The thyroid gland, or "thyroid gland," as it is commonly called in the people, is one of the most important glands of internal secretion, which is part of the human endocrine system. It is located on the neck, somewhat lower than the thyroid cartilage, consists of an isthmus and the right and left lobes. The isthmus is located on the external surface of the trachea, and the right and left lobes adjoin it on the sides.
The connective tissue from which the thyroid gland consists is saturated with blood vessels and lymphatic systems. On the inner surface of the cells of the follicles, the smallest vesicles in the connective tissue, there are thyreocytes - cells responsible for the synthesis of thyroid hormone( iodothyronine: thyroxine and triiodothyronine), which are the main regulators of human homeostasis. Under their influence, all biochemical reactions in the cells of our body are accelerated.
Functions of thyroid hormones
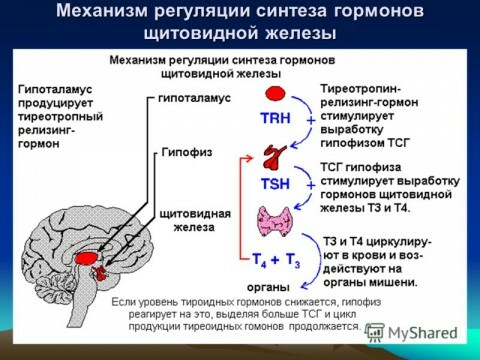
Functions of thyroid hormones are as follows:
- they regulate the temperature exchange;
- under their influence tissue cells produce the energy necessary for the body;
- regulate oxygen exchange, oxidative processes;
- are involved in the process of formation of new cells, their structural division, as well as in apoptosis( programmed death of the old ones);
- affect the physical, mental and mental development of our body throughout life;
- approximately 80% of iodine found in the body is contained in the thyroid gland, which is its reserve storage;
- controls all immune processes.
In addition to thyroxine and triiodothyronine, calcitonin is also secreted in the thyroid gland, which stabilizes the calcium content in the blood.
In order that all the systems and organs of our body function normally and develop, the blood must contain a strictly certain amount of free hormones.
Norm
Norms for thyroid hormones:
- TTG, tyrotropin 0.4-4, 0 mIU / mL;
- T4, free thyroxine 9.0-19.1 pmol / l;
- T3, free triiodothyronine 2.63-5.70 pmol / L;
- TG, thyroglobulin less than 4.1 IU / mL;
- AT-TG, antibodies to thyroglobulin & lt;4.1 IU / ml.
Any deviation of these indicators can lead to quite serious endocrine pathologies. To date, endocrine diseases associated with impaired gland function, occupy the second line of risk, following diabetes. Depending on the level of free hormones contained in the blood, it is common to subdivide all the diseases listed below, taking into account belonging to the main groups:
- Thyrotoxicosis - occurs if, for some reason, the hormones are released more than normal, there is a significant acceleration of all internal reactions and biochemical processes.
- Hypothyroidism - if the secretion is lower than normal.
- Euthyroidism - if violations from the functional activities are not detected, but with all this there are pronounced changes in its structure.
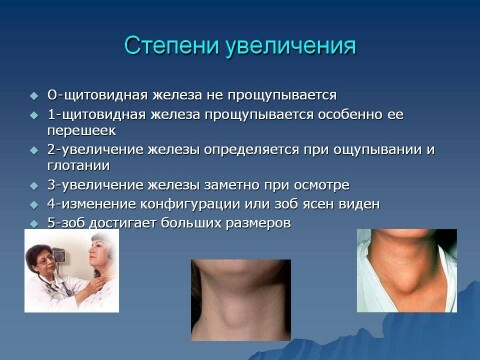
Regardless of which of the listed diseases belongs to one or another pathology, they all have a common feature - the appearance is easily detectable visually in the neck region of the goiter, characterized by a prominent bulge .For this pathology and received in the endocrinology its second name - goiter. In terms of severity, it corresponds to three stages, knowing about which it is easy to determine the pathological process:
- 1 stage - if the increase is not determined by palpation and visually;
- 2nd stage - if there is a slight deviation from the norm, which does not lead to deformation of the neck;
- Stage 3 - if there is a change and there is deformation in the neck.
Definition of goiter at home

It is possible to determine the presence of the disease not only with visual examination and palpation. The mobility of the thyroid gland and its density can also help to identify pathology.
- By its nature, iron has an elastic dense consistency, if the organ is sufficiently dense or even woody, then it can be unequivocally said that the norm is broken, there is a certain pathology, perhaps cancer.
- During the swallowing, the thyroid gland together with the cartilage must move, if this does not happen, a conclusion is made about a possible oncological process.
- During palpation there are unpleasant painful sensations, uncharacteristic for the normal state of this organ. If even minor pains appear in the area under examination during the examination, it can also indicate the presence of a disease or inflammation.
Symptoms of
Symptomatic picture of such diseases is diverse, the brightness of symptoms depends on the nature and stage of the pathological process. But, despite this, they have common symptomatic manifestations.
- permanent, nagging character, pain in the neck, especially noticeable in its anterior part;
- causeless nervousness and irritability;
- sleep disturbance and a constantly awakening sense of anxiety;
- edema, dry skin is noted;
- weakness, rapid fatigue, not a consequence of physical exertion;
- change in body weight;
- is plentiful, independent of external factors sweating;
- pain arising from swallowing food, as well as drinking;
- decreased the mobility of the gland, it ceases to move together with the cartilage while swallowing;
- when squeezing the thyroid trachea, a cough appears, and breathing disorders occur;
- due to compression of the esophagus there is hoarseness in the voice, the feeling of being in the throat of a coma does not give the patient peace.
The larger the increase, the brighter the symptoms. But do not forget that at the initial stages of the disease there may be no obvious symptoms. It can be very easily confused with a common cold, as well as all sorts of complications that arise after stretching the muscles of the cervical region, which is dangerous.
Reasons for an increase in thyroid
- are genetically determined predisposition;
- is a wrong, unbalanced diet that causes in the body a shortage of iodine and salts;
- dysfunction of the pituitary and hypothalamus;
- hormonal changes that occur throughout life in the body in women;
- weakening of the immune system by infectious diseases and frequent stresses.
It is generally accepted that the main cause of the increase are hormonal changes in the body. Therefore to such diseases are more likely to women , because it is in their body at a certain stage of life there is a greater number of such rearrangements - during puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, onset of menopause.
The listed reasons can not become an excuse for the development of pathology without the influence of certain factors that can give impetus to the development of the pathological process. These factors include:
- chronic diseases that last long in the human body;
- environmental conditions of residence and work;
- bad habits, including excessive use of alcohol, smoking;
- improper food, hunger strikes.
Treatment and Diagnosis
In the treatment of diseases associated with enlargement of the gland, a thorough and competent examination is necessary, which allows to identify the cause of the disease. For this purpose, a patient is assigned a test, which includes the appropriate ultrasound, aspiration biopsy( with a size of glandular nodes of more than one centimeter), a blood test for the level of hormones and antibody titer. If necessary, assign additional methods.
Based on the results of the examination, the endocrinologist chooses the most suitable technique for treatment:
- Replacement hormone therapy, in the case of hypothyroidism with the use of the drug L-thyroxine. Treatment can last quite a long time, from several months to two years, until the norm is restored.
- Treatment, inhibiting the secretion, is assigned to adolescents and children during the period of growth. In such cases, drugs that reduce the activity of the gland( Thiamazole, Metizol, Mercazolil, etc.) are prescribed.
- Treatment with radioactive iodine.
Surgery is also possible, but is an extreme measure in solving this problem.



