 The concept of compartmental syndrome, like many other terms in medicine, came to us from abroad. What does "syndrome" mean is not difficult to guess, but the "compartment", contrary to the translation, can be interpreted as a camera or a confined space.
The concept of compartmental syndrome, like many other terms in medicine, came to us from abroad. What does "syndrome" mean is not difficult to guess, but the "compartment", contrary to the translation, can be interpreted as a camera or a confined space.
It is difficult to accurately determine when the concept of "compartmental syndrome" was applied, but the approximate start came a little later than the removal of the iron curtain. However, the absence of a term for designation does not mean that there is no pathology. Naturally, many physicians also faced this syndrome in Russia, and not only did they meet with this, but also adequately treated this disease.
In this case, such terms as "squeezing", "hypertension" were used. So, if we translate a foreign name into our language, then this disease can deservedly be called "Closed Space Syndrome".
Contents of the article
- What is
- syndrome Acute and chronic lesions of
- Acute form of
- syndrome Chronically acquired
- Why does the fascial pressure increase?
- Degree of lesion and symptomatology
- Difodiagnostics
- How should it be treated?
What is the syndrome
? The syndrome is a complex of various symptoms, the distinguishing feature of which is an excessively high fascial pressure. This in turn leads to the blocking of blood access to the tissues, and as a result, the skin and the fascial cases themselves die out.
The syndrome is divided into two different forms:
- Myofascial form ( also called local syndrome syndrome).Often, this type of disorder causes such consequences as the disturbed metabolism of muscle tissue and as a consequence its death.
- Abdominal compartment syndrome( more serious form).

Acute and chronic forms of lesions
The syndrome of the syndrome is divided into two types according to the severity of the manifestation. They differ for reasons of their appearance, as well as how long and how acute each of the symptoms develops.
Acute form of the syndrome
The causes of acute syndrome are mechanical deformations of tissues, from the usual fracture, to the gypsum imposed by the doctor incorrectly.
The syndrome is caused due to the squeezing of tissues, in one form or another. Developing an acute compartment syndrome is also capable, as the continuation of long and dangerous operations.
There may also be some eccentric reasons, such as a snake bite, or pressurized fluids into the subcutaneous space.
It is also often possible to observe a similar problem with inaccurate treatment of rescuers with people who are unconscious under the rubble.
Chronically acquired
This form of disruption is manifested regularly in powerlifters and bodybuilders, that is, anyone who draws iron tries  as hard as possible to destroy their muscles, so that they increase in volume. And paying for it often serves as a compartmentalized syndrome.
as hard as possible to destroy their muscles, so that they increase in volume. And paying for it often serves as a compartmentalized syndrome.
In addition, there is a violation and hypertension inside the tissues, where there is a lot of pressure on the bones and muscles. A good example is the shin.
But still, most people develop the syndrome, which are constantly on their feet, and among professional athletes, it's natural marathon runners running to outrageous distances, constantly loading the entire lower body, while having high blood pressure in the norm.
Why does the fascial pressure increase?
There are several reasons, among which:
- bruises and bruises formed after extensive subcutaneous hemorrhage;
- the same hematoma, but already inflamed;
- pressure exerted on the body area;
- cancers of the body
In order to measure the excess pressure, it is compared to the normal one, which for most people keeps in the altitudes of 8-9 mm Hg. When, however, the pressure of the myofissic space rises several times, then it is diagnosed "compartmentsyndrome".
Depending on how much this pressure differs from normal, classify the lungs and severe forms of the disease.
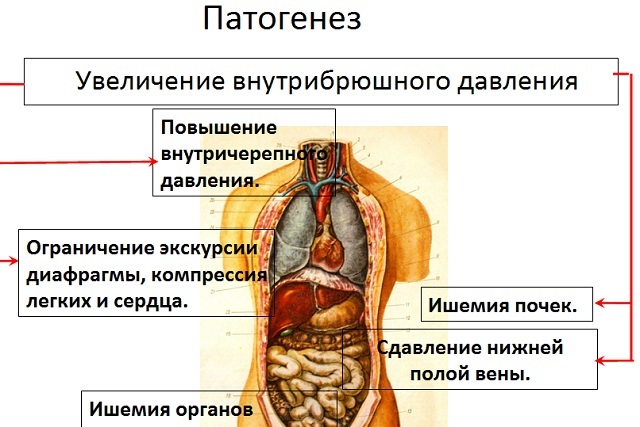
Degree of defeat and symptomatology
Classify the following types of impairment depending on the severity of the lesion:
- Light form of violation - The limb tissues are not cold, the homeostasis and metabolism of tissues and organs persists, there is no change in the pulse of changes. Subfascial pressure differs from diastolic pressure by 32-42 points. This is the easiest and sometimes even a form of the syndrome.
- Average form of - Noticeable pallor of skin tissues, colder limb. Lack of oxygen in tissues, as well as other factors, lead to hypoesthesia or limb anesthesia. The pulse can still be felt, but it is much weaker than it should be in the norm. Diastolic and padophosic pressures are equal.
- Heavy form of - No pulse at all, strong pallor of tissues and noticeable coldness of the limb. The subfacial pressure greatly exceeds the diastolic pressure.
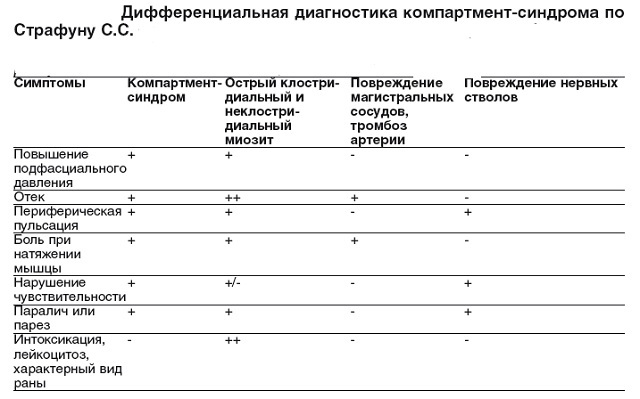
Difiagnosis
It is important to distinguish this syndrome, and some diseases are similar in symptomatology.
Among others distinguish:
- blood clots in the arterial canals and mechanical vascular damage;
- problems with CNS and nerve damage;
- various forms of myositis.
Find out the compartment syndrome allow the following criteria:
- pulsation around the perimeter of the limb;
- swelling prominent to the naked eye;
- functions of nerve endings are disrupted;
- positive blood tests for excessive leukocytosis;
- increased subfascial pressure.
Pulsation will be noticeable almost always, with the exception of the moments when arteries and vessels are further clogged with thrombi.
Swelling may also not be noticeable, but only when nerve trunks are affected. But blood tests can identify only infectious processes. But the measurement of subfascial pressure allows you to clearly identify the patient's illness.
How to treat it?

Conservative treatment of the compartment of the syndrome requires:
- it is necessary to isolate the affected tissue segment from any mechanical compression, you can not impose any bandages and gypsum to prevent possible ischemia;
- removal of spasms of blood vessels in order to return blood circulation;
- disposal of various infections;
- reception of anesthetic, and the first couple of days can be used narcotic drugs;
- it is necessary as much as possible to reduce edema on the affected surface;
- requires a variety of drugs that dilute the blood and allow you to cope with possible thrombosis.