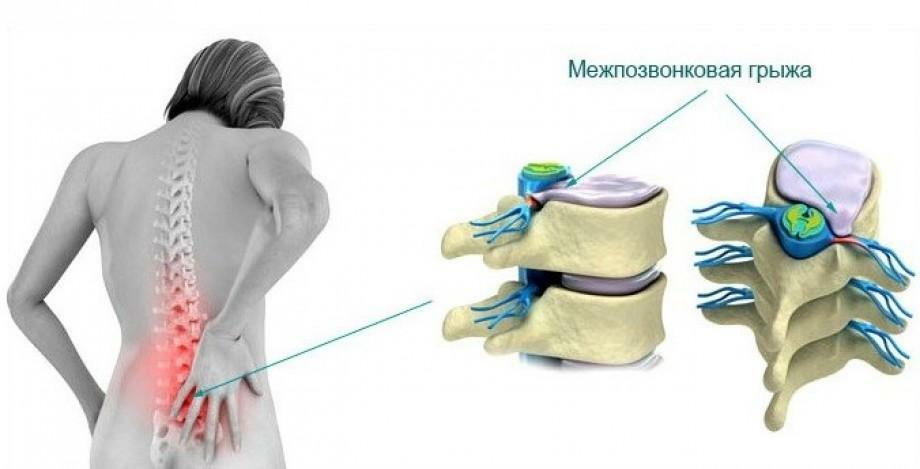
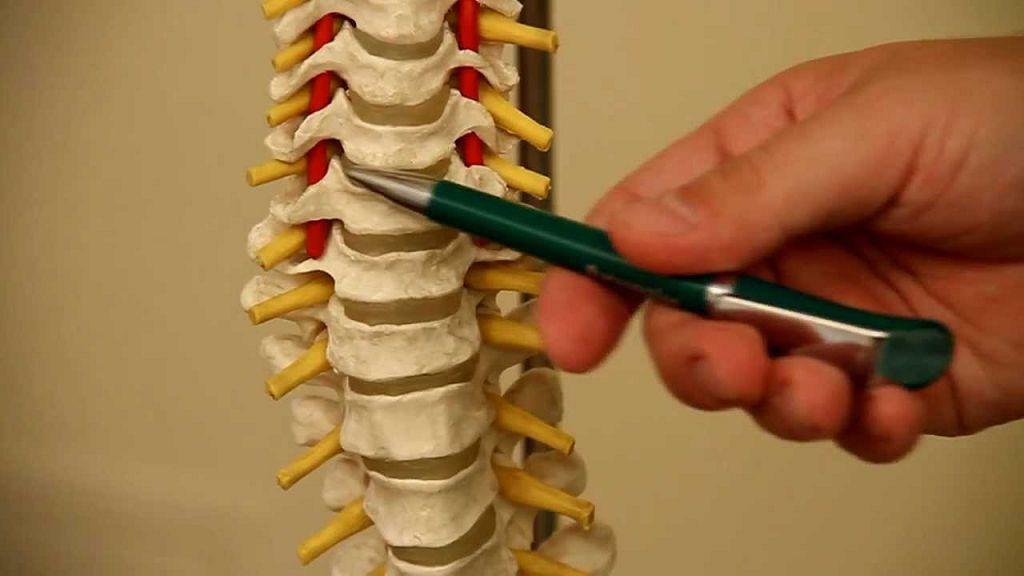
Shortness of breath for osteochondrosis is a nonspecific symptom of this pathology. It signals a violation of the blood supply of tissues and, as a consequence, the development of hypoxia. This condition is dangerous for the health and life of the patient and requires timely diagnosis and treatment.

Dyspnoea with osteochondrosis: symptoms
Content of material
- 1 Features of pathology
- 2 Dyspnea with osteochondrosis
- 2.1 Clinical picture of dyspnea with osteochondrosis
- 3 What is the danger of dyspnea with osteochondrosis?
- 3.1 Video - Lack of air in cervical osteochondrosis
- 4 Prophylaxis of dyspnea with osteochondrosis
Features of pathology
Osteochondrosis is a pathology in which degenerative-destructive processes occur in various joints. In the vast majority of cases, disorders affect vertebrae and intervertebral discs. The most common osteochondrosis of the thoracic and lumbar region. In addition, isolate the diseases of the cervical and sacral vertebrae. To determine the presence of pathology, the specialist conducts a physical examination of the patient and instrumental studies: radiography, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. When interviewing a patient, the doctor should also pay attention to a number of concomitant symptoms that indicate a severe course of the disease:
- headaches;
- shortness of breath and breathing disorder;
- paralysis and paresis;
- muscle cramps;
- dizziness and fainting.
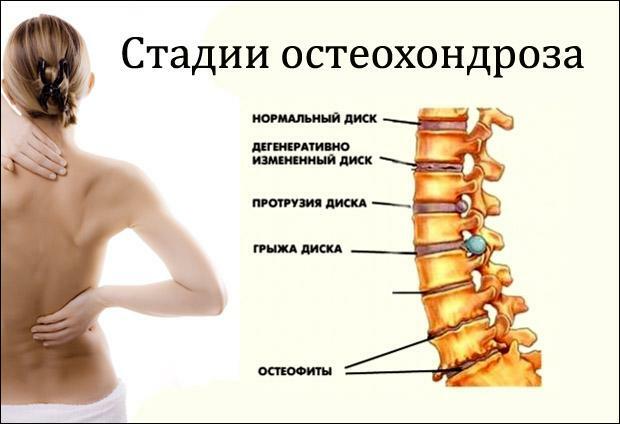
Stages of osteochondrosis of the spine
Development of osteochondrosis develops in most cases with excessive load on the spine, regular weight lifting, muscle weakness and trauma. Normally, the intervertebral disc is adapted to a sufficiently intense external action. Located in the center of the disc, the pulpous nucleus damages under load and protects the joint and bony part of the spine from abrasion. Gradual thinning or sudden rupture of the nucleus leads to a sharp increase in the load on the spine and surrounding tissues and the violation of their integrity.
The first symptoms of the pathology are manifested during exercise: sports, jumping, weeding the garden, etc. In osteochondrosis, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- Long-lasting dull or aching pain in the back.
- Numbness in the joint area, impaired sensitivity of the back muscles in the spine.
- With sharp movements, sharp, shooting pain arises.
- Restriction of the volume of movements, difficulty in tilting.
- Appearance of pain syndrome in the muscles of the hands, the collar zone.
- Cefalgia. The pain is blunt and intensifies with tension.
- Shortness of breath and dizziness due to vertebral artery syndrome.
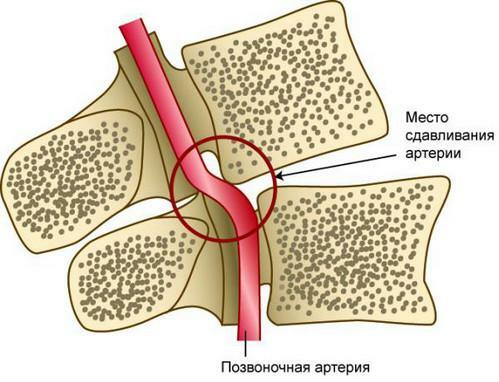
Vertebral artery compression
Dyspnoea with osteochondrosis
In most cases, dyspnea or dyspnea is a sign of the pathology of the cardiovascular or respiratory system. In osteochondrosis, this symptom is a sign of impaired blood flow or muscle tissue damage. Dispnoe manifested by difficulty breathing, changing its frequency and depth, coughing, deterioration of well-being at physical activity, slopes. The patient can complain of chest pain, tachycardia and dizziness.
Warning! Dispnoea with osteochondrosis may also indicate the development of other pathologies: pneumonia, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, heart failure, etc.
Dispnea in osteochondrosis is a dangerous symptom, indicative of lesions of the chest and respiratory depression. If such a sign appears, the doctor should be contacted urgently.
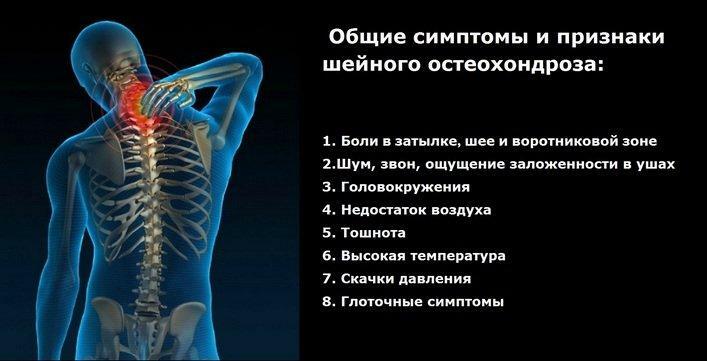
Symptoms and signs of cervical osteochondrosis
Clinical picture of dyspnea with osteochondrosis
In most cases, dyspnea with osteochondrosis develops against the background of vascular compression. Various tissues of the patient's body, including the brain, begin to experience oxygen starvation, as they do not receive the amount of blood they need for normal functioning. In an attempt to get more oxygen, a person begins to breathe more often. If the patient has compression of the arteries in a mild form, then a certain period of time this measure makes it possible to compensate for hypoxia. However, gradually the blood vessels contract more and more, dyspnea becomes more pronounced, and the patient's condition worsens.
This condition is especially dangerous because with cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis, the vertebral artery is narrowed, which feeds the brain oxygen. Because of hypoxia, neurons are dying. The patient thus worsens memory, cognitive function and working capacity decreases, there are intense headaches and fainting.

General information about dyspnea
Shortness of breath is not a specific symptom in osteochondrosis, which is why it is diagnosed late. Therefore, to establish the diagnosis, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- pain in the back, neck and chest;
- sensation of a lump in the throat;
- dry cough;
- deterioration of well-being at loading and inclinations;
- fainting, ripples before the eyes.
Attention! Some patients also experience an imbalance and eructation caused by a lack of blood flow to the middle ear, where the center of balance is located.

Symptoms of dyspnea
Shortness of breath caused by a lack of blood supply to the tissues of the body is manifested by the characteristic signs:
- memory impairment and cognitive function;
- dementia;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- lowering of blood pressure.
Also, dyspnea with osteochondrosis can occur as a result of the destruction of the spine, ribs and muscle tissue around. This leads to a disruption of the mobility of the chest during breathing and a decrease in the amount of oxygen entering the body.
Warning! With pathological changes in this part of the spine, a characteristic symptom is the inability to breathe in full. The patient has an attack of cough, shortness of breath, pain in the back and chest.

Causes of dyspnea with osteochondrosis
What is the danger of dyspnea with osteochondrosis?
Vascular spasm in osteochondrosis leads to the development of various complications, which often do not associate with the underlying diseases that caused them. The work of various organs and systems is disrupted. Patients complain of weakness, they have pallor or cyanotic skin and epithelium, fainting, a violation of the sensitivity of the limbs.
Also, osteochondrosis leads to the development of intercostal neuralgia. Because of the compression of the nerve endings, any movement in the patient produces an acute extremely intense pain syndrome. This condition provokes a violation of breathing, as the patient can not breathe in full. The result of the development of neuralgia is dyspnea.
Attention! The specific feature of intercostal neuralgia in osteochondrosis is frequent superficial breathing and soreness in palpation of the chest.

Treatment of air shortage
As a result, any inhalation causes a sharp shooting pain in the sternum, which makes the patient unable to breathe in full. Together with the disruption of the vascular system, this leads to acute oxygen deficiency and hypoxia of various organs and systems. The cardiac muscle in an attempt to compensate for this condition begins to contract more rapidly, which is manifested by tachycardia attacks and a sensation of pulsation in the temples, dizziness, weakness.
Dyspnoea with osteochondrosis is a symptom of oxygen starvation of the body, which can lead, in the absence of treatment, to severe enough complications:
- heart failure;
- acute circulatory disturbance in various organs;
- angina attack;
- infarction;
- muscle atony;
- ischemia of the brain.
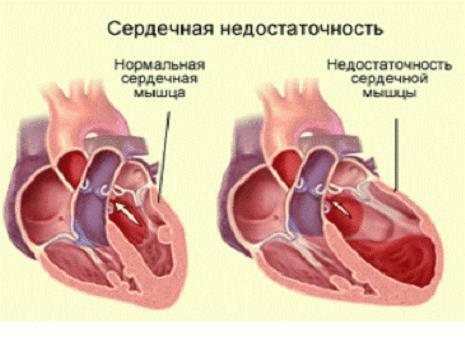
Heart failure
The development of such pathologies often goes unnoticed against the background of dyspnea and a regular pain syndrome in osteochondrosis. Therefore, it is necessary to establish the cause of the disturbance in good time.
Forms of pain syndrome for different pathologies
| Disease | Localization of pain | Characteristic | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteochondrosis | Spine region along the spine, neck and collar zone. May disturb pain in the chest along the ribs | Prolonged aching or dull, strengthened with exercise, partially suppressed by analgesic and resting | of moderate intensity, sharply enhanced with tilts, jumps, sharp inhalation |
| Angina | Neck, lower jaw, area behind the sternum on the left | Pressing, intensive, accompanied by an attack of tachycardia and cold sweat | From 1-1,5 to 15 minutes |
| Infarction | Behind the sternum on the left, gives in the arm, shoulder and lower jaw, abdomen | Acute, compressive,fifth unbearable and leads to loss of consciousness | On average, 15 to 60 minutes |
Attention! If you suspect an attack of angina or a heart attack, you should immediately call a doctor. Lack of medical care can lead to the death of the patient.
Video - Lack of air in cervical osteochondrosis
Prophylaxis of dyspnea with osteochondrosis
In case of osteochondrosis, the patient should follow the recommendations aimed at preventing vascular changes and, accordingly, dyspnea. These activities include the implementation of specially adapted for sick gymnastics, proper nutrition and intake of various vitamin-mineral complexes.
Warning! Self-correct improper treatment of dyspnea with osteochondrosis can lead to general deterioration of the patient's well-being and development of complications.
Prevention of dyspnea and other complications in this pathology includes the following activities:
- In the morning, you need to perform special therapeutic gymnastics aimed at strengthening the muscles of the chest, back and neck and improving overall blood flow.
- A full 8-9 hour sleep on an orthopedic mattress and a thin cushion.
- For the relief of dyspnea, it is recommended to use essential oils of eucalyptus, pine, fir.
- Daily walks in the open air, swimming, aqua aerobics.
- Refusal from bad habits, especially the use of alcohol, since alcohol leads to a violation of the tone and elasticity of the vascular wall.
- Proper nutrition that provides the body with a sufficient number of proteins, amino acids, calcium and potassium.
Shortness of breath for osteochondrosis is an alarming symptom, indicative of the progression of the disease and involvement in the pathological process of the vascular system. This condition requires urgent treatment to the doctor and a full-fledged complex therapy of pathology.