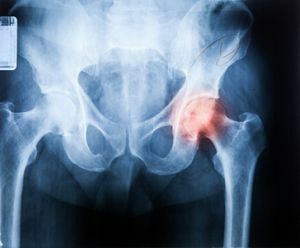
 Neoplasm or a tumor is called a cluster of cells that divide rapidly and in unlimited quantities. Such a cellular cluster can form in any organ. Bones are no exception.
Neoplasm or a tumor is called a cluster of cells that divide rapidly and in unlimited quantities. Such a cellular cluster can form in any organ. Bones are no exception.
The causes of tumors in most cases do not bear the exact etiology. Some neoplasms appear due to genetic nature.
Tumors are benign and malignant( cancer).Sometimes benign neoplasms degenerate into malignant ones.
Contents of the article
- Bone cartilage tumor
- Background of tumor formation
- Localization of education
- Development stages
- Complexities of symptomatology
- Diagnosis
- Treatment: objectives and methods
- Forecast favorable
- How to prevent danger?
Bony cartilage tumor
One of the benign bone tumors is the osteochondroma. A tumor is formed from bone-cartilaginous cells.
This is a smooth and shiny build-up on the bone, which has arisen due to impaired enchondral ossification.
The formation is a bone base containing bone marrow tissue and covered with cartilaginous tissue. There are solitary exostosis( single education) and multiple.
Under the cartilaginous layer, otherwise called a cap, there is bone tissue under which the spongy bone is located. In the center is the bone marrow, connected with the bone marrow canals of the maternal bone.
The tumor is more often located in the spongy bone. Sometimes a bag is formed above it, filled with cartilaginous tissue.
This kind of neoplasm is the most common among the types of benign bone tumors. Its percentage relative to all benign tumors is about 40%, relative to bone tumors - 12%.
Education, in most cases, is not associated with any feelings. Large neoplasms can create discomfort during movement.
Patients are diagnosed with osteochondrosis accidentally on palpation of any part of the body. Sometimes the tumor manifests itself on prophylactically made X-rays or when examined for other reasons.
Background of tumor formation
Bone cartilage exostosis is most often observed in childhood and adolescence( ten to twenty years).
Tumor growth occurs during the growth of the skeleton with the same intensity as the bones of the skeleton. The growth of the tumor stops when the children's skeleton is formed.
Very rarely, build-up grows and grows at an older age after 30 years.
In children, the bones have a thicker cartilaginous layer, which, as it grows, becomes thinner and turns into a thin plate.
Reasons for the formation of ecodes:
- hereditary;
- as a result of injuries;
- after receiving radiation;
- developmental defects;
- endocrine disorders;
- is an inflammatory process.
The cause of the growing tumor, according to most orthopedists and traumatologists, may be the developmental defects of the skeleton.
In this case, multiple proliferation can develop. According to statistics, it occurs in 12% of the irradiated.
Another cause is hereditary disease. Disease is detected in adolescence. Passes the disease in an autosomal dominant type.
Also in a number of cases, the emergence of ecstocks after injuries. Tumors are formed due to improper healing of the bone at the site of the former hemorrhage. This can occur in cases where the periosteum has been damaged.
Localization of education
The formation of cartilaginous ecostosis occurs mainly near the long tubular bones in the region of the joints. Tumor growth
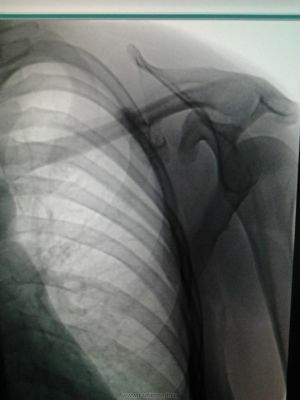
On the photo of the osteochondroma of the
scapula occurs in the direction from the joint.
Relative to the bones of formation. Their size can reach several tens of centimeters.
Osteochondroma is often observed on:
- of the tibia and femur;
- they appear less often on the bones of the forearm;
- is also observed in pelvic bones, on shoulder blades, vertebrae, ribs and collarbone.
The most rare case is the formation of such tumors on the phalanges of the fingers. They are the formations under the nails, reaching a centimeter in diameter.
When the nail begins to exfoliate due to the growth of the tumor, the patient may experience pain.
Education in other parts of the body is usually pronounced pain and discomfort does not deliver. With the appearance of painful sensations it is possible to suspect the degeneration of the neoplasm into a malignant one.
Stages of development of
There are three stages of tumor development:
- 1 stage of the disease. A tumor develops from the epiphasal plate, a region of cartilage located in a long tubular bone. Thanks to this plate, the bones grow. The osseochondroma at this stage consists of cartilaginous tissue and is not probed.
- 2nd stage .Education in the center ossifies, outside is covered with a thin layer of cartilaginous tissue. This tissue grows, formation thus increases in sizes.
- 3rd stage .The tumor grows due to the thickening of its cartilaginous membrane. The tumor can go beyond the bone and become noticeable. The patient may have difficulty moving and pain.
Difficulty of symptomatology
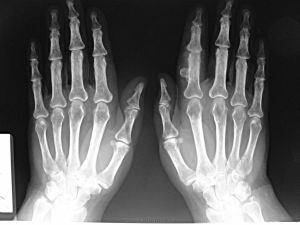
Osteochondroma of the fingers of the hand
Usually the osteochondroma is asymptomatic. In cases of large formations, patients may experience discomfort. With the pressure of a growing tumor, nerve endings can cause pain.
Rapid growth of neoplasm is dangerous because the tumor can mutate and degenerate into a malignant one.
The first symptom of degeneration of education in malignant is its rapid growth.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease includes such types of studies:
- X-ray;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- clinical trials;
- taking tissue on a biopsy.
On X-ray images, patients can see changes in the bone contour. This is due to the formation of a tumor whose surface resembles a cauliflower with uneven edges.
Sometimes neoplasms closely adhere to the bone, and some are connected to it by a thick pedicle.
The cartilage layer is not visible in the pictures, except for calcification foci.
Treatment: goals and methods
Treatment of osteochondrosis begins with taking tissue on a biopsy. The aim of the study is to exclude malignant degeneration.
The treatment plan for bone-cartilaginous ecostosis is made individually.
During surgical treatment, a tumor is resected. In this case, the surgeon captures part of the healthy tissue.
Purpose of treatment: remove the entire area in which the tumor is located. Therefore, the tumor is removed by the block, not partially.
After removal of the neoplasm along with part of the bone, bone reconstruction is usually not required.
Cut tissue must be sent to a biopsy. 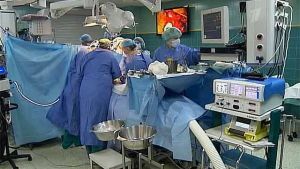
After the operation, a patient under medical conditions undergoes medical therapy. The joint is immobilized for two weeks with a gypsum lingo. After discharge, the patient is under observation for a year.
If the neoplasm is located on the back of the bone, the resection is started from the healthy bone tissue, gradually deepening inside. Neoplasm is removed together with the base and part of the bone. At the end of the operation, a tire is applied to the site to be operated.
Children have a special design, the height of which increases as the child grows.
Prognosis favorable
In most cases, with a successful treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Relapses of the disease usually do not manifest.
The degeneration of solitary tumors into malignant tumors in statistics is found in 2% of cases, multiple formations degenerate in 5% of cases.
The change is typical for tumors located in the pelvic bones and shoulder blades. This is manifested by the rapid growth of education, sometimes with pain. Growth is due to the cartilage component.
How to prevent danger?
 For preventive maintenance it is necessary to avoid traumas, fractures, to control the course of hereditary diseases. Also, children who are predisposed to this disease by hereditary indicators need to undergo an annual x-ray examination.
For preventive maintenance it is necessary to avoid traumas, fractures, to control the course of hereditary diseases. Also, children who are predisposed to this disease by hereditary indicators need to undergo an annual x-ray examination.
Osteochondroma is a disease requiring constant monitoring by the attending physician. If you have pain, difficulty in movement or an incomprehensible kind of education that is palpable in any part of the body, you can not postpone visiting a doctor and hope that the illness will pass by itself.
Health is the most valuable wealth in a person that can not be lost.