Inflammation is a protective local response of the body to the action of a damaging agent.
Rubor, tumor, carol, dolor and functio laesa( redness, swelling, "local heat," pain and impaired function) - so almost in rhyme in Latin described the essence of the inflammatory process of the great doctors of antiquity Celsus and Galen.
At the turn of the XIX - XX century.clinicians have found other terms for describing this phenomenon - alteration, exudation, proliferation( damage, exit of cellular elements of blood into interstitial spaces and the beginning of healing by the formation of an inflammatory infiltrate).
The modern concept of inflammation is based on the teachings of II Mechnikov: the central process that characterizes inflammation is phagocytosis, intracellular digestion of pathogenic agents.
Content
- 1 reasons purulent inflammation
- 2 forms of purulent inflammation
- 3 purulent inflammation of the skin
- 4 Complications of suppurative inflammation
- 5 Treatment of purulent inflammations
- 6 Antibiotics in purulent inflammations
reasons purulent inflammation
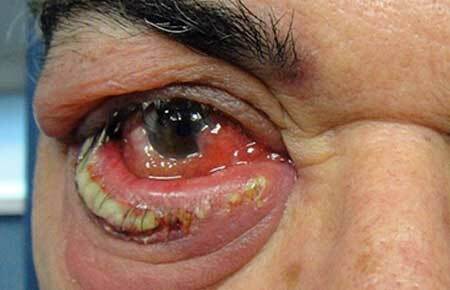
purulent inflammation of the eyelid, photo
Inflammation develops from exposure to external factors:
- of infection andits toxins,
- action of physical stimuli( burn, frostbite, irradiation),
- mechanical( bruises, injuries),
- chemicalagents.
Internal factors can cause inflammation( tissue necrosis, hemorrhage, salt deposition).
Processes occurring in the inflammation zone of
It is easiest to examine the essence of inflammation in a situation with a splinter that is familiar to everyone. At first, it is very difficult to extract a deeply implanted thorn from the soft tissues. But after a couple of days it can be squeezed out together with pus from the swollen and reddened damaged area.
On the action of a traumatic agent, the body responds with a flow of blood to the scene. The permeability of the walls of local blood and lymphatic capillaries increases, and the plasma, together with cellular elements of the blood( red blood cells, leukocytes, lymphocytes, platelets) fills the space between the cells of the damaged tissue. Each kind of blood cells does its job.
When breaking the integrity of the outer cover, sickle-shaped platelets stick together, overlapping each other and form a protective crust on the wound. Erythrocytes provide additional tissue for the injured tissue, and plasma is the nutrients for the fastest healing.
The most important task falls to white blood cells - they fight with pathogens in the wound.
The role of white blood cells in the development of inflammation
The function of leukocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes is literally in hand-to-hand combat with microbes penetrated through the damaged space. They fight one on one.
White blood cells are large, with a small nucleus and a significant amount of protoplasm. Such a structure allows them, approaching the microbe, to embrace it from all sides and absorb into itself.
This phenomenon is called phagocytosis( literally translated - "devouring cells").
After this, the leukocyte dies, its own vacuoles, filled with digestive enzymes, are destroyed, and the fat degeneration of a small brave defender occurs. Fat, as is known, has a yellowish color, which determines the color of pus. If the tissue disintegrates at the site of the injury, the white blood cells act in exactly the same way: they absorb the dead particles and die themselves.
The contents of their vacuoles continue to melt the tissues in which the "battle" occurred, paving the way with pus on the surface. Together with pus, all foreign bodies and necrotic tissues are rejected. The wound cleans and heals.
The sensation of pain arises from the effects of cell decay products on the nerve endings in the tissue and squeezing them with an inflammatory effusion.
Substances contained in the sweat affect the nerve centers that regulate the activity of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, metabolic processes, forming a common response of the body to local inflammation.
Forms of purulent inflammation
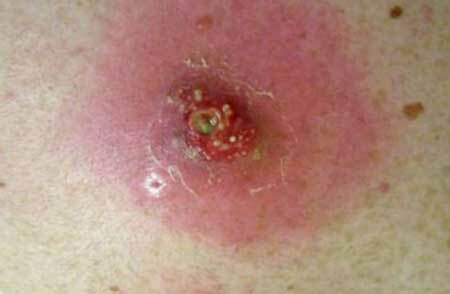
single purulent inflammation on the skin( abscess), photo
Depending on the place of origin of the inflammatory focus and the state of human immunity, the process can take many forms.
Abscess is an abscess located in the thickness of tissues and delimited from them by a connective tissue capsule. An abscess is formed under normal immunity, when the body is able to resist the pathogens that have penetrated.
Around the nidus of inflammation containing pus, a protective shaft, a cover, prevents the spread of infection. Gradually a fistulous course is formed, through which the abscess empties spontaneously. If it lies deep and is surrounded by a dense capsule, surgical intervention is required.
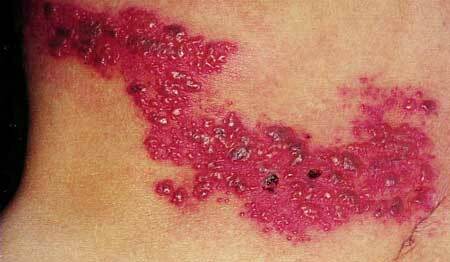
Phlegmon is called spilled fibrous inflammation - loose connective tissue in intermuscular spaces. It develops with reduced immunity, when the body does not have time to build a "line of defense", and the infection freely spreads in breadth and depth.
Phlegmon is a dangerous condition, especially when it develops in the maxillofacial area, where there are many vital organs( brain, respiratory tract, carotid artery).Such a diagnosis requires the patient to be hospitalized.
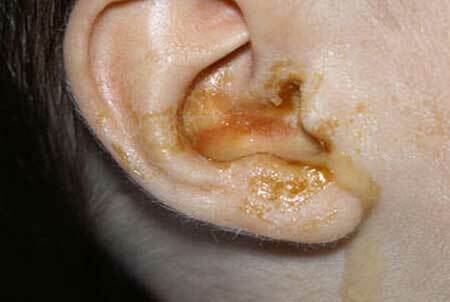
Empyema is a collection of pus in the hollow organs. Walls of such abscesses are not connective tissue membranes, built by the body around the focus of inflammation, and the natural walls of the organ - the pleura, appendix, gallbladder, middle ear, joint.
Especially painful acute otitis( purulent inflammation of the middle ear) occurs, usually due to the spread of infection from the nasopharynx with angina, rhinitis, sinusitis.
The cause of severe pain is that the bony walls of the middle ear can not change the volume in the swelling of the tissues, and the compressed nerve endings send intense signals to the brain.
Purulent inflammation of the skin
Skin and mucous membranes protect the body from the harmful effects of external agents, while they themselves, especially the skin, easily become victims of attacks of streptococci and staphylococci, less often another microflora.
Pyodermia is a purulent skin lesion resulting from its clefts, small cuts, insect bites, contamination or metabolic disorders in the body. It looks like multiple tiny bubbles with cloudy contents on the reddened skin.
Folliculitis - a lesion of the hair sac in the form of a purulent small head on the skin. It occurs with sweating, rubbing the skin with clothing, poor body hygiene. Easily passes into a boil.
Furuncle is a purulent-necrotic melting of the hair follicle and sebaceous gland under it. This abscess is dangerous when placed on the face - it gives mortally dangerous complications: thrombosis of facial veins and meningitis.
The cycle of its development has 4 phases approximately for three days each - if you knock off the furuncle before the maturation phase, the cycle starts anew, the healing is delayed. The causes are the same as in folliculitis.
With a decrease in immunity, a disease develops with multiple abscess formation - furunculosis, which causes much suffering to a sick person.
Carbuncle is a large ulcer on the skin, in the formation of which several hair follicles are involved. It flows very hard - with a local reaction and a general intoxication of the body. After it is emptied, a large cavity remains in the skin, healing with the formation of a scar.
Hydradenitis - purulent inflammation of the sweat gland with the formation of a painful abscess, develops in the armpit and inguinal areas in violation of hygiene rules( more on hydradenitis).
Complications of purulent inflammation
The outcome of purulent inflammation depends on several factors:
- virulence( infectivity, aggressiveness) of microbial pathogens,
- extent and depth of occurrence of the process,
- state of human immunity.
When emptying the abscess, a loose, easily bleeding granulation tissue grows in its place, which is gradually replaced by a mature tissue inherent in the inflamed organ, often with the formation of a scar.
If the factors influencing the outcome are not in favor of the body, then complications may occur:
- spreading the process across the area with the involvement of new organs and tissues;
- purulent meltdown of vascular walls, infection in the bloodstream with development - sepsis;Bleeding;- Vascular thrombosis;
- necrosis of affected tissues;
- dystrophic processes in the kidneys, liver and other organs as a consequence of the general weakening of the body.
Treatment of purulent inflammation of
Treatment of purulent inflammation depends on the type of inflammatory process, the type of pathogen, the severity of the patient's condition, the availability of the focus for manipulation, the prevalence of the process.
A mandatory condition for treatment is the appointment of drugs that increase the body's resistance( glucose, calcium, vitamin therapy).
The amount of surgical care depends on the type and stage of the purulent process.
- Abscess - under anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision and rinses the abscess cavity, followed by rapid healing.
- Phlegmon - appointment of local treatment with a wide opening of the abscess and subsequent drainage and intensive general treatment with the use of antibiotics.
- Empyema - the tactics of the surgeon depends on the location of the focus and the importance of the organ: the gallbladder and appendix are removed, the pleura is opened and the pus is released, the middle ear is treated mainly by conservative methods with the use of antibiotics.
Treatment of purulent inflammation of the skin of the skin begins( in order to avoid the spread of infection) with inhibitions on:
- skin contact with water( no washing, no washing!);
- any compresses and applications;
- massage.
Antiseptic treatment of the skin with alcohol solutions of aniline dyes( for example, with diamond greens) and concentrated potassium permanganate is necessary.
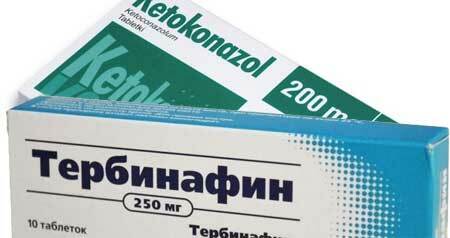
- The use of antibiotics and sulfonamides after determining the sensitivity of microflora to them.
- Among the curative measures - correction of carbohydrate metabolism by establishing a proper diet.
- Furuncles and carbuncles in the head and neck area are treated only in the hospital.
Antibiotics for purulent inflammation
Special mention should be made of the use of antibiotics in the treatment of purulent inflammation. Where one can stop the course of the pathological process without their participation( abscess, single furuncle on the body, pyoderma with good immunity, taking place without general intoxication), one should not resort to them "for better and quicker effect", especially when self-medication.
Uncontrolled use of antibiotics will do more harm than good.
Only the doctor, if necessary, will prescribe antibiotics, selecting the drug that is optimal for each specific case.