Men are often exposed to diseases of the genital area. Some are relatively common, others are rare. One of these pathologies is atrophy of the testicles, which is quite rare in practice, although the potential for its occurrence is available for each male. Atrophy is characterized by gradual development, manifesting independently of age.
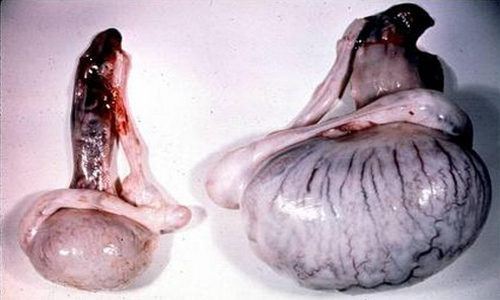
It is very common misconception that testicular tissues die only in bodybuilders and athletes because of the abuse of steroids. Not always the atrophy is caused by steroid influence. More often this disease affects children of the male sex, in which one( or two) testicles could not descend into the cavity of the scrotum( congenital cryptorchidism).
Modern hormonal preparations taken by bodybuilders are distinguished by an improved intake scheme, in which the likelihood of such consequences as atrophy of the genital organs is practically absent.
Common causes of atrophy
So, atrophy of the testicles is a pathological decrease in their volume, accompanied by impaired hormonal production and the processes of sperm formation. Strong sex at any age can detect signs of development of atrophy. The most common cause of exhaustion of the testicles is congenital cryptorchidism, when in the childhood there is no descending of the testicles.
Therefore, if cryptorchidism is detected, treatment should be started immediately, as late therapy of such a deviation is fraught with dangerous complications. Negative consequences are caused by impaired blood flow in the testicles, the cause of which is the surgical treatment of cryptorchidism. Blood circulation problems provoke deficiency of oxygen supplied to the testicles and nutrients. This condition often plays the role of a factor that provokes the atrophy of the testicles.
If pathological symptoms were found only on one organ, then in the absence of therapeutic actions, atrophic changes inevitably affect a healthy testicle.
In addition to cryptorchidism, there are other causes that contribute to the depletion of testicles:
- Imbalance of sex hormones;
- Torsion of testicles;
- Pathological conditions of infectious origin;
- Traumatization of genital organs;
- Orchitis;
- Vertebral injuries, provoking innervational disorders of the gonads;
- Dropsy testicles or varicocele( varicose veins);
- Obesity;
- Operations on the scrotum;
- Some hormonal drugs;
- Circulatory disorders in the scrotal area caused by vascular lesions such as atherosclerosis, etc.
Regardless of the causes that caused the exhaustion of the testicles, lack of therapy or an incorrect approach to treatment can provoke irreversible male infertility.
Signs of the pathology of
The development of the death of testicular tissues is not noticeable enough, since the pathology is notable for its clear manifestations:
- Rapidly decreasing testicles, accompanied by their flabbiness. There are cases when only the shell remains in place of the testicle, and the necessary contents are absent;
- The man is gradually dulled by sexual attraction;
There is an apathetic attitude to the environment and life in general, depressed moods, weakness and impotence; - In boys, feminization of the body can be observed, that is, it acquires feminine outlines.
Atrophy and pregnancy
In the case of tissue necrosis, irreversible dystrophic changes occur, so the affected organ must be immediately removed to avoid the spread of pathological processes to the second healthy testicle. If both organs are struck immediately, the reproductive function of the man ceases to function.
Early detection and elimination of the problem will help avoid such consequences and prevent the full development of the pathology before the onset of the stage, at which testosterone production decreases, the development of azoospermia and other characteristic abnormalities begins. The presence of one unaffected testicle gives a chance for paternity, although the probability of pregnancy is significantly reduced.
Diagnostic features of
An important diagnostic moment is differentiation of atrophy with testicular hypoplasia. The difference is as follows:
- Atrophy is manifested by the rapid decrease in testes, the tissues of which subsequently gradually die off;
- Hypertrophy is the initial lack of development or underdevelopment of the testicles, which is why the testicles do not reach the proper physiological dimensions.
Spermogram helps to determine the extent of pathological changes. Such an analysis will show even minor violations, since at the beginning of development, the disease is characterized by a decrease in the volume of seminal fluid and the number of spermatozoa in it.
Tactics of treatment of
To date, therapeutic measures, which provide a 100-percent guarantee for effective treatment of atrophy, do not exist. Therefore, conservative-medicamentous therapy is justified only in the presence of pathological factors provoking necrosis of tissues. These include inflammatory and infectious diseases, testicular injuries or torsion.
In cases when vascular disturbances are the cause of atrophic changes, etiotropic treatment can stop further necrosis, in this situation, presupposing medications that restore normal nutrition and blood circulation of tissues( Actovegin, Trental, Pentoxifylline, etc.).Atherosclerotic causes of atrophy of testicles shows the use of antiplatelet agents such as Aspirin-Cardio or Trombo-ACC.If there are neuroregulatory disorders in the genitals, then drugs based on galantamine( Nivalin, etc.) can help, although they are highly allergenic.
Attention! With complete atrophy, the affected testicle can not be cured. To avoid spreading to a healthy testicle, resort to surgical removal of the dead organ.
With special care resort to hormonal therapy, constantly observing the patient's condition. In the early stages of the disease, sexual function is restored by HCG therapy, which involves the use of human chorionic gonadotropin. In the absence of therapeutic effectiveness, the use of steroids is canceled. If hormone therapy brings more benefit than harm, then therapy is continued, but subject to strict monitoring of the patient.
If the root cause of pathological processes are serious hormonal disorders, dysfunction of the sex glands, traumatic factors or a significant degree of obesity, the prognosis is not very favorable. In such cases, only the surgical removal can save the situation, and the implant is implanted into the place that has been freed in the scrotum. With one healthy testicle the man is still able to become the father of the family, but this will have to be done, since the probability of conception is significantly reduced.



