A hemiopathy( hemiopia) is an ophthalmic disease with a neurological nature, the development of which results in the loss of half or a fourth of the field of vision.
A hemiopathy( hemiopia) is an ophthalmic disease with a neurological nature, the development of which results in the loss of half or a fourth of the field of vision.
If in these areas there is a decrease in visual function, then in this case it is said about relative blindness. When in the fields of vision a person does not get to distinguish colors, then this condition is called hemichromatopsia.
The hemianopsia is right-sided and left-sided, with pathological changes in the right and left eyes respectively, depending on the size of the invisible site, the pathology is divided into partial, full and square.
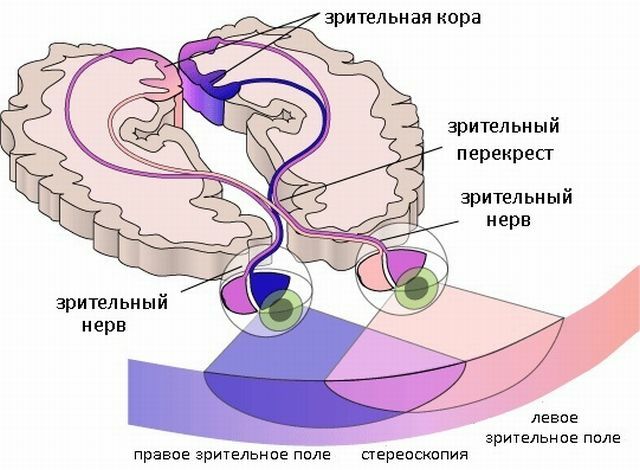
Scheme of the optic path

Scope of the visual path

Contents of the
Scope
- Causes and mechanism of vision loss
- Consequence of neurological disorders
- General symptomatology
- Classification and varieties of violation
- Homonym form is one of the most frequent forms
- Heterosexual form
- Bitemporal form is the most frequent
- Binasal hemiopia
- Diagnostic criteria
- Methods of treatment and prevention
Causes and mechanism of loss of fields of vision
Disease can occur against the background of the damage to visual trsuch as are for, as well as central parts of the visual pathways, and parts of the cerebral cortex.
This is due to various reasons. Most often the disease develops because of previously acquired pathologies. For example, when meningitis occurs squeezing the areas that provide the conductivity of nerve impulses to the cerebral cortex.
Pathology can also develop with various injuries and neoplasms in the brain. Another factor that provokes the loss of visual fields is a violation of the blood circulation of the brain due to thromboembolism or an aneurysm of the cerebral vessels.
The efficiency of the visual pathways may be compromised due to increased blood pressure and increased blood volume. In the end, they can atrophy altogether.
If we talk about congenital blindness, then the cause of the disease is found in malformations, namely hydrocephalus, microcephaly, etc.

Consequence of neurological disorders
The disease most often develops due to damage to the brain areas, as well as various diseases of the neurological profile.
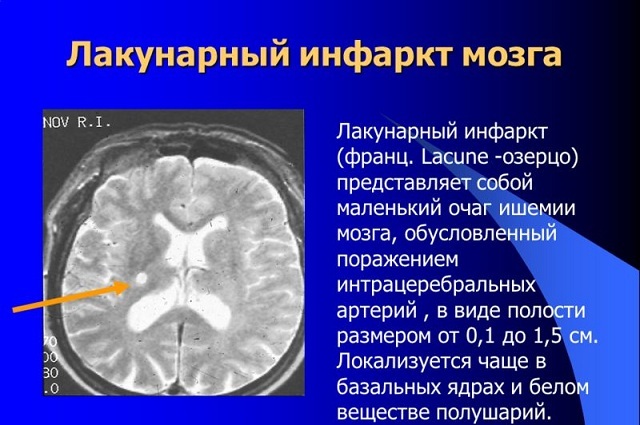
In order to find out the cause, as well as determine the site of the lesion, a study is being carried out - MRI of the brain. Depending on the type and nature of brain damage, various kinds of hemianopsia develop:
- Homonymous hemianopia develops due to circulatory disorders and damage to the hemispheric cells to which the posterior cerebral artery passes, often diagnosed in ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
- The upper quadrant hemiopsis occurs when the region of the cerebral cortex is located, which is lower in relation to the spurs in the temporo-occipital part.
- The cause of appearance of the lower-quadrant form of the disease is the lesion of the cortex site located higher in relation to the furrow groove.
- More serious pathologies develop against the background of the defeat of the occipital lobes from two sides. As a result, the visual hallucinations may even develop, the patient will not distinguish colors and will cease to recognize familiar people.
Sometimes a homonymous form of disorder develops against a background of a heart attack that occurs in the areas to which the posterior cerebral artery is drawn.
Its boundaries with the middle cerebral artery are able to oscillate. Often, the role of such a conventional boundary is the sylvian furrow. However, in some cases, the blood supply to the external parts of the occipital lobe occurs at the expense of the middle cerebral artery.
Without giving concrete examples it is difficult to explain what patients experience when they have this pathology. So, patients with a diagnosis of right-sided homonymous hemianopsia will complain about what they can not see with their right eye. However, on examination, it is revealed that a person can not see the right side of the field of view with his right and left eye.

General symptomatology
In clinical manifestations, it is common to separate homonymous and heteronymous hemianopsia. In the first form of the disease, patients will say that they are unable to see the right or left half of the eye.
When the left and right visual tract is injured, the right and left eyes are blinded respectively in the patient.
When the disease develops, the patient may experience visual hallucinations. This manifests itself in not recognizing familiar objects, the appearance of flares, etc. Often, patients develop pro-spagnosia, that is, the inability to recognize familiar people.
If patients remain orientated, they most often deny their disease. This condition indicates a positive syndrome of Anton-Babinsky. Patients in this case can fix a sight on only one subject, and the surrounding objects will not enter their field of vision.
Most often, the first symptoms that indicate a hemianopia occur after a person has had a stroke. Patients who begin to develop the disease, mostly complain that their performance is reduced, because doing any action becomes much more difficult.
People face such problems: inability to find the right subject, loss of orientation in space, difficulty in eating, etc.
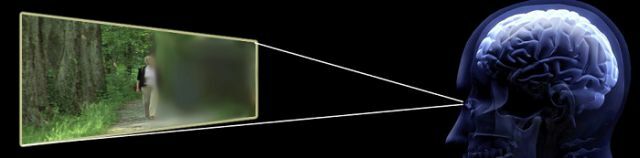
Classification and varieties of violation
Modern medicine distinguishes several types and subspecies of hemianopsia.
The homonymous form is one of the most frequent forms of
. Homonymic anopia is a pathological condition in the course of development of which the patient ceases to perceive the right or left field of view.
Homonymous hemianopsia can be either right-handed or left-handed. It arises because of the defeat of the cortex of the occipital lobes, with the right side on the left, and with the left side on the right.
This pathology is also subdivided into full, square and partial. The type of disease depends on which area is affected.

In addition, this form of the disease is divided into congenital and acquired. The acquired homonymous hemianopsia is observed when the CNS and brain are affected due to stroke, traumatic brain injury, an unsuccessful operation or a tumor.

All this leads to inflammation of the optic nerves. They are squeezed, because of what blood circulation is disturbed, additionally they are affected by toxins. In this situation, dysfunction of the visual tract develops.
Transient homonymous hemiopia is a pathology that is caused by diseases of the cerebral vessels. It is also called transient, because in this case there is a disturbance of blood circulation in the vessels of the brain.
In all described situations, the focus of inflammation has a specific localization. Thus, if the parietal lobe is affected, the lower square homonymous hemianopsia develops in a person. Due to the defeat of the temporal region, the upper square or full form of hemiopia develops.
Symptoms that indicate the onset of the disease, in particular after a stroke or other brain damage, is primarily the onset of visual hallucinations.
Heterometric form
Heterodynamic hemianopia is a pathology accompanied by loss of perception of nasal or temporal areas of the visual field. Here, too, the complete, partial and square form of the disease is identified.
Bitemporal form - the most frequent
Bitemporal hemianopsia is characterized by a lack of visibility of the upper parts of the field of vision in both eyes. This pathology occurs in patients more often than the two previous ones. Lead to it can:
- defeat the pituitary part in the place where optical fibers intersect;
- lesion of the medial part of the chiasma.
The localization of the blind area will depend on what pressure is applied to the chiasm.

Binasal hemiopia
Binasal hemianopia is a disease that occurs with a loss of visibility of the inferior, in other words, nasal field of view. 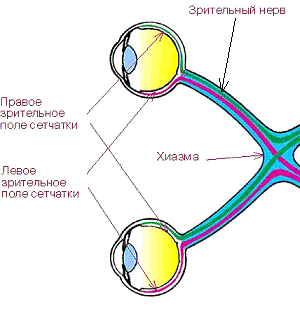
Heterodynamic Binasal Blindness is a pathology accompanied by the emergence of several lesions at the same time, exerting pressure on the literal region of the chiasma.
The development of this form of disorder is affected by chiasmatic arachnoiditis, as well as the syndrome of the empty Turkish saddle.
The development of pathology in one eye with complete blindness of the second is a disease accompanied by a loss of visibility of the field of view, which extends only to one eye, and the second becomes completely blind.
This pathology is divided into nasal and temporal. The difference between the latter is that one eye becomes completely blind, while the second one has a fall of the upper half of the field of vision. Such a state develops with complete damage to the optical fibers of the chiasma.
The diagnosis of "nasal hemianopsia" is very rare. Its difference lies in the fact that in this case, the lower half of the field of view falls out.
This state, as a rule, develops for a long time. First, partial blindness occurs immediately in both eyes. Later it starts to progress and in case of wrong therapy or in the absence of treatment, after a while, the left or right eye becomes completely blind.
Bilateral hemianopsia is a disease in which visibility disappears immediately in both eyes. In this case, several lesions occur immediately above the chiasma. 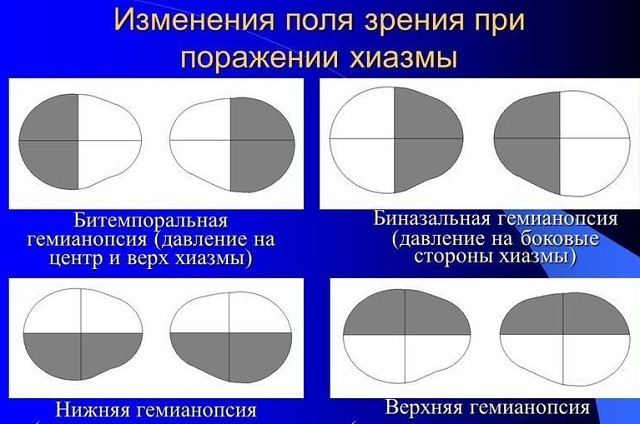
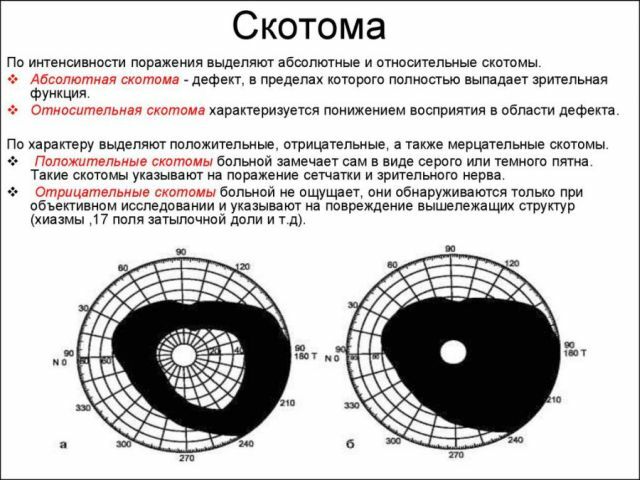
Scott is called the dark area formed in the field of view. It can be of different shapes. The scotoma has no connection with the peripheral boundaries, and therefore is able to manifest itself absolutely in any part of the field of vision.
Diagnostic criteria
In case of complaints, the patient should undergo a series of studies, as well as visit specialists - the ophthalmologist and the neurologist.
To diagnose the disease use:
- CT - computed tomography;
- UZGD - ultrasound dopplerography of vessels;
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging, etc.
Only surveys will help to find out the exact cause of the development and the nature of the disease.
Methods of treatment and prevention of
Therapeutic measures in the acquired hemianopsia should be necessarily aimed at eliminating the cause of its occurrence.
If injuries or injuries are severe, often patients need surgery. However, not all pathological conditions affecting vision are amenable to treatment.

Partially assisted glasses with special lenses
In this case, the patient should be assigned rehabilitation, which will help to facilitate life and establish interaction in the external environment. To do this, various eye exercises are used, which the patient should be trained by a rehabilitator doctor.
Special mirrors, prisms, which are built into the patient's glasses, help to remove certain manifestations of the disease. There are also computer techniques that improve visual functions and facilitate the patient's orientation in space.
Possible consequences and complications directly depend on the form of the disease. Usually, if you diagnose and start treatment on time, you can get rid of it completely.
But when the pathology that led to a visual impairment will progress, the patient may eventually become completely blind.
Modern methods of rehabilitation can not completely compensate for the symptoms of the disease, but they can greatly facilitate the life of patients.
There are no effective preventive measures. To avoid problems and not to start the disease, it is necessary to undergo a preventive checkup once a year, and also to consult a doctor immediately after the appearance of complaints.
Fatigue, dizziness, frequent headaches can talk about serious problems with the central nervous system.