 If the patient has a difficult circulation in the head area, in particular a lack of oxygen supply to the brain, the cause may be vertebral artery syndrome( SPA).
If the patient has a difficult circulation in the head area, in particular a lack of oxygen supply to the brain, the cause may be vertebral artery syndrome( SPA).
Disease is a pathology that occurs when compression of the vertebral artery or the entire sympathetic plexus that surrounds it occurs.
Contents of
- Basics of anatomy and physiology
- Causes of a disorder
- Mechanism of development of pathology
- Features of
- symptoms Functional disorders
- Ischemic stage
- Clinical variants
- Diagnosis of
- syndrome Therapeutic package package
- Complications of the disease and its consequences
Basics of anatomy,as well as physiology
The brain feeds on oxygen from the blood, which comes to it along the four main arteries:
- lionth and right;
- total;
- sleepy;
- left and right vertebrates.
Approximately 70 to 80% of the total blood flow passes directly through the carotid artery, so its dysfunction and consequent blood flow disturbance leads to acute complications, which are called ischemic strokes.
Only 15 to 30 percent of the blood goes to the brain through the vertebral artery. There are no fatal complications, but the consequences can also be very unpleasant, chronic and can bring a lot of inconvenience to a person, in some cases even lead to disability.
The vertebral artery extends upwards and slightly backwards, being behind the carotid artery, it is laid in the recess of the transverse process, which is on the cervical part of the spine. Then the vertebral artery goes straight up, through the same holes of the other vertebrae, and the main occipital foramen comes into the head, directly into the brain.
Supplying blood to such parts of the brain:
- cerebellum;
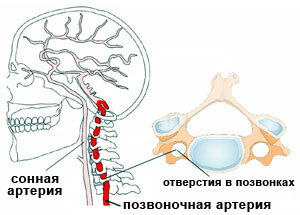
- temple, temechko, nape of the skull;
- organ of the hypothalamus;
- solid membrane of the brain;
- calloused tissue;
- central brain.
Before entering the skull, parts from the vertebral artery that supply blood to the spinal cord, as well as its shell, branch off. Therefore, when the operation of the vertebral artery is disturbed, symptoms that speak of hypoxia( lack of oxygen) of certain parts of the brain can be observed.
Causes of
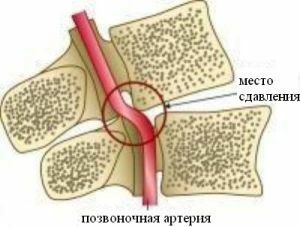
Violation Throughout its length, the vertebral artery contacts the hard tissues of the ridge, and the soft tissues surrounding it. It is pathological violation of these tissues that promotes the development of SPA.
There are three main groups of factors contributing to the development of vertebral artery syndrome:
- acquired at birth features of the construction of the vertebral artery;
- disease, which lead to a reduction in the cross section of the artery;
- compression of the artery from the outside.
It happens and so several factors contribute to the development of the syndrome.
Mechanism for the development of the pathology
 In most cases, the syndrome begins to progress to the left, caused by some anatomical details of the left artery: it branches off from the aorta( its arc), which sometimes contains atherosclerotic changes.
In most cases, the syndrome begins to progress to the left, caused by some anatomical details of the left artery: it branches off from the aorta( its arc), which sometimes contains atherosclerotic changes.
Another common cause, together with atherosclerosis, is degenerative-dystrophic disease. Often the syndrome of the vertebral artery develops with cervical osteochondrosis.
The bone through which the artery passes is very narrow and at the same time mobile. If there are osteophytes in the region of the transverse parts of the spine, they can compress the vertebral artery and prevent the normal flow of blood through it.
Symptomatic features of
The process of development of the vertebral artery syndrome usually develops in a stage: functional dysfunction,( dystonic), and organic type( ischemic).
Stage of functional disorders
Very often, when this stage passes, headaches are observed: permanent type, can be strengthened when the patient moves his head, or aching pain, baking species that appears in the nape and temples.
At this stage of the disease, the patient is disturbed by various forces of dizziness: beginning from mild instability, and ending even with a sense of rotation that can lead to the patient falling. Sometimes there is noise in the ears.
Ischemic( organic) stage
At this stage, the patient has impaired blood flow to the brain, a transitional type: transient ischemic attacks. In this case, sudden dizziness( like an attack) manifests itself, coordination of movements is lost, vomiting and nausea are observed, and the patient's indistinct speech is present.
Such symptoms of the vertebral artery syndrome are accompanied by a sudden and sharp tilt or turn of the head. They can weaken and disappear if the patient lies down.
Clinical variants of
Among clinical types of the spinal artery syndrome, the following types are distinguished:
- drop-attacks ( the patient may fall, he throws back his head, the ability to move or the more to rise, no);
- syncopal syndrome, otherwise Unter Harnstaidt's syndrome ( if you sharply bend your head or try to turn it, or when the head has been in one position for a long time, a person can suddenly lose consciousness;
- posteriorly is cervical sympathetic, it is the Bare-Liuu syndrome is characterized by periodic headaches that appear in the nape, and eventually spreads to the front of the skull
- vestibulo - atactic syndrome ( a person feels unstable, his head is spinning, he losesI feel a sense of balance, can darken before my eyes, the patient feels sick, vomiting may occur, cardiovascular system dysfunction( heartache, excessive shortness of breath, etc.),
- basilar migraine ( both eyesight is disturbed, patient is unsteady, he is dizzy, speech is not clear and noises in his ears
The patient then feels a strong pain in the back of his head, starts to vomit and loses consciousness and the following syndromes begin to appear:
- ophthalmic syndrome ( eyes suffer most oftenShortbread "eye, conjunctivitis, tears flow);
- cochlea - vestibular syndrome ( hearing impairment is abnormal( the patient hears a whisper badly), the patient can stagger, he makes noise in his ears, it seems that things are spinning around,
- is a syndrome of vegetative disorders ( the patient can shiver or vice versa, he constantlysweat, hands wet);
- transient ischemic attacks ,( a person is constantly experiencing impairment with the musculoskeletal system, speech and vision are disturbed, the head is spinning, there is vomiting, the patient is sick, it is hard to swallow.)
agnostic of the
syndrome Based on the patient's testimony, the physician should make an initial diagnosis and determine the following diagnostic  techniques:
techniques:
- x-ray of the cervical spine;
- magnetic resonance or alternative computed tomography;
- duplex check of the arteries passing through the spine
- vertebral dopplerography usingloads of the functional plan( neck exercises, flexing bends, etc.).
If, after carrying out additional studies, the suspicion of the SPA is confirmed, the doctor immediately prescribes a treatment package. Depending on how much it will be the correct result will be positive.
Complex of therapeutic measures
As with other diseases, the syndrome of the vertebral arteries is treated well if the patient has turned in time to the hospital: the earlier and more accurately the diagnosis, the easier it will be to defeat the disease. Treatment of the spinal artery syndrome by the complex is carried out in three directions at once:
- dysfunction therapy for the entire vertebral column of the cervical region;
- restoration of the canal through which the artery passes;
- additional treatment options.
 In order for nerve cells to recover, the body must receive a sufficient amount of vitamin B. In order to eliminate the factors that put pressure on the artery, you need to apply a set of physical measures( special exercises for the neck and back that can improve the mobility of the spine).
In order for nerve cells to recover, the body must receive a sufficient amount of vitamin B. In order to eliminate the factors that put pressure on the artery, you need to apply a set of physical measures( special exercises for the neck and back that can improve the mobility of the spine).
SPA vertebrogenous species is eliminated with the help of manual therapy. With sufficient qualification of the attending physician, such therapy is able to restore the normal position of the vertebrae, and remove the blocks of their displacement. Thus, the hernia is prevented and the normal blood circulation of the spine is restored.
Muscle spasms, back pain and swelling can be eliminated with the help of physiotherapy, as well as massage. Also, ultrasound and laser therapy help, they stimulate the body perfectly and provide an analgesic effect.
The syndrome is treated with medication, but only in those cases when the disease is not caused by problems with the vertebral column itself. Of the drugs used antispasmodics, tablets to combat atherosclerosis( they raise rheological parameters of the blood), and funds for the treatment of a symptomatic type.
The main measures to prevent SPA are a healthy lifestyle in general, and sufficient sleep on convenient accessories( best if they are orthopedic type).
If by virtue of circumstances you keep your head in one place( for example, working for a PC or with documents), it is very desirable sometimes to interrupt and do exercises for the neck.
Complications of the disease and its consequences
The most sad end of the vertebral artery syndrome may be ischemic damage to brain tissue due to lack of air. If you do not treat the spinal artery syndrome or treat it incorrectly, the brain is threatened by such consequences:
- A greater or lesser disruption in the function of supplying the brain with oxygen .Initially, in this way,
 can only get nerve impairments of a rolling type.
can only get nerve impairments of a rolling type. - Stroke .In this case, it is usually ischemic. A stroke occurs when one of the arteries or its branches, under the influence from the inside or the outside, overlaps so much that it can no longer supply its portion of the brain with oxygen.
- Physiological compensation of dysfunction of blood supply to the brain by increasing pressure .The main factor is the growth of arterial pressure due to the narrowing of the cross section of one channel or their combination. In the first case, the brain region may suffer, in the second, the entire brain. Such people often feel dizzy, they can fall and do not lose consciousness, lose balance and coordination of movements, lose the ability to work and even sometimes the opportunity to serve themselves.
Remember! PA syndrome does not necessarily in each case lead to an extreme situation - a stroke, but due to the fact that the function of the arteries is broken and the brain is not fully supplied with oxygen, disability occurs very often.


