Infectious mononucleosis is common in children and adolescents. In rare cases, this pathology worries adults. The disease occurs with characteristic symptoms of angina, lymphadenopathy and enlargement of the liver and spleen.
With normal immunity, after a month or a little more, the symptoms of the disease completely disappear and the patient returns to the usual life.
What is it?
Infectious mononucleosis is a viral infectious disease accompanied by damage to the lymph nodes, mouth and pharynx, enlarged liver and spleen, and characteristic changes in the hemogram( blood test).
The causative agent of the disease is a virus from the family of herpes viruses( one of the forms of infection of the Epstein-Barr virus), which settles in other cells and causes their active reproduction.
The virus is practically unviable in the external environment and quickly dies under the influence of high and low temperatures, sunlight or antiseptics.
- The source of infection is a person in the midst of a disease or at a stage of recovery. There is a hidden carrier of the virus.
The disease is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets. The virus actively accumulates in saliva, so a contact path of transmission is possible at kisses, through objects of personal use, during sexual intercourse. There have been cases of transmission of infection during labor and blood transfusion.
The susceptibility of people to the virus is very high, but due to immune protection, minor degrees of severity of the disease prevail. In the presence of immunodeficiencies, generalization of the infection and the development of severe consequences are observed.
Contents
- 1 Infectious mononucleosis in children
- 2 Symptoms of infectious mononucleosis
- 3 Treatment of infectious mononucleosis, preparations
- 3.1 Forecast
- 3.2 Consequences of
Infectious mononucleosis in children

The disease is predominantly found in children - usually they become ill with adolescents aged 12-15 years. Less often the infection affects children of younger age.
Infectious mononucleosis in adults is practically not found, except for people with severe immunodeficiency, for example, with HIV infection or after taking cytotoxic drugs.
The outbreaks of infection are increasing in the autumn-winter period. Contribute to the spread of the virus close household contacts, the use of common toys, utensils, hygiene items.
Symptoms of infectious mononucleosis
 The incubation period of infectious mononucleosis( the time from the moment of getting the virus to the appearance of the first signs of the disease) is from several days to one and a half months. The first symptoms of infectious mononucleosis in children develop gradually: weakness, subfebrile temperature, nasal congestion and discomfort in the mouth.
The incubation period of infectious mononucleosis( the time from the moment of getting the virus to the appearance of the first signs of the disease) is from several days to one and a half months. The first symptoms of infectious mononucleosis in children develop gradually: weakness, subfebrile temperature, nasal congestion and discomfort in the mouth.
In the acute period of the disease the symptoms are aggravated:
- Raises the temperature to febrile values.
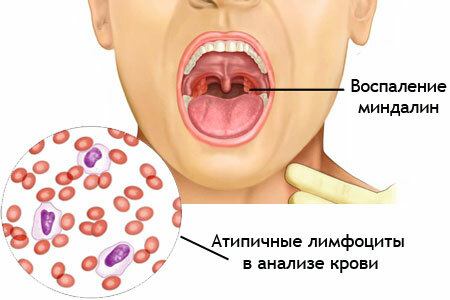
- Sore throat, which is worse when eating and swallowing saliva. Because of this symptom, the disease is often confused with sore throat.
- Severe headaches.
- Signs of body intoxication: aches in muscles and joints, weakness, loss of appetite.
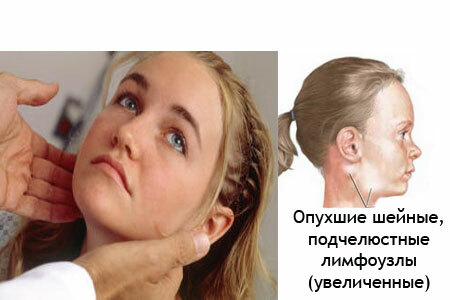
- Enlargement of lymph nodes. The patient can detect enlarged lymph nodes in almost all areas available for inspection. Most often it is noticeable on the submaxillary, cervical and occipital lymph nodes.
- Increased liver and spleen size. In this case, the patient can develop icteric syndrome: dark urine, yellow eyes sclera, rarely there is a rash all over the body, associated with a violation of the liver.
The acute period lasts for several weeks. The temperature can rise for another month, after which the recovery period begins. The patient's state of health gradually improves, the lymph nodes return to normal sizes, and the temperature curve stabilizes.
Important! A feature of the course of infectious mononucleosis in adults is the predominance of symptoms associated with liver damage( jaundice, dyspeptic disorders, etc.).Dimensions of the lymph nodes increase little as opposed to children.
Clinical signs of infectious mononucleosis are quite simply confused with angina, diphtheria, lymphogranulomatosis and some other diseases. The most typical sign is a specific change in blood composition. With this disease, atypical mononuclears and an increase in the number of leukocytes and monocytes are found in the blood.
These atypical cells appear immediately or at the 2-3 week of the disease. During recovery, a small amount of them can also be found in the blood.
Important! Adults with infectious mononucleosis are often recommended to perform additional tests for HIV infection, because similar changes in blood and symptoms are observed in the stage of initial manifestations of HIV infection.
Treatment of infectious mononucleosis, preparations
Treatment of infectious mononucleosis in children takes place at home, however, as in adults( with some exceptions).Patients with severe liver disorders may be hospitalized.
Specific therapy for this virus is not developed, so parents are very worried about the topic than treating infectious mononucleosis in children. For therapy, various groups of medicines are used to eliminate the main symptoms of the disease:
- Local rinses with solutions of antiseptics and herbal decoctions.
- Antihistamines.
- Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory( Ibuprofen).In children, does not recommend to use aspirin to knock down temperature because of the risk of developing Ray's syndrome.
- Hepatoprotectors.
- Antibiotic therapy is indicated only in case of secondary infection.
- With a severe swelling of the pharynx and tonsils, short courses of glucocorticosteroids are used.
Physical activity should be limited for the entire period of the disease( 1-2 months) - there is a risk of rupture of the spleen.
Parallel to the patient prescribed a gentle chemical and thermal diet, rich in vitamins and trace elements. Exclude fatty, fried and smoked dishes, so as not to overload the liver.
How long to treat infectious mononucleosis?
Acute manifestations of the disease last for several weeks, during this period the patient receives symptomatic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
In addition, detoxication therapy is provided, it is possible to use immunomodulators. At the stage of reconvalescence, the patient continues to adhere to the diet, restricts physical activity and, if necessary, undergoes local treatment of the pharynx.
Complete recovery occurs only after a month and a half. The infectious disease doctor treats such patients.
Forecast of
In most patients, the prognosis is favorable. The disease proceeds in a mild and worn form and can be easily treated with symptomatic treatment.
Problems occur in patients with low immunity, in which the virus begins to multiply actively, which leads to the spread of infection.
Preventive measures against infectious mononucleosis do not exist, except for the general strengthening of the body's immune system through balanced nutrition, hardening and physical activity. In addition, you should avoid places where people are crowded, ventilate the premises and isolate such patients, especially children.
Consequences of
The most common complication of the disease is the attachment of a secondary bacterial infection. Patients with weakened immunity against infectious mononucleosis may develop bronchitis, pneumonia and inflammation of other organs.
Non-observance of bed rest can cause a rupture of the spleen. In rare cases, severe hepatitis and bleeding develop due to disorders of the blood coagulation system( the platelet content falls sharply).
Such complications are more typical for patients with weakened immune system and severe concomitant diseases. In most cases, the symptoms disappear without a trace, but the virus remains in the body after treatment of infectious mononucleosis throughout life, and can again manifest itself with a decrease in immunity.