Not all men with an inflammation in the prostate are sent to see a urologist, but in vain. After a long inactivity against the background of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland leads to the formation of calcinants or stones in it. That is, calcinates in the prostate are inorganic, density-structured formations localized predominantly in the acini( functional unit of the organ) and excretory ducts.
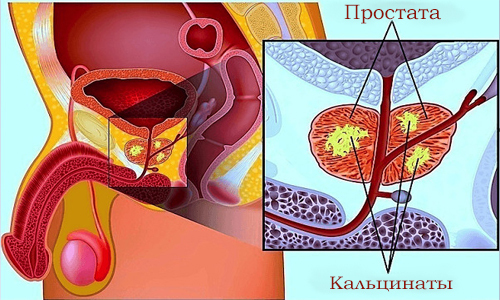
Symptoms of formation of calcitates
Calcine formation is predominantly affected by males for 45. The clinical picture of calcifications in the prostate consists of such signs as:
- Pain syndrome - can be observed in the scrotum, perineum, groin, radiating to the sacrum, lumbar region,sharp character. Prerequisites for intensifying pain are sexual acts, excessive physical overload, the process of urination;
- Blood extraction. Bloody spots can be present in sperm or urine;
- Violations of urination - may be manifested by increased urgency, regardless of time of day, cutting and soreness in the process of emptying the bladder.
Similar symptomatology is usually observed in patients in the case of formation of infected calcifications. If there is no infection, then calcification in the prostate a man may not bother. A similar situation occurs in urological practice quite often, which is very dangerous, since the latent formation and development of calcifications can lead to the neglect of the disease.
Warning! Such symptoms may indicate the presence of other dangerous pathologies in the genitourinary area of men, so do not ignore such manifestations, especially self-diagnosis and self-medication.
Why the formation of
stones occurs in the prostate In scientific circles, there are several assumptions about the causes of the formation of prostatic calcifications. Based on the first theory, similar formations are formed from the components of the prostatic secretion, which performs motor and nutritional functions for spermatozoa when their  moves to the egg. When the epithelial cells of the secretion begin to disintegrate, amyloids are formed, which act as the nucleus of the future calculus. Then calcium carbonates and phosphates begin to accumulate on it. According to the second theory, prostatic stone formation occurs against the backdrop of chronic inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary and reproductive system of men.
moves to the egg. When the epithelial cells of the secretion begin to disintegrate, amyloids are formed, which act as the nucleus of the future calculus. Then calcium carbonates and phosphates begin to accumulate on it. According to the second theory, prostatic stone formation occurs against the backdrop of chronic inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary and reproductive system of men.
Advocates of another theory blame the formation of calcification of urinary reflux when there is a return outflow from the bladder to the ureter. This is confirmed by the composition of calcinates, which includes urinary components. During a reverse cast, urine enters not only into the ureter, but also into the prostate. Such a phenomenon occurs mainly after trauma or surgical intervention on the prostate gland, although it also meets a reflux, the causes of which can not be ascertained.
According to statistics, the formation of calcitans takes place in approximately 8 out of 10 patients suffering from adenoma or prostatitis after 50.
Many factors contributing to the formation of prostatic calcifications have been identified by specialists:
- Hypodynamic lifestyle, low mobility;
- Sitting professional activity;
- Absence of sexual contacts or their irregularity;
- Presence of chronic infectious foci in the body;
- Frequent constipation;
- Subcooling;
- Incorrect diet.
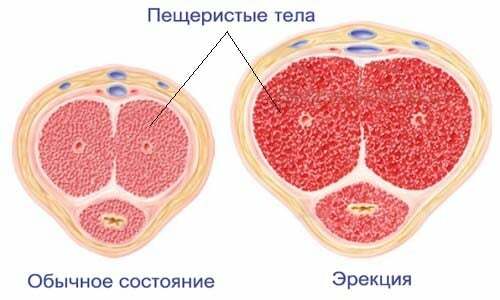
Crosters of low-dose organs contribute to the obstruction of the prostatic ducts, which leads to stasis of secretion and provokes the formation of concrements. In the presence of inflammatory foci, the body tries to protect itself by covering them with calcium shells, which later become the raw material for calcite formation. Unregulated sexual intercourse and unrealized erection provoke stagnation of the secret, predisposing to prostatic stone formation.
Urological and genital infections when ingested into prostatic tissues also provoke the formation of concrements. As a result of the research, it was found that nicotine and alcohol dependence, the predominance of fatty, sharp, heavy meals in the diet leads to a change in the chemical composition of the prostatic juice, which also increases the risk of prostate stones.
Methods of treatment
The method of treatment of prostatic stones is selected individually and depends on factors such as the number of stones, their size, the cause of the formation, the clinical picture and the concomitant diseases. In any case, one of the following methods is used: conservative therapy, crushing or surgical intervention.
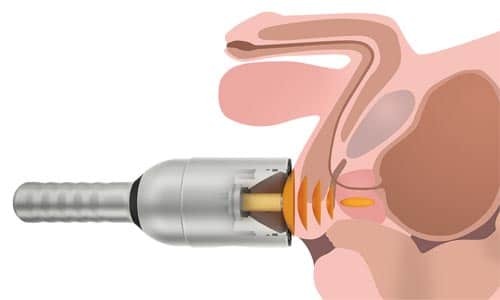
Conservative therapy
Immediately specify that conservative methods do not relieve stones. Sometimes a doctor simply chooses observing tactics and simply follows the changes. But such a technique of non-interference is relevant in small pebbles that do not cause the patient any discomfort.
Warning! In the presence of prostatic calcifications, it is strictly forbidden to perform finger massage of the gland, as concrements can injure glandular tissues.
In some cases it is necessary to slow down or stop the further stone formation. In this case, resort to conservative drug therapy, in other words, the patient is prescribed the appropriate drugs. In addition, with the help of drug treatment, the main pathology, which became the primary cause of calcification formation, is eliminated. In addition, taking medication, the patient gets rid of problems with urination and stops pain.
Stone crushing
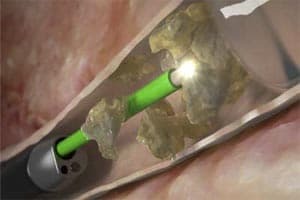 The most commonly used are ultrasonic or laser crushing of calcinates, as a result of which the crushed formations independently go out through the glandular ducts. But this technique has many opponents who claim that especially large fragments can remain in the gland and provoke further formation of calcinates. Although in most cases this technique is most effective.
The most commonly used are ultrasonic or laser crushing of calcinates, as a result of which the crushed formations independently go out through the glandular ducts. But this technique has many opponents who claim that especially large fragments can remain in the gland and provoke further formation of calcinates. Although in most cases this technique is most effective.
Surgical treatment of
If calcification is particularly large, operative removal of calculi is indicated. Such an operation can be carried out in various ways:
- Open intervention - when removal is performed by opening the abdominal wall;
- Transurethral route - when the procedure for removal is through the urethra;
- Laparoscopy - when removal is performed through minor punctures in the abdomen.
When serious and unremovable glandular lesions occur, then prostatectomy or removal of the prostate gland is resorted.
There is no specific prevention of calcification, it is necessary to avoid the factors provoking their formation. In other words, you need to lead a regular sex life, choose the right diet, avoid sexual infections, limit alcohol and timely to take medical measures to eliminate genitourinary diseases.