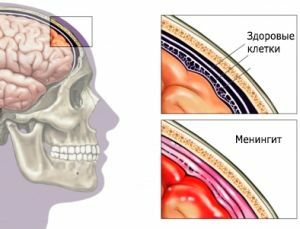
Under encephalitis is to understand a group of diseases associated with inflammation of the brain, which combines both infectious and allergic, toxic types of damage.
Under encephalitis is to understand a group of diseases associated with inflammation of the brain, which combines both infectious and allergic, toxic types of damage.
According to the nature of brain tissue damage, is isolated:
- panencephalitis - a lesion of gray and white matter;
- polioencephalitis - a lesion of only a gray matter;
- leukoencephalitis - a lesion of only white matter.
Content
- Causes encephalitis
- Risk Factors
- Classification of Diseases
- symptoms characteristic of the disease
- Diagnostics
- How to treat encephalitis brain
- Complications
- disease prevention
- Video: Effects of tick-borne encephalitis
Causes encephalitis
causative agents of encephalitis brain can act different viruses, protozoa, helminths, fungi, as well as microorganisms - rickettsia, mycoplasmas and bacteria.
The most common is viral encephalitis of the brain.
The carriers of viral encephalitis are ticks and mosquitoes that infect humans when bitten, can also be transmitted by airborne droplets.
Rabies can also result in encephalitis. Encephalitis may be a consequence of of certain diseases, such as malaria, rubella, smallpox, etc. Allergic encephalitis occurs, on the products of the life of the pathogen( eg herpes or smallpox).
Risk Factors
About encephalitis can be safely affirmed - from this infection no one is immune. But in some people the chances of getting encephalitis are much higher. Risk factors directly are tied to:
- age - encephalitis, which arose due to herpes affects people aged 20 to 40 years, but viral encephalitis is more often affected by small children and elderly people;
- geographical location - as a rule, viral encephalitis has a certain range;
- weakened immune system - this includes people with HIV infection, taking medicines that suppress immunity, and suffering from certain diseases that reduce the defenses of the body;
- rest and work in nature - higher chance of being bitten by infected mites and mosquitoes;
- summer-autumn period - peak activity of the above-mentioned arthropods occurs in the summer and early autumn.
 Why is hydrocephalus in an adult more dangerous than children. What methods of prevention and treatment are offered by modern medicine.
Why is hydrocephalus in an adult more dangerous than children. What methods of prevention and treatment are offered by modern medicine. Get an answer to the question of how to treat a migraine with an aura you can after studying our material. Also in the article you will find information about medications for migraines.
Classification of the disease
There are two forms of inflammation of the brain of encephalitis: primary and secondary.
- Primary encephalitis is viral, microbial and rickettsial. Among viral isolates: seasonal, arbovirus, transmissible, enterovirus( Coxsackie virus), herpetic, rabies virus and encephalitis from unknown viruses. To the microbial carry neurosyphilis and typhoid fever.
- Secondary encephalitis is a complication of such diseases as: rubella, chicken pox, influenza, toxoplasmosis, osteomyelitis, measles and brain abscess.
Symptomatology, characteristic of the disease
There are two trends in the disease - light and heavy. Each is characterized by its symptoms. Symptoms of brain encephalitis are the same for all age groups.
Light Current:
- high temperature;

- headache;
- photophobia;
- nausea;
- there are epileptic seizures;
- impaired consciousness;
- persistent drowsiness.
Severe course:
- stiffness( petrification) of the occipital muscles;
- coma;
- paralysis or paresis of the limbs;
- elevated leukocyte counts in blood and lymphocytes in CSF;
- visual impairment and visual hallucinations;
- problems with hearing and speech;
- is an olfactory hallucination.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of encephalitis is based on based on the history of ( questioning the patient or someone who monitors his condition), the general clinical picture and the results of laboratory tests.
If there is a suspicion of encephalitis, a lumbar puncture is prescribed, followed by a study of cerebrospinal fluid, which makes it possible to establish the fact of inflammation in the central nervous system.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are also used, which provide a detailed picture of the brain with foci of inflammation. In the early stages of tomography are not effective.
How to treat brain encephalitis
Treatment of brain encephalitis begins with the patient being hospitalized, followed by continuous monitoring.
Depending on the type of illness the patient is sent to the infectious or neurological department .Ticks and mosquito encephalitis are treated with antiviral drugs, inject interferon and gamma globulin from the donor.
 If the patient has purulent minogenoencephalitis, antibiotics are indicated. Patients carry out activities aimed at reducing the level of toxins in the body, also in the treatment of calcium-containing drugs, ascorbic acid, trental( a drug that improves blood microcirculation).
If the patient has purulent minogenoencephalitis, antibiotics are indicated. Patients carry out activities aimed at reducing the level of toxins in the body, also in the treatment of calcium-containing drugs, ascorbic acid, trental( a drug that improves blood microcirculation).
When edema of the brain, corticosteroids ( anti-inflammatory effect) are actively used. Sometimes patients have problems with breathing - connecting to the device of artificial ventilation, additionally prescribe anticonvulsants and analgesics.
For normalization of vital activity - massage and physiotherapy exercises .
Complications of the disease
In patients with mild form complete recovery occurs in two to three weeks and usually without complications.
Complications can persist for several months.it can be:
- hearing, vision and speech problems;
- mental disability( inherently acquired dementia);
- lack of complete muscle control - impaired coordination of movements;
- various memory problems;
- change of personality and consciousness;
- paralysis;
- mood disorders, the so-called affective disorders;
- increased fatigue and weakness.
Prevention
Prophylaxis for each type of encephalitis has its own specificity:
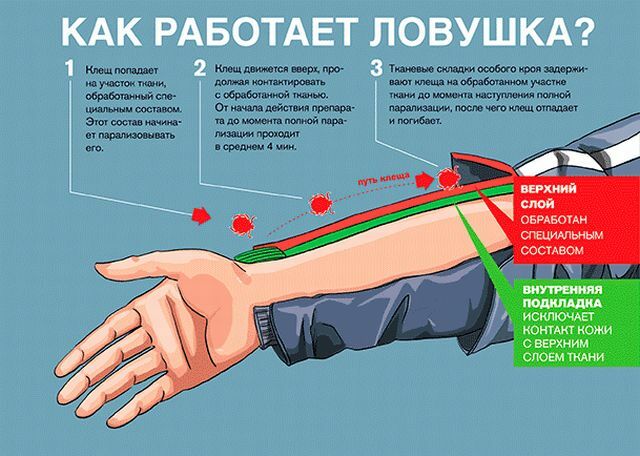
- Tick-borne encephalitis is the destruction of ticks by regulating the numbers of rodents, hares, which are natural reservoirs of infection. Apply vaccination - a reliable preventive measure. If a sucking mite is found, after its removal, intramuscularly the immunoglobulin is administered. It is necessary to observe certain rules of behavior in the forest: keep track, wear light clothing( it is well marked with ticks), mandatory examination of the whole body after the hike, use of permethrin repellents, wearing long sleeves, pant legging in high socks, wearing hats.
- Mosquito encephalitis - regular anti-mosquito measures, vaccination of the population.
- Encephalitis ECONOMO - because the pathogen is not detected, and the disease is transmitted by contact and airborne, prevention is reduced to isolating the focus and monitoring it.
- Herpetic encephalitis - for the prevention of infection by airborne droplets conduct the same measures as in ARI.Condoms are used to block the genital way of infection.
- Measles encephalitis - the introduction of measles gamma globulin, all who contacted the patient. .
- Encephalitis with chickenpox - isolation of the patient, the introduction of intramuscular gamma globulin to those who contacted.
- Influenza encephalitis - prevention is the same as with influenza.
Also, no one abolished the general prevention rules for all types of encephalitis and not only from him:
- is more often my hands, especially after visiting the bathrooms, public places, before and after meals;
- you can not use other people's plates and cutlery;
- if you are going to a region where there is a possibility of infection, be sure to consult a specialist for vaccination.
Video: Consequences of tick-borne encephalitis
Encephalitis is a viral infection characterized by fever, intoxication and damage to the gray matter of the brain. What is fraught with the disease and what consequences can the victim expect?