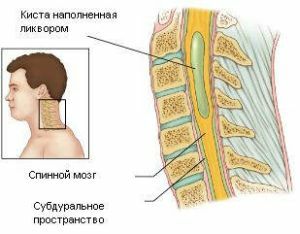
Epiduritis is a disease manifested as an inflammatory process in the epidural space in the spinal cord. It also often affects the outer surface of the hard shell and the roots of the spinal cord.
Epiduritis is a disease manifested as an inflammatory process in the epidural space in the spinal cord. It also often affects the outer surface of the hard shell and the roots of the spinal cord.
Infection with epiduritis occurs due to the onset of an infectious process. Sometimes the inflammatory process begins as a result of an autoimmune reaction of the body.
The disease is recognized as dangerous, despite the fact that many carelessly refer to its treatment. In this case, it is not enough to apply antibiotic therapy and analgesics. After all, the infection can quickly hit the body, from the spinal cord and ending with the brain.
In severe forms of manifestation, impairment leads to a person's inability to lead a normal life. In extremely dangerous cases, you have to resort to the help of resuscitation doctors. People who have a herniated disc, as well as patients with spondylosis, are at risk.
Varieties affected by
The disease is expressed in several ways. Depending on the localization of the disease, epiduritis is isolated:
- is limited to - the affected area is limited only by hernial protrusion;
- unrestricted - the inflammatory process is observed in the descending and ascending segments;
- common unilateral - inflammation is observed only on one side;
- is a common bilateral - the process of inflammation captures both sides.
The disease can occur in acute and chronic stages. Among the main types of epiduritis are two forms of manifestation:
- Purulent is characterized by the presence of diseases with an inflammation of a purulent nature in the epidural space.
 includes osteomyelitis of the spine, posterior mediastinitis, paravertebral abscess, lung abscess. Sometimes inflammation is caused by sepsis, purulent tonsillitis, pyelitis, furunculosis, infection during abortion. Place of localization of purulent epidurit - lower thoracic region. During the disease 3-4 vertebra are affected. Inflammation does not extend to soft membranes and the spinal cord due to the inability to penetrate the abscess through the solid layer of the medulla.
includes osteomyelitis of the spine, posterior mediastinitis, paravertebral abscess, lung abscess. Sometimes inflammation is caused by sepsis, purulent tonsillitis, pyelitis, furunculosis, infection during abortion. Place of localization of purulent epidurit - lower thoracic region. During the disease 3-4 vertebra are affected. Inflammation does not extend to soft membranes and the spinal cord due to the inability to penetrate the abscess through the solid layer of the medulla. - The non-greasy often has a latent flow pattern. In the course of the development of the disease, there is no occurrence of disturbances in the neurological plan. Sluggish processes can lead to changes in epidural fiber, as well as disrupt the integrity of the dura mater. Often the fibrous tissue grows, and the inflammation passes to the soft membranes of the spinal cord. Violated liquor circulation, the vessels are squeezed. The result of this effect is ischemic changes in the spinal cord. Epiduritis of a non-natural character appears as a result of the defeat of the body by tuberculosis, breccellosis, syphilis, and after trauma to the spine. Most often, the disease occurs in the thoracic and lumbar regions.
Causes of the disease
The inflammatory process in the epidural space is almost always a consequence of the disease in the body of various origins. Epiduritis can develop in the background:
- of spinal tuberculosis;
- destruction of vertebrae;
- infection of the body, including during puncture;
- presence of foci of purulent lesion;
- caries.
The appearance of purulent epiduritis is due to secondary infection of the body. In this case, an inflammatory process of epidural nature is added to the focus of inflammation in the main disease.
Infections penetrate into the epidural space from the main location along the blood and lymphatic capillaries.
Clinical picture of the disease
 Acute forms of the disease are characterized by pus accumulation in the epidural space, often with blood streaks in it. Symptomatology of the disease at the initial stage is manifested in the form of acute pain in the area of squeezing the roots.
Acute forms of the disease are characterized by pus accumulation in the epidural space, often with blood streaks in it. Symptomatology of the disease at the initial stage is manifested in the form of acute pain in the area of squeezing the roots.
The person feels a sharp rise in body temperature. There are also meningeal symptoms. At the general or common serious status of the patient can be observed:
- stiffness of the occipital muscles , in which head movements are limited;
- Kerning symptom - sharp pain in the knee and hip joints with straightening of the bent leg;
- symptom of Brudzinsky - pulling of bent legs to the abdomen during passive head bending, as well as the same manifestations with increased pressure on the pubic articulation area;
- photophobia( phobia of light) and phonophobia ( phobia of loud sudden sounds).
Painful sensations can be amplified during movement, deep breathing, sneezing, coughing, defecation process. This is due to an increased degree of muscle tension and increased pressure on the membranes of the brain.
Clinical manifestations are expressed depending on the degree of lesion of the epidural space and the level of location of the focus of purulent inflammation in relation to the segments of the spinal cord. A person can feel the weakness of the upper and lower extremities.
The work of the organs in the small pelvis is broken in the form of inability to retain urine and feces. There is also a state of alternation of delay and urinary incontinence.
With lesions of the upper segments of the neck, tetraparesis, tetraplegia can develop. During these reactions, the motor functions of the hands and feet are upset. If the pus accumulates in the thoracic and lumbar regions, then motor disorders can occur only in the legs.
The person is affected by the sensitivity of pain, temperature, tactile and muscular direction.
In the chronic form of the disease, the period of exacerbation is replaced by remission.
Diagnosis and clinical recommendations
When diagnosed, the clinician notices the presence of clinical symptoms that are markers of the disease. During the analysis of the data, epidural differentiation from acute myelitis, spondylitis, abscess, and tumor is revealed.
The liquor block can be detected during carrying out liquorodynamic tests and myelography. The location of the purulent focus of  is determined in the course of computed tomography.
is determined in the course of computed tomography.
Treatment of purulent and non-purulent epiduritis is carried out using a certain sequence of measures.
In purulent inflammations, a laminectomy is performed, an operation in which part of the bone tissue of the vertebra and the intervertebral disk is removed. The procedure is performed to decompress the area of the spinal cord that was squashed.
In this case, the dura mater should not be touched. After this, the epidural space is cleaned of purulent formations. Further therapy includes the administration of antibiotics( Ampicillin, Gentamicin, Kefzol, Penicillin).Medicines for fighting infection are selected depending on its etiology.
 Spinal epiduritis of the spine is also treated surgically. Before and after surgery, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics( most often Benzylpenicillin or Ampicillin), as well as physiotherapy. In the course of treatment, the reception of muscle relaxants( Midokalm, Baclofen) is shown, which allows to relieve muscle tone and spasm.
Spinal epiduritis of the spine is also treated surgically. Before and after surgery, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics( most often Benzylpenicillin or Ampicillin), as well as physiotherapy. In the course of treatment, the reception of muscle relaxants( Midokalm, Baclofen) is shown, which allows to relieve muscle tone and spasm.
Glucocorticoid drugs( Dexamethasone) are used to relieve the pain syndrome. They are an important part of restorative therapy. It is also necessary to use medicines that restore the structure of the spine.
During treatment, the patient shows rest, strict observance of bed rest, exclusion of physical exertion.
Consequences of the disease and the prediction of
Early diagnosis allows us to begin timely treatment and reduce the negative consequences of the disease. To do this, it is necessary to identify in a timely manner the causative agent of the infection process and to perform competent operative intervention.
If treatment was started untimely, then epiduritis can go into a chronic form. Among the consequences in this case, there are violations of motor abilities in the form of paresis, plethysy, sensitivity. Pelvic organs suffer from this.
A person can have bedsores and a urogenital infection. If the outcome is unfavorable, the patient may permanently remain disabled.