One of the most important hormones for the female body is progesterone. It is also called the "pregnancy hormone".After all, it allows a woman to bear a child without problems, helps the body to reorganize, and the egg to attach and develop in the uterus. Very often, the inability to become pregnant is associated with its increased or decreased content. There are some factors that affect its level. These include
- pregnancy;
- intake of oral contraceptives containing this hormone;
- menopause;
- stress;
- woman's food.
But the most important, of course, is the menstrual cycle. After all, it is divided into several phases. Consequently, the level of progesterone can not be constantly the same.
Norm of the hormone in the luteal phase of the
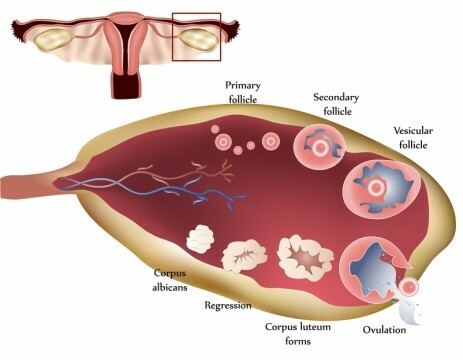
The luteal phase is the fourth phase of the cycle. It lasts 13-14 days. It is during this period that the yellow body, which remains in the ovary after the release of the egg, begins to produce progesterone quite actively. Thus, the body is preparing for a possible pregnancy.
In the luteal phase, the level of the hormone is much higher than in other periods. The progesterone content is from 6 to 56 nmol / l, while for other phases the maximum value is approximately 9 nmol / l. If doctors do not see this increase in the tests, then this indicates that a woman can have any violations in the body.
How to pass the tests
To ensure that the test results are as accurate as possible, there are some rules that must be observed.
- first of all, a woman should tell the doctor the dates of the beginning and end of menstruation. He, in turn, will determine the most suitable day to donate blood;
- you can not eat 8 hours before the tests. Even better, if it takes 12 hours. You can only drink clean water;
- a day before going to the hospital it is worth to give up alcohol and fatty foods, and also from physical exertion;
- in addition, it is worth informing the doctor about the medications taken.
As a result of the studies, the hormone content in the woman's body is determined. Basically, the tests are given on day 23-35 of the cycle, in the luteal phase. After all, the norm of progesterone fluctuates quite strongly in this period, which allows the doctor to determine the deviations in the body, if any.
Elevated Progesterone Indices
If the level of this hormone is elevated, then this may be a sign:
- of a woman's pregnancy. After all, in this condition, progesterone begins to be produced in increasing quantities to create favorable conditions for the fetus;
- if there is no pregnancy, then progesterone may be higher than normal with uterine bleeding, amenorrhea;
- moreover, sometimes it indicates the occurrence of a yellow body cyst;
- sometimes the content above the norm is a symptom of any problems with the kidneys or adrenal glands.
Underestimated hormone
If, however, this hormone is reduced in the luteal phase, this may be a sign of
- of chronic inflammation of the ovaries;
- any violations of the functionality of the yellow body;
- lack of ovulation;The
- menstrual cycle is disturbed;
- in addition, with a lowered level of this hormone, a fertilized egg simply can not gain a foothold in the uterus. And this means one thing - miscarriages and infertility.
This condition is called deficiency of the luteal phase. This disease is a big problem for those women who are planning a pregnancy. After all, the progesterone that is produced is simply not enough for this.
Reasons for decreased hormone
The reasons for the luteal phase deficiency are somewhat:
- sometimes due to any injuries or severe stresses, the pituitary gland may malfunction. As a result, there may be problems in the woman's reproductive system;
- if a woman has chronic inflammatory processes, adhesions, infections of the reproductive system;
- if there is a metabolic disorder;
- and even improper nutrition can affect the level of progesterone produced;
- if during the cycle the yellow body receives insufficient blood, i.e.its inflow is violated.
Consequences of such a disease usually become infertility, i.e.impossibility to become pregnant. In addition, if the pregnancy does occur, there is a constant threat of miscarriage.
Diagnosis
To determine whether this disease is present, the following method can be used. Basal temperature is measured, and if the difference between the two measurement steps is more than 0.6 degrees, then it is worth considering. Although this method is not 100% accurate, it is better to consult a specialist if any suspicions arise.
In any case, abnormalities are signs of any hormonal failures in the body of a woman, problems in the work of her reproductive system.
The expert should consider the results of the tests. And only he can prescribe the right treatment. In no case can not choose the medication yourself, because you can cause more damage to the body. The specialist himself will choose what is best in this case - pills or injections.
If a woman plans to have a baby in the future, then it's worth taking care of her health, taking all the tests on time, so that in the future there will be no problems with conception and the course of pregnancy. It is worth turning to good specialists, so that if necessary they can provide professional assistance.