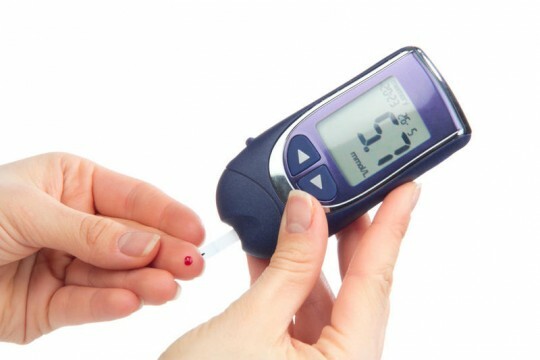
Many complications arise in the body in diabetes mellitus. The most dangerous - diabetic foot - is a pathology that is associated with the development of peripheral neuropathy, the destruction of blood vessels and capillaries.
Changes in tissues occur under the influence of excess sugar in the blood with insufficient production of the hormone insulin. The toxic effect of glucose leads to deformation, inflammatory processes in the joints and bones, necrosis and gangrene.
Contents of
- 1 Who is at risk? Causes of development of
- 2 Types of diabetic foot syndrome
- 3 Infections affecting diabetic foot
- 4 Initial stage of diabetic foot, photo
Who is at risk? Causes of development of
The development of diabetic foot syndrome is potentially dangerous for all patients with diabetes mellitus. In half of the diseased, pathological processes are observed, which serve as criteria for determining the risk group.
The doctor assesses the condition of the feet, the sensitivity of the skin, palpated on the arteries, examines the condition of the nails and the presence of injuries and wounds.
By the degree of risk, three groups are classified:
- No pronounced changes. Pulse and sensitivity are normal. Monitoring of the state annually.
- Deformities of the foot are appreciable, the pulse on the distal side is reduced or absent, the sensitivity is weak. Checkup every 6 months.
- Loss of sensitivity, lack of pulse. The patient had ulcers, possibly suffered an amputation. Inspection is done every three months.
The diabetic foot syndrome is considered as a collective concept for all complications of diabetes in the late stage.
In patients of type I, the pathology of the foot is diagnosed after 8-10 years from the onset of development of diabetes mellitus, in type II this can happen from the first months of the disease.
As the causes of the development of pathology are the changes that occur in the body under the influence of excess sugar in the blood. Blood vessels and nerve fibers suffer from this.
The organs do not receive the necessary nutrition, and insufficient blood supply worsens wound healing. In the lower extremities blood circulation worsens, stagnant phenomena lead to the defeat of nerve endings and the development of neuropathy.
Loss of sensitivity leads to the fact that the patient does not immediately feel the formation of wounds and injuries, which are dangerous for the formation of trophic ulcers. Minor abrasions, cracks and calluses are easily infected, and due to ongoing stagnant phenomena in the feet do not heal.
A person does not immediately notice the formation of ulcers because of decreased sensitivity, so often the process affects adjacent tissues, tendons and bones. In advanced cases, gangrenous changes are diagnosed, treatment involves partial or complete amputation of the foot.
Traumatism is promoted by improperly selected footwear, which deforms with time and prevents the foot from correctly distributing the pressure of the body - this leads to deformation, corns and calluses.
Tight shoes interfere with weakened blood flow, strengthens fluid stagnation and promotes inflammatory processes.
- advice on the choice of footwear and prevention
Atherosclerotic changes in large vessels disrupt the blood supply of the lower limbs in diabetics.
The lack of nutrition and oxygen causes the death of skin and tissue areas, if the patient does not notice the changes occurring, there is a risk of additional trauma to these areas. There is an intensification of the ulcerative process and necrotic lesions of the foot tissues.
World practice has 70% of amputations due to diabetes, although more than 80% of cases can be avoided with timely detection of skin lesions.
Types of diabetic foot syndrome
Depending on the ongoing processes and symptoms, it is common to divide the foot injury by type.
# 1.Neuropathic.
The common factor of diabetic foot syndrome is pain. In some cases, the nerve endings are damaged, which leads to the formation of peripheral neuropathy. There are three main types of it: sensory, motor and vegetative.
Most patients experience sensory neuropathy. This manifests itself as a disproportion between the intensity of pain and visible damage.
For example, simply touching the skin, a person experiences severe pain, which is present simultaneously with numbness of the foot. Sensory symptoms are manifested by burning, tingling or piercing pain.
In motor neuropathy, damage to the nerve endings leads to weakness of some muscles that are involved in walking: the muscles of the thigh, the lower leg and the small muscles of the foot.
These changes cause an imbalance and an incorrect leg position, which helps to rub the foot in the shoes, inflame the skin, create cracks on the heels and pain.
Vegetative neuropathy affects nerves that are not under conscious human control. The mechanism of sweating changes, the person notes the thickening of the skin on the soles, it becomes stiffer, cracks and calluses are formed.
Bacterial or fungal infection becomes a likely cause of increased pathological processes.
# 2.Ischemic.
Circulatory problems in the legs contribute to soreness, even with partial numbness of the limbs. This occurs under the influence of high blood sugar in the arteries, capillaries and veins.
Arteries are affected behind the knee and lower leg by fatty plaques, the process is accelerated with diabetes. There is thickening of the walls and calcium deposition may form. Inflow of blood to the lower limbs partially or completely blocked.
Since the tissues are starving in the absence of oxygen, this is associated with pain. Such a condition the patient describes, as if the legs are squeezed by the vice.
The walls of the capillaries are thickened, become stiff, the efficiency in the delivery of oxygen and nutrients is reduced. Arteries can not cope with the flow of blood, it rushes through small vessels into veins, instead of trying to pass through blocked arteries.
Often the blood volume comes in more than the veins can handle. They are overflowing, the valves are torn. Blood from the vessels seeps into the skin, creating ulcers, which are very painful.
# 3.Mixed.
Muscular and joint problems in diabetics are a frequent source of discomfort and pain. Muscles suffer from diabetic neuropathy, impaired blood circulation and atrophy. The tendons that attach the muscle to the bone become stiff and shortened due to peripheral neuropathy.
There is an imbalance in walking, the load on the feet and joints is not properly distributed. Worse, they "get used" to be in a bent position due to excess blood sugar in combination with proteins in the joints. This is called diabetic joint glycosizing.
Such stiffness leads to bursitis, spurs, tiny fractures and dislocations of bones( Charcot's foot).Changes lead to pain, the development of infections, ulcers.
Infections Affecting the Diabetic Foot
Diabetics become more susceptible to bacterial, fungal and yeast infections. The skin of the feet becomes irritated, ulcerated and easily eradicated. Symptoms of bacterial infection include redness, swelling, increased local temperature, pain, damage and pus.
Blind diabetics detect infectious foci by touch, sometimes by smell. If the inflammation affects the bone, osteomyelitis develops.
It is interesting that even with a loss of sensation on the legs, a person can feel pain with a bacterial infection. Medical care should be treated without delay.
Fungal and yeast infections affect the feet. Irritated skin serves as a good breeding ground for microbes.
Nail plates become thick, easily crumbled, loose, often grow into the skin or form corn grooves. Dirt accumulates under the fingernail and causes irritation around.
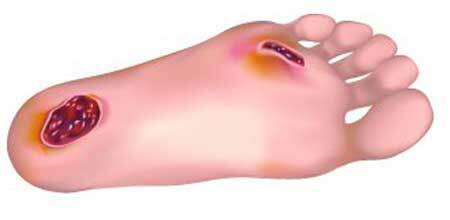
The initial stage of the diabetic foot, photos
Diabetics are required to monitor the condition of the feet, and to notice signs of the initial stage of the diabetic foot in time. Numbness, tingling, burning, running "goosebumps" are forerunners of pathology development.
Signs of the development of the diabetic foot syndrome for which it is necessary to pay attention and immediately contact a doctor:
- skin lesions that do not heal for a long time, fester;
- skin and nail damage by fungal infection;
- ingrown nail plate in the skin;
- nail color change or darkening;
- corns, skin irritation from shoes, puffiness;
- cracks on the skin of the heels, wetting eczema between the fingers;
- deformation of the foot( curvature of the fingers, enlargement of the bone on the thumb).
Photo of the initial stage
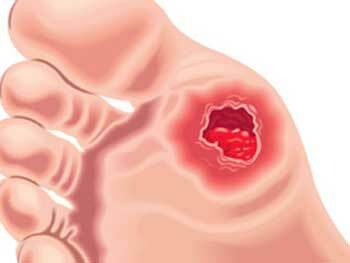
Non-healing lesions, photo 1
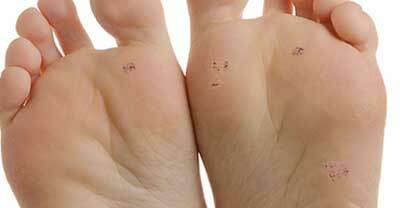
initial stage, photo 2
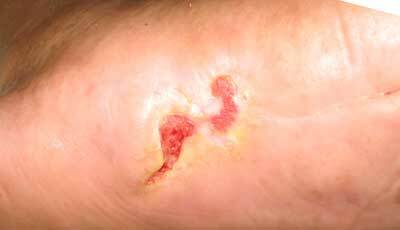
disease progression, photo 3
Next:
- Symptoms of diabetic foot, treatment methods