypothyroidism. The term "subclinical" itself indicates that there is a violation of the hormonal background, but the external symptomatology is either expressed implicitly or not at all. In this case, the final diagnosis is made based on a blood test. The main causes of this disease can be:
- deficiency of iodine in the body,
- consequences of thyroid medication treatment with radioactive iodine preparations,
- surgical removal of the thyroid gland or part thereof,
- drug therapy with thyreostatics.
In this case, often the symptomatology is atypical and is expressed by the following signs, which are characteristic for other somatic diseases:
- decrease in sexual activity,
- by dry skin and hair loss.
- lethargy and sluggishness,
- digestive disorders,
- obesity.
In modern medicine, there is an opinion that at normal levels of free hormones T3 and T4, an adjustment to the elevated TSH is not necessary. However, if the adjustment of the hormonal background is not carried out in full scale, this is fraught with the most undesirable consequences. After establishing an elevated level of thyroid stimulating hormone, treatment with Levothyroxine is prescribed. Unfortunately, this drug has a large number of contraindications and has a significant number of side effects, which means that it is undesirable to take it during pregnancy.

Subclinical hypothyroidism in children is determined immediately after the birth of the baby by taking a blood test from the heel. The main symptoms of this disease in newborns are:
- baby's hoarse cry;
- rejection of breast nutrition;
- the presence of congenital jaundice.
Treatment of pediatric subclinical hypothyroidism is carried out by synthetic thyroid hormones. At the same time if you do not have hormonal treatment in time, then the disturbance of the body's normal functioning can last a lifetime.
Conclusion
As can be seen from the above review, periodic monitoring of the hormonal level allows you to start treatment in the early stages of the disease, which in turn ensures the preservation of human health and the absence of side-effects that may arise from the imbalance in the synthesis of TSH andindependent hormones T3 and T4.In this case, it is necessary to take into account the feedback that exists between all three substances.



