Aseptic meningitis( English aseptic meningitis) is an inflammation of the meninges, which, as a rule, has a soft stroke, but in some cases may be life-threatening.
Aseptic meningitis( English aseptic meningitis) is an inflammation of the meninges, which, as a rule, has a soft stroke, but in some cases may be life-threatening.
The disease is usually caused by some viruses, but it can not be said that it is a synonym for viral meningitis.
Contents
- Pathogenesis of the disorder
- Pathogenesis of the disorder
- Epidemiology
- Phases of the disease and clinical picture
- What causes the infection
- Clinical picture and complaints
- Diagnosis and examination of the patient
- Medical care
- Consequences of the disease
- For the prevention of
Pathogenesis of the
violation Most pathogens spread at the entry point inbody, which is usually represented by the mucosa of the respiratory tract or gastrointestinal tract.
After overcoming local defense mechanisms, they spread into the blood, during viremia or bacteremia, it can go to overcoming the blood-brain barrier and penetrating the central nervous system.
The presence of a pathogenic microbe in the subarachnoid space causes the accumulation of immune cells, predominantly T cells, and later B cells, which, after conversion into plasma cells, initiate intrathecal synthesis of specific immunoglobulins.
Inflammation in the central nervous system can also occur as a manifestation of immunological reactions to pathogenic agents, and in this case, the symptoms of CNS lesions develop, approximately, 1-3 weeks after the onset of the disease.
Epidemiology
The disease occurs during an epidemic in places where many people contact each other, for example, in military barracks during mobilization, school campuses, and during the annual pilgrimage to Mecca. The spread of the epidemic in the risk zones is associated with several factors. 
These include:
- medical conditions( immunological susceptibility of the population);
- demographic conditions( travel and travel of a large number of people);
- socio-economic conditions( overpopulation and poor living conditions);
- climatic conditions( drought and dust storms);
- concomitant diseases( acute respiratory).
Inflammation provokes edema, hyperemia of the meninges and their infiltration of lymphocytes. Affects the surface of the brain( less often dorsal).
Phases of the disease and clinical picture
Aseptic meningitis undergoes three stages of development:
- prodromal phase - characterized by fever, pain in the muscles and throat, diarrhea, rash, fatigue and malaise;duration - 3-7 days;
- phase of waiting - 2-5 days, practically, without symptoms;
- phase of neuroinfection - photophobia, headache, nausea or even vomiting, dizziness, meningeal symptoms, drowsiness;recovery, as a rule, occurs within 2 weeks.
In some cases, the disease can occur asymptomatically or only with the 1 st phase.
What causes infection of
 In most cases, aseptic meningitis is caused by ECHO and Coxsackie enteroviruses. In rare cases, the cause may be adenovirus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Bar virus and arenaviruses.
In most cases, aseptic meningitis is caused by ECHO and Coxsackie enteroviruses. In rare cases, the cause may be adenovirus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Bar virus and arenaviruses.
In some cases, aseptic meningitis can develop as a complication of diseases such as tuberculosis, syphilis, measles or HIV infection.
The disease can also develop due to herpes simplex virus and chicken pox and arise as a side effect of mumps.
Non-infectious causes of meningitis include tumor infiltration, breakthrough of intracranial cysts, endolumbial administration.
Possible development of reactive inflammation in systemic administration of drugs, as a reaction in hypersensitive people.
Medications that cause hypersensitivity reactions include, mainly, Ibuprofen, antimicrobial agents( in particular, sulfonamides) and immunomodulators( intravenous immunoglobulins, monoclonal antibodies, Ciclosporin).
Clinical picture and complaints
Symptoms of aseptic meningitis may appear several hours after its attack on the body, or develop slowly over several days, usually 3-6 days.
These include:
- headache;

- heat;
- stiffness of the occipital muscles( impaired ability to free tilt of the head);
- photophobia( sensitivity to light);
- lethargy;
- muscle pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- chills;
- angina;
- abdominal pain;
- sometimes - confusion and visual hallucinations;
- is sometimes a rash;
- meningeal signs;
- spinal symptoms( impossibility to touch forehead to the knee);
- Brudzinsky's symptom( when the doctor tries to bow the patient's head, he flexes the limbs reflexively);
- Kernig symptom( when the doctor attempts to bend the patient's leg in the hip joint, he reflexively bends the knees).
Diagnosis and examination of the patient
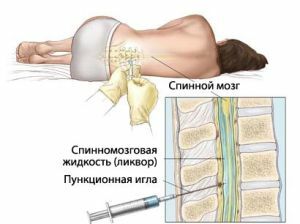
In diagnosis, the physician relies on a thorough examination, objective findings and cerebrospinal fluid for lumbar puncture. In epidemiological history, attention is drawn to tick bites, contact with animals, picnics or staying abroad.
About aseptic meningitis:
- is a clean or slightly turbid cerebrospinal fluid;
- low or moderate pleocytosis with a predominance of mononuclear cells;
- only slightly increased proteinurahia;
- is the normal level of glucose in the liquid.
 At the very beginning of the disease, the superiority of granulocytes can be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid, especially when the disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus.
At the very beginning of the disease, the superiority of granulocytes can be detected in the cerebrospinal fluid, especially when the disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus.
Unusually high pleocytosis( 1000-3000 / 3 elements) occurs with meningitis, which arose as a complication of mumps and lymphocytic choreomeningitis.
For a disease caused by the herpes virus, mumps and lymphocytic choreomeningitis, moderate hypoglycorhychaemia is sometimes observed.
Parameters of acute inflammation in the blood, in contrast to infectious meningitis, are only slightly increased. For etiologic diagnostics, microbiological and serological tests are needed, oriented to the causative agent of the disease.
For differential diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude:
- subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- insufficiently cured infectious meningitis;
- reactions to paramagnetic infections( sinusitis, mastoiditis, osteomyelitis of the skull bones);
- cervical-cranial syndrome.
If non-infectious causes of aseptic meningitis are identified, it is necessary to differentiate toxic causes( arsenic poisoning, lead), allergic origin( eg serum sickness) and meningitis associated with sarcoidosis.
Medical assistance
In case of detection of meningitis caused by the herpes virus or Epstein-Barr virus, acyclovir drugs are used for its treatment.
For people with a weakened immune system and young children, antiviral therapy with intravenous Immunoglobulin is necessary. To reduce intracranial pressure, patients are prescribed diuretics, such as Furosemide or Lasix. 
In more complex cases, doctors prescribe intravenous administration of saline solutions that can reduce intoxication. This is Ringer's haemodes, albumin and glucose. To significantly reduce the headache and reduce intracranial pressure, a spinal puncture is also prescribed.
If aseptic meningitis affects a child, then if the temperature is kept above 38 degrees, various antipyretic agents, for example, Acetaminophen, are prescribed.
The package of measures for the treatment of the disease includes the use of antihistamines, which not only reduce fever, but also alleviate the symptoms of the disease. This is mainly Tavegil, Suprastin and Zodak.
 If a patient has convulsions, prescribe medications Domosedan or Seduxen. During treatment, patients are recommended silence and peace, in the room where the person is staying, it should be dark in order to prevent eye irritation.
If a patient has convulsions, prescribe medications Domosedan or Seduxen. During treatment, patients are recommended silence and peace, in the room where the person is staying, it should be dark in order to prevent eye irritation.
It is also necessary to include vitamin C, B6, B2 and cocarboxylases during treatment. As an adjuvant therapy, oxygen treatment is used. Correct and timely treatment of aseptic meningitis in adults and children ensures a quick and full recovery without any complications.
Consequences of the disease
With meningitis, the meninges are hyperemic, which breaks the blood-brain barrier, which leads to brain edema. 
Pus is produced, which can enter the brain vessels and cause inflammation and ischemia of the brain tissue. Abscesses containing pus that can inhibit brain tissue can form.
Depending on the damage to the brain, there are various types of paralysis, visual impairment and hearing loss, mental retardation.
Sometimes bleeding in the adrenal gland is possible. Acute and life-threatening circumstance is the onset of sepsis.
For the prevention of
To reduce the risk of developing aseptic meningitis, the following precautions should be observed:
- often wash hands, especially after being in close contact with a sick person and after changing diapers to a sick child;
- on time vaccination.
With proper therapy, positive changes in the patient's condition occur within 3-5 days, the person recovers without any further consequences.