There are such categories of people who are completely unaware of medical terminology. So, in the clinic, an accidentally heard phrase prompted the writing of this article. The phrase sounded like this: "I was found in the spine on the rengen shmorl."
The unhappy patient did not know that this formation - a special hernia is named Hans Christian Schmorl. This German pathologist in the interval between the first and second world war wrote the book "Healthy and sick backbone", in which he first described these formations.
Contents of
- 1 Schmorl's hernia - what is it?
- 1.1 Types of Schmorl hernia - small, multiple, complicated, etc.
- 2 Symptoms of Schmorl's hernia
- 3 Treatment of Schmorl's hernia - drugs and techniques
- 4 Complications - what is the risk of hernia Schmorl?
- 4.1 Forecast
Herniated Schmorl - what is it? Of course, since Shmorl was a pathologist, he could see from his own experience of the observations, leafing through the history of the illnesses of the deceased patients, that these interesting intervertebral disc formations were an accidental finding: patients did not present any complaints of pain or symptoms., and died from very different diseases.
In Germany, an X-ray study was already widely distributed, and subsequently these hernias were diagnosed intravital as a curious radiographic phenomenon. They also received the name "cartilaginous nodules".
In the first decades it was believed that these hernias are completely harmless, but then it was discovered that this is not quite so: under certain conditions they can cause significant harm. But first things first.
The modern definition is: "Schmorl's hernia is a vertical defect of the intervertebral disc, consisting in the penetration of its part into the spongy substance of the bones of the body above - or the underlying vertebra".
What is their difference from conventional hernias?
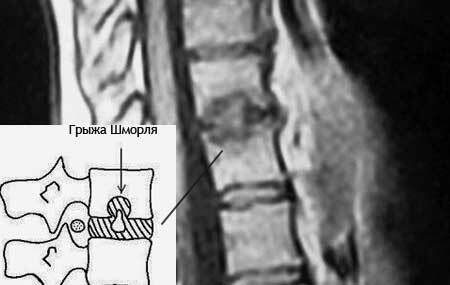
The difference between Schmorl's hernia and ordinary intervertebral hernias consists in the following: the usual hernias and protrusions, whatever the clinical picture accompanies their appearance, are located in the horizontal plane.
They can be located "on different clocks", when viewed from above, and squeeze various structures, from the nerve root to the central canal, cause compression of the spinal cord with the onset of myelitis symptoms, in rare cases. But most often, the usual hernia is a source of pain in various parts of the back.
Schmorl's hernia is implanted into a bone substance that is devoid of nerves. Therefore, they do not cause any symptoms for a very long time, and maybe even throughout their life. Nevertheless, they can be "time bombs".
Types of Schmorl hernia - small, multiple, complicated, etc.
Like any hernias and protrusions, Schmorl's hernias can be localized in different parts of the spine. Of course, the greatest factor of penetration into the adjacent spongy substance is the force of the pressure of the discs on each other. Therefore, the largest hernias occur where there is strong pressure, large intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies.
Small Schmorl hernias often appear in the thoracic, and especially in the cervical region. Since the load on the cervical region is small, the hernia of the Schmorl's cervical region is much less lumbar. But, since the vertebrae are smaller, the relative size of the defects in the bone tissue is quite comparable.
These hernias can be either single or multiple. And they can be multiple as within the spine, one anatomical department( for example, multiple Schmorl hernias of the thoracic spine).
These hernias can also be located in adjacent vertebrae, which significantly weakens the strength. The most unfavorable variant of a hernia is when these cartilaginous nodules are located in one vertebra from above and below.
This suggests that the body of the vertebra is practically destroyed, and the question of its fracture is only a matter of time.
Finally, there are multiple hernias in one vertebra, but on the one hand. This is much less common than the presence of single protrusions.
In addition, hernias can be complicated and uncomplicated. With complicated hernias, there are further violations of intervertebral discs, which will be described below.
Symptoms of Schmorl's hernia
These cartilaginous nodules are quite "treacherous" elements: they tend to be completely asymptomatic until the lesion becomes significant. Only then there is a slight, aching pain in the back.
The fact is that with this type of hernia there is an accidental "stabilization" of the disc. After all, his penetration into the neighboring body of the vertebra contributes to its dense "attachment" to it.
There is such a functional unit, and, as long as this cartilaginous nodule does not disintegrate from existing loads, as a rule, normal hernias and protrusions do not arise at this level, due to the small mobility of this disc.
As can be seen, the hernia of Schmorl symptoms is very meager, and it can be determined only with instrumental types of examination, or because of complication. What are the risks of these formations?
Treatment of Schmorl's hernia - drugs and techniques
You can treat Schmorl's hernia, but to cure it conservatively is almost impossible task. Imagine a dense cartilaginous node, which is safely hidden in the depth of the bone tissue of the adjacent vertebra. All the vertebrae are connected by an abundance of tight ligaments, muscles.
Therefore, the only way to get rid of a hernia is planned surgery. Hernia Shmorlja the lumbar department of a backbone, treatment which conservative ways lasts long years without results - is quickly treated by an operative way.
Given the fact that "until the thunder does not break," the patient has no complaints, then he does not hurry to the planned operation. Of course, in Western Europe, where patients have developed self-awareness of preventive treatment, you can routinely replace the intervertebral disc, putting a full artificial prosthesis - an implant.
In this case, the affected cartilage is simply removed, and the "hole" in the spongy substance of the vertebral body is filled with the patient's bone autograft( taken, for example, from the iliac bone).After such a planned treatment, the patient can for years forget about that vertebra, which potentially threatened a person with a fracture, and prevented him from engaging in active life.
In the Russian Federation, a prophylactic approach to one's own health, unfortunately, seems absurd: there are so few money and pay them "in advance" until nothing happened, our people are not used to it. Therefore, Schmorl hernia is treated symptomatically, and does not cure, because it is impossible to do this with the help of massage, acupuncture, or therapeutic physical training .
At best, it is possible to remove secondary signs caused by a disintegrating disc: a tonic spasm of smooth muscles and pain. But Schmorl's hernia itself is inaccessible to any effect, except operative.
About
preparations A certain effect is also given by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve pain.
Chondroprotectors used in tablets and capsules are ineffective even without these cartilaginous nodules. Therefore, the use of such drugs as "Artra", "Alflutop", "Teraflex", "Inoltra" enrich only the pockets of manufacturers: the use of glucosamine in the United States has long been withdrawn from drugs into nutraceutical( food additives), and the effectiveness of chondroitin sulfate in a number of randomized trials "did not reach "to the evidence level.
Even the use of artificial substitutes for articular fluids injected directly into the affected vertebra is pointless: the intervertebral disc movement is limited, as it is "anchored" in the body of the adjacent vertebra by a cartilaginous junction.
Complications - what is the risk of Schmorl's hernia?
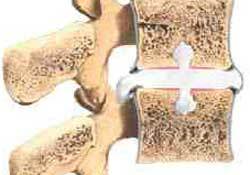 In any case, the defect of the intervertebral disc - it's not good. And it does not matter whether the protrusion has occurred sideways or upwards, one thing is clear - its integrity is broken. If the cartilaginous nodule "dived" into a massive and large vertebra( such as the Schmorl hernia of the lumbar spine), the integrity of the vertebral body also decreases, since a defect in the spongy substance occurs.
In any case, the defect of the intervertebral disc - it's not good. And it does not matter whether the protrusion has occurred sideways or upwards, one thing is clear - its integrity is broken. If the cartilaginous nodule "dived" into a massive and large vertebra( such as the Schmorl hernia of the lumbar spine), the integrity of the vertebral body also decreases, since a defect in the spongy substance occurs.
This is fraught with at least two complications that lead to the development of severe symptoms:
1) Over time, when there is more and more dehydration of the disc due to age-related changes and osteochondrosis, it ceases to densely enter the bone material.
If the hernia is located above the disc, in the body of the overlying vertebra, it may crumble, fragment and begin to occupy a place on the upper surface of the disc. As a result, the formation of normal hernias and severe wear of the disc are provoked.
2) If the hernia of the lumbar spine is located between the disc and the underlying vertebra, the situation may be somewhat worse: under the same conditions of progressive osteochondrosis, excessive body weight and a sharp increase in physical activity( for example, when trying to pick up a bag of potatoesshoulder), this disc may completely or more of its part fall into this hole, because instead of an even surface of the body of the vertebra under the disk a hole was formed.
This condition is fraught with the appearance of acute pain in the back, the development of radicular symptoms, and the appearance of indications for neurosurgical surgery.
3) The third, more rare type of complication is that there is simply a fracture of the vertebra, weakened by the existence of a significant defect in its wall.
Of course, this basically happens when there is weakness and brittleness of the bone tissue itself: often this condition occurs when there are signs of osteoporosis in the elderly and old age.
Schmorl's hernia in the lumbar spine may be an indirect "culprit" of a vertebral fracture.
In the event that cartilaginous nodules appear in the vertebra from two sides at once, it is the "right candidate" for a fracture, even with a small load.
Therefore, the patient should be warned about this danger: if displacement of the vertebral body fragments causes compression of the central canal and ischemia with compression of the spinal cord, then as a result one can get complete paralysis, below the lesion.
All these complications do not allow us to treat these entities "through the sleeves".Therefore, medical science studies them, and suggests ways to prevent complications.
Forecast
Therefore, patients can recommend moderate curative gymnastics, swimming to unload the spinal column, and constant monitoring of their bone tissue for osteoporosis and deepening of the lesion of the vertebral bodies.
- When bone tissue becomes fragile, and hernia increases, you need to start treating osteoporosis, use a corset and exclude the lifting of gravity.
- In case the hernia is stable for many years, it is necessary to monitor the weight, not allowing it to increase, and to conduct an X-ray examination of the spine in two projections every year, which is enough for the primary control of the situation.


 In any case, the defect of the intervertebral disc - it's not good. And it does not matter whether the protrusion has occurred sideways or upwards, one thing is clear - its integrity is broken. If the cartilaginous nodule "dived" into a massive and large vertebra( such as the Schmorl hernia of the lumbar spine), the integrity of the vertebral body also decreases, since a defect in the spongy substance occurs.
In any case, the defect of the intervertebral disc - it's not good. And it does not matter whether the protrusion has occurred sideways or upwards, one thing is clear - its integrity is broken. If the cartilaginous nodule "dived" into a massive and large vertebra( such as the Schmorl hernia of the lumbar spine), the integrity of the vertebral body also decreases, since a defect in the spongy substance occurs.