 Myofascial pain syndrome is a special painful condition, manifested by the onset of of painful muscle spasm and muscle dysfunction of .
Myofascial pain syndrome is a special painful condition, manifested by the onset of of painful muscle spasm and muscle dysfunction of .
The disease is preceded by the appearance in the muscle fibers of painful seals, called trigger points. Usually they are localized in places of spasm, in compacted muscle beams or in fascia.
Perhaps there is no person who has never experienced pain in his life in his muscles. Therefore, our calm attitude towards these painful manifestations is fully justified.
Most people assume that all this has a natural character. But, unfortunately, in the overwhelming majority of cases, pain in the skeletal muscles are symptoms of myofascial syndrome.
The area of the back is usually the problem area, as most often the patient presents the doctor with complaints of pain in the back. Often, this soreness is caused by problems associated with the muscular apparatus.
For myofascial pains, is characterized by the formation of compaction sites in muscle fibers or in their fascia called trigger zones. They often arise in the background of the osteochondrosis of the spine under the influence of muscle tension.
Muscles almost all the time respond to painful impulses with a tonic reflex reaction.
Physiologically, muscle tension, following any pain, is justified by immobilization of the affected area of the body, the creation of its muscular corset. But the muscle itself is a source of additional pain.
Also, the muscles can be affected primarily without morphological or functional disorders of the spine. Any excess types of muscle tension can lead to tissue dysfunction with the formation of a pain syndrome.
 In what diseases do osteophytes of the spine occur most often and what treatment methods do exist. Replacement or endoprosthetics of the knee joint - in which cases surgery can not be avoided, and what needs to be remembered when lying down on the operating table.
In what diseases do osteophytes of the spine occur most often and what treatment methods do exist. Replacement or endoprosthetics of the knee joint - in which cases surgery can not be avoided, and what needs to be remembered when lying down on the operating table. Article Contents
- Reasons syndrome
- Localization
- pain Clinical manifestations
- Diagnostic techniques
- Treatments
- Addressing the causes of pain
- Treatment of pain
- Rehabilitation and
- recovery Possible complications
reasons
syndrome Myofascial syndrome is a lot of people at the constant playing sports or heavy physicalwork.
Periodic minor injuries cause damage to individual muscle beams, resulting in inflammation, which results in the formation of areas of scar tissue.
When the scar is located close to the nerve fibers, a very pronounced and intense pain syndrome can occur.
The most common reason for the occurrence of vertebrogenic myofascial syndrome is osteochondrosis .
Osteochondrosis irritates the nerve of Lutsaka, innervating the structure of the spinal column. This is what causes the reflex spasm of the near-vertebral and distant muscles. Due to prolonged presence in the state of spasm, in the muscle after a while active trigger points are formed.
Anomalies in the development of the human body are also the cause of myofascial pain.
The main factor in this case is the asymmetry of the body and the difference in length of the legs. Different length of legs is common enough, but it has a value at a difference of more than one centimeter.
Uneven distribution of the load on the feet, shin, hips and lumbar region, their constant tension leads to spasm and the development of trigger points.
Pain syndrome develops not only against the background of anatomical disorders, it is associated with some habits. For example, myofascial pain syndrome of the face, is associated with the habit of jaw compression under stress.
The risk factors that contribute to the development of the pain syndrome include:
- stoop;
- wearing pressure clothing or accessories, such as corsets, over tight belts, heavy bags on one shoulder;
- sports and heavy physical work;
- significant weight( obesity);
- immobilized limbs;
- of the spinal column;
- emotional instability.
Pain localization
The syndrome can manifest in different muscle groups. Therefore, the following myofascial pains in localization are distinguished:
- lumbar pain;
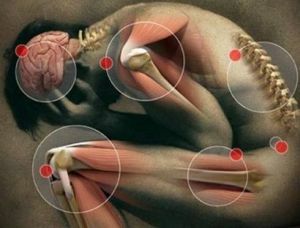
- pain in the shoulder and neck;
- thoracic pain;
- abdominal pain;
- pelvic pain;
- thigh pain;
- headaches;
- pain in the jaw;
- lower limb pain;
- upper limb pain.
The most commonly diagnosed myofascial syndrome of the cervical region, most rarely - the pelvic floor.
Clinical manifestations of
The syndrome usually has clear symptoms that are associated with the appearance of muscle spasm, the presence of trigger points, a decrease in the volume of movements of the affected muscle.
There are two types of trigger points:
- Active trigger points are characterized by pain, manifested as the location of the location of the point, and in remote areas. Pain occurs both in rest and motion. Each point has a specific place of reflection of pain. At the site of the lesion, changes in sweating, skin color, and the appearance of hypertrichosis may occur. When stimulating the trigger point, a local convulsive response arises, the so-called "jump symptom", manifested by muscle contraction and severe pain.
- Latency trigger points are more common than active ones. With their palpation, local soreness appears, pain reflection in remote areas does not occur. Latent trigger points are triggered by provoking factors such as hypothermia, pozotonic overstrain, emotional stress, excessive physical stress, anxiety, and others. With short-term rest, warmth and adequate therapy, the transition of the active trigger point into a latent state is possible.
There are three phases of the flow of myofascial pain dysfunction:
- The first phase of is acute. It is characterized by a constant painful pain in especially active trigger points.
- The second phase of the is characterized by pain that occurs only during movement and is absent at rest.
- The third phase of the is chronic. It is characterized by the presence of dysfunction and a sense of discomfort in the relevant area.
Diagnostic Techniques
For muscular pain, it is first of all necessary to exclude inflammatory etiology, as well as vertebrogenic compression radicular and spinal pathologies.
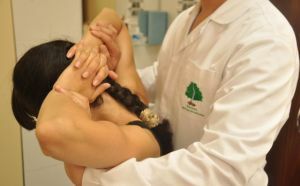
To identify trigger points, you need to own the correct technique of palpation.
It is necessary to stretch the muscles along the length, at the peak of stimulation of pain, among the relaxed muscles, the cord will be palpated in the form of a tight cord, along it the point of greatest soreness is located, when pressed, pain is reflected.
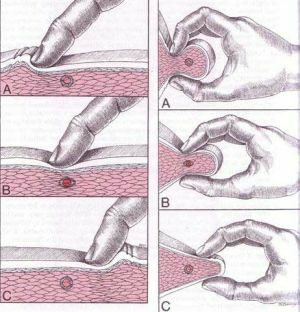 Two methods of palpation are used: is deep and tick-borne.
Two methods of palpation are used: is deep and tick-borne.
When performing deep palpation, the doctor with fingertips follows across the muscle fiber.
When carrying out tick-borne palpation, the doctor grasps the abdomen of the muscle with the thumb and the rest of the fingers, then it "rolls" the muscle fiber between them, revealing the trigger points.
When diagnosed, they are guided by the following criteria:
- The presence of a pain connection with physical overload, pozotonic overstrain or supercooling.
- Definition in muscles of dense painful cords. Absence of hypo- or muscle atrophy.
- Pain spreading in the areas of the
- far from the tensed muscle The presence of areas of even greater muscular compaction within the strained muscles. When you press on them, soreness increases dramatically - "a symptom of a jump".
- Reproduction of reflected pain during compression or puncture of the trigger point.
- Removability of symptoms with a special local effect on stressed muscles.
Treatment procedures
When diagnosed, myofascial pain syndrome occurs in several ways.
Elimination of the causes of pain
The first is to eliminate the cause of pain.
It is also a prevention of the appearance of pain. Disorders of posture need to be adjusted with the help of a special pathogenetic complex of exercises. With different length of legs use special insoles with a thickening of 0.3-0.5 centimeters. And so with every violation.
Treatment of pain syndrome
The second is aimed at treating pain syndrome.
There are two directions of drug therapy in : effect on the vicious circle of pathogenesis and effects on the central nervous system. 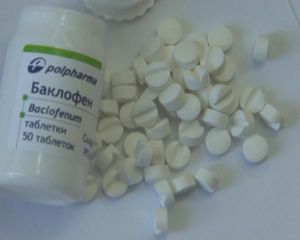
To break the vicious circle of pathogenesis, the disease is prescribed by muscle relaxants, as they provide a reduction in the flow of painful impulses from the periphery. Doctors usually prescribe such drugs as Baclofen, Midokalm, Sirdalud.
To prevent the transition of pain to the chronic form with the formation of a syndrome of autonomic dystonia, GABA -ergic drugs such as noophen, adaptol are prescribed;sedatives, antidepressants, vegetotropic drugs.
Non-pharmacological treatment of consists of the use of methods such as post-isometric relaxation of the affected muscle, puncture of trigger points, acupressure, massage and physiotherapy.
The procedure is then repeated three to five times, depending on the degree of muscle tension.
Rehabilitation and rehabilitation
The third direction is rehabilitation. The main goal of rehabilitation is to create the right motor stereotype, teach the patient the ability to own one's own body, create and strengthen the muscular corset.
Special attention is paid to the complex of corrective and tonic exercises, which correct the posture when correctly performed.
Possible complications
 The started myofascial pain syndrome is fraught with the development of fibromyalgia.
The started myofascial pain syndrome is fraught with the development of fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disease characterized by symmetrical pain almost throughout the body.
People suffering from this disease can not sleep properly, they have problems with digestion, chronic fatigue arises.
Therefore, attention should be paid to the presence of myofascial pain and timely treatment.