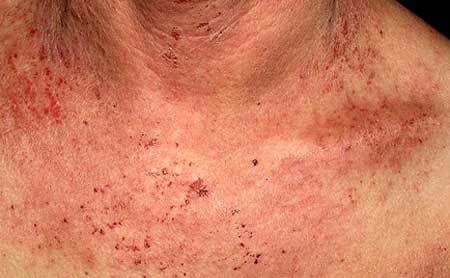
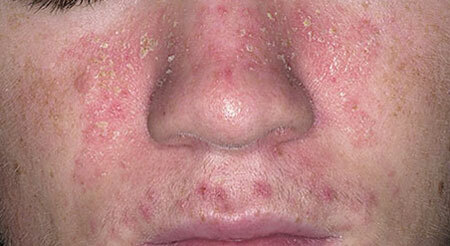
Skin diseases can sometimes be hidden under clothing, and this creates additional difficulties in communicating the sick person with the surrounding people. The rash, ulcers and purulent abscesses cause a feeling of disgust and fear of catching the infection, which is why the desire for a relationship with the bearer of such shortcomings is lost.
But not every disease is transmitted by domestic and airborne droplets. Although soaking eczema on the hands and fingers is noticeable even in a cursory examination, it is the patient, not his surroundings, who is worried: pathology does not spread by contact.
Contents
- 1 Wet eczema, what is it?
- 2 Causes of the disease
- 3 Stages of wet eczema
- 4 Symptoms of wet eczema by species
- 5 Treatment of moccasive eczema
- 6 Prevention
Wet eczema, what is it?
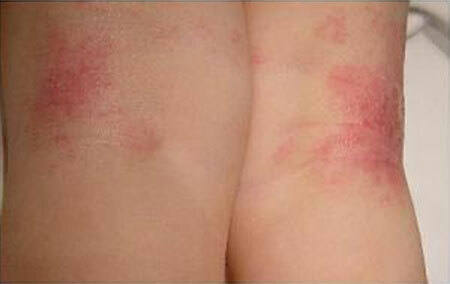
With mozhnushchimi eczema, the skin becomes covered with such a pronounced rash that the dermatologist does not have any doubts about the diagnosis. At first, the outer cover turns red, then the tiny vesicles filled with liquid appear. Bubbles open spontaneously, without even having time to take shape in large structures.
In place of vesicles "wells" are formed - depressions in the skin, which are constantly filled with serous exudate. Hence the name of the disease is wet eczema. The size of the depressions is very small, but their number is so large that the affected areas of the patient's skin do not dry out.
Appears wet eczema on the hands, feet, head or all over the body. Possible variants of both the local course of the disease and the generalized.
Causes of the disease
Currently, moknuschuyu eczema scientists treat as an allergic disease. There are several forms of pathology, but all of them are accompanied by skin erosion. Physicians find it difficult to name any one cause of the disease, leaning towards a whole set of factors:
- The effect of allergens( chemical, food, etc.).
- Diseases of internal organs( kidney, liver, heart, glands, etc.).
- Mechanical damage to the skin.
A decisive role is not assigned to either exogenous or endogenous factors. In the early stages of the study, it was believed that wet eczema on the legs and hands develops due to a nervous breakdown. In particular, the appearance of such a rash when there was a violation of innervation due to trauma was noted.
In modern medicine, the notion of a close relationship between the immune and nervous systems is prevalent, so the meds call these factors mutually complementary.
Modern data indicate the high importance of allergens in the development of the disease. Probably, many people are familiar with a runny nose and tear because of pollens of ragweed or poplar fluff in the air? Eczema has a similar nature, although such symptoms are absent. The principle itself is important: the disease arises as a reaction to external stimuli provided internal imbalance.
In the human blood, protective compounds are represented by peptide chains, which are called immunoglobulins. They play the role of a natural barrier to the spread of alien genes. There are several types of immunoglobulins, and each of them performs a specific function.
The laboratory analysis of the blood of patients with wet eczema shows a marked imbalance of protective compounds. For example, IgE is present in excess, although in the normal state the plasma is not at all rich in them. Also, the concentration of IgG, the main substance responsible for the secondary immune response, is also exceeded.
Physicians note a deficiency of IgM immunoglobulin, which is embedded in the B-lymphocyte membrane and recognizes foreign antigens. Synthesis of protective cells in the disease is increased, but they do not acquire "weapons" due to a lack of IgM.Thus, wet eczema is rightly considered a pathology of the immune system.
Heredity also plays an important role. Each person has genes that are responsible for the immune response. And if the parents have an allergy to anything, then the children's chance of developing eczema rises by 40%.
Stages of wet eczema
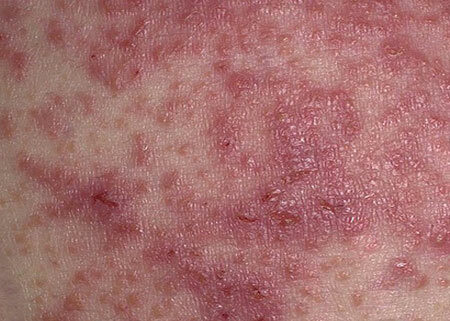
A key feature of wet eczema is a rash on the skin, accompanied by the release of serous exudate. Doctors call 4 stages of the course of the disease, which are characterized by certain symptoms:
- Erythematous( reddening of the skin).
- Vesicular( there are vesicles filled with liquid).
- Wetting( bubbles burst, a "well" is formed with abundant exudate).
- Cortical( wounds dry and crusted, under which a new layer of epithelium is formed).
It rarely happens that eczema affects only a small area. Usually the foci of the disease appear on the face and limbs, gradually spreading to other parts of the body. In this case, the patient is concerned about pronounced itching, which is aggravated by the aggravation of the pathological process. Sometimes a person on the background of eczema even develops neurotic disorders in the form of insomnia and irritability.
Pathology is characterized by a wavy current, i.e.at any one time there may be signs of each stage. When treating the acute form of moccasive eczema, the symptoms lose their intensity, but the disease often returns - the chronic form develops. At the same time, the skin undergoes a process of lichenization, which doctors call a secondary consequence of the rash:
- changes the pattern of the outer cover;
- increases scaling;
- is broken pigmentation;
- skin thickens;
- is often a disease spread throughout the body.
Therefore, the treatment of moccasive eczema should not be shelved, otherwise it will be much harder to get rid of it. In clinical practice, even cases of long-term course of the disease have been reported.
Symptoms of wet eczema by types
Doctors distinguish several types of ailment. Of course, all of them are accompanied by skin erosion, however, various factors can provoke the pathological process. So, the classification is as follows:
1. True eczema:
- all stages are expressed;
- focal boundaries are poorly delineated;
- it is difficult to establish the allergen that caused the rash.
2. Microbial:
- appears due to pathogenic activity of bacteria;
- clear boundaries;
- , in addition to serous exudate, pus is also formed.
3. Mycotic:
- The cause is allergic to fungal infection;
- clear boundaries;
- is severely treated because of the resistance of fungi.
4. Seborrheic:
- develops against the background of seborrhea - an increased function of the sebaceous glands;
- on the skin spots are formed in the form of rings and garlands.
5. Professional:
- often affects people whose work is related to chemicals;
- all signs of true shape.
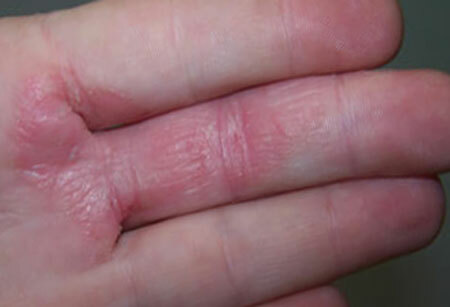
6. Dyshidrotic:
- is localized on the palms and soles;
- redness of the skin is mild;
- vesicles can merge, forming large vesicles;
- often extends to nails, hands and feet.
7. Tylot:
- also develops on the palms and soles;
- in place of the blisters formed corns.
8. Pediatric:
- is the most pronounced wetting stage;
- often develops against the background of artificial feeding;
- recorded cases of death from eczema in infants.
9. Varicose:
- is localized in the area of veins enlarged due to varicose veins;
- clear boundaries;
- mild itching;
- is sometimes confused with microbial eczema.
10. Sycosiform:
- occurs against the background of inflammation of the hair follicles - sycosis;
- severe itching;
- is rapidly developing skin lichen.
11. Nipple eczema:
- crimson foci;
- the crusts layer and crack;
- clear boundaries( around the nipples);
- is treated with difficulty;
- is often the result of a trauma in breastfeeding.
As can be seen from this list, wet eczema occurs for various reasons. And although the underlying pathological immune response to stimuli, the symptoms of the disease are not the same.
In some cases, erythema of the skin is not observed at all, in others - the stages of vesicle formation or discharge of serous exudate are sharply expressed, in the third - the foci are formed only as a consequence of another disease. In general, the therapeutic course will depend on the diagnosis.
Treating wet eczema

Curing wet eczema can be very problematic. The fact is that there are certain difficulties with the detection of allergens to which a person has a reaction. Antibiotics are used primarily against the microbial form of the disease, but after such therapy one should concentrate on a set of measures aimed at eliminating eczema itself:
1. Establish an allergen and exclude contact with it:
- chemical compounds( detergents, detergents, powders, cosmetics andother);
- food products( sweet, salted, smoked, etc.);
- vegetable components( pollen, fluff, etc.).
2. Reduce body sensitivity:
- gluconate and calcium chloride( intravenously);
- should not be given intramuscularly, otherwise necrosis and an abscess will occur at the site of the injection.
3. Relieve inflammation:
- antihistamines( Zirtek, Telfast);
- corticosteroids( Prednisolone, Dexamethasone).
4. To reduce intoxication:
- is intravenously injected with Hemodez-H, saline and the like;
- orally ingest Enterosgel or Polysorb( toxins often get through the intestines).
5. To correct immunity:
- vitamin complexes( A, E, C, group B);
- interferon preparations( Cycloferon, Viferon).
6. Strengthen vessel walls and reduce blood viscosity:
- Xanthinal nicotinate;
- Trental.
7. Relieve nervous tension:
- preparations of valerian, mint, motherwort;
- bromides( Bechterew's medicine);
- sleeping pills in small doses.
8. Improve the work of the digestive tract:
- sour-milk products;
- enzymatic complexes( Mezim, Festal).
9. Eliminate itching:
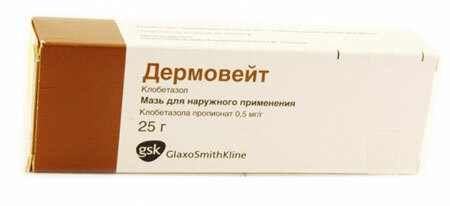
- ointments based on hormones( Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone);
- folk remedies( aloe juice, menthol oil).
Washable eczema on the legs can be treated well by special baths. For this purpose, it is required to take 5-6 cones and 2 twigs of pine. Pour the ingredients 3 liters of boiling water and leave for 1 hour, then filter and add to the warmed water. The temperature of the bath should be 40-50 ° C.
A similar procedure is performed with a known anti-inflammatory agent such as chamomile. To prepare the infusion, take 1 tablespoon of dried and crushed plants per 1 liter of water.
Doctors usually recommend hydrocortisone ointment from damp eczema. The drug has a hormonal nature, so it is not always possible to avoid side effects in the form of increased blood pressure and suppression of adrenal function.
In order not to harm the body, folk healers are advised to apply ointment based on mother-and-stepmother:
- 50 g of fresh leaves are scrolled in a meat grinder.
- Add 25 grams of fresh milk.
- Stir thoroughly.
- Insist for 2 hours.
- Before bedtime, smear affected areas.
- Wrapped with cellophane.
- Repeat procedure for 3 consecutive days.
Prevention
If a person gets sick with a wet eczema, then you need to do your best to get rid of the disease. With insufficient treatment, the patient may return and take a chronic form. And although eliminating allergens from life is not easy, adherence to preventive recommendations will significantly reduce the risk of recurrence:
- Use only natural tissues( no synthetics!).
- Stick to a diet that excludes food allergens.
- Exclude cosmetics if it was the cause of eczema.
- Choose household products that do not cause allergies.
- Use moisturizing creams.
- Strengthen immunity( vitamins, hardening, sports).
- Avoid psychoemotional loads( provoke physiological disruptions).
Concomitant eczema arises from a pathological immune response to external and internal stimuli. The mechanism of development of an allergic reaction and the appearance of a rash is so complex that there is no special medicine that prevents the disease. Yes, and cure eczema is also difficult. Therefore, it is worth every possible to avoid contact with substances that can cause allergies.