1 Information of the
investigation The appearance and development of symptoms of gastrointestinal lesions( soreness in the stomach, discomfort, nausea, vomiting, flatulence) is an occasion to turn to specialists and undergo a comprehensive specialized examination. This procedure is unpleasant, but it will allow you to check the organs of the digestive tract, find pathology in the early stages. The sooner treatment of pathology begins, the more likely a quick and full recovery.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "It's easy to cure gastritis at home for 1 month." A proven method is to write down a recipe. ..! "Read more & gt; & gt;
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with
- Symptoms of esophageal narrowing
- Symptoms and treatment of ulcer DPC
- What is done and what the biochemical blood test shows in adults, children
- Effective agent for gastritis and stomach ulcer
Before the procedure of fluoroscopy of the stomach, the patient must be examined by the following specialists:
- doctor-radiologist;
- of the doctor-diagnostician;
- doctor-gastroenterologist.
The diagnostic method under consideration is conducted only after the conclusion of the above-listed specialists. X-ray of the stomach and esophagus can investigate the following:
- the shape and size of the structures of the gastrointestinal tract;
- working capacity of sphincters;
- condition and integrity of the walls of the organs, their functionality.
Stomach is a hollow structure, making it difficult to study it and get a clear image. Many diagnostic methods are not suitable for stomach examination. Before conducting possible studies, it is necessary to contrast the organ.
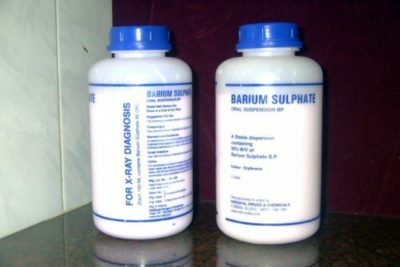
For this, doctors use a barium sulfate solution. It is possible to introduce gas. X-rays of the stomach, performed with contrast, allows you to carefully consider the folds of the structure, to measure and evaluate the condition of the mucous membrane. The x-ray of the stomach shows the contours of the organ filled with contrast. They study the dynamics of the entry of contrast from the esophagus into the stomach, the speed of its movement into the intestine and removal from the body.
2 Stepwise contrasting
For a complete examination of the gastrointestinal tract, contrasting is carried out in 2 stages:
- At first the contrast weakly envelops the mucous membrane of the GIT structures - the period of weak filling. It is used to assess the folds of organs.
- Next, the structure of the digestive system is filled completely - the period of tight filling. They study the size, shape, localization of the organ, its condition, contours, contractions, the time of liberation from barium.
The timing of the passage of contrast on the organs of the digestive tract is as follows:
- Esophagus. Barium passes through it for a few seconds and enters the stomach.
- In the stomach of barium is about 1.5 hours. After a tight filling( about 250 ml), the first 125 ml is removed for 30 minutes. The rest is for an hour;
- Intestine. In the duodenum, the contrast falls after 30 seconds after it is taken, but leaves it quickly enough. Portional passage of barium through the gut lasts up to 1.5 hours.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
Knowing the time limits for finding a contrast in one or another organ, one can judge motor disorders of organs. By the uniformity of the distribution of contrast, one can study the state of folds, the presence of neoplasms and mucosal defects. Knowing such regulations will help the doctor to diagnose correctly for further treatment.
3 Indications and contraindications for prescribing
Indications for fluoroscopy of the stomach are as follows:
- suspected of stomach and duodenal ulcer;
- group at risk of developing neoplasms of the stomach( benign and malignant);
- defects in the development of the gastrointestinal tract;
- changes in the walls of the stomach during the development of polyps and diverticula, deformations in the form of saccule protrusions;
- changes in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract are of an inflammatory nature;
- for diagnosing the cause of abdominal pain in the navel, the presence of blood and mucus in the stool, dyspeptic disorders, heartburn, anemia and weight loss.
Gastrointestinal X-ray is not performed in the following cases:
-
 Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
- is too serious a patient;
- pregnancy, namely I trimester, for II and III the procedure is possible if there is evidence and permission from the gynecologist;
- prolonged bleeding from the digestive system.
These indications, except bleeding, are referred to relative - in each individual case they decide the importance of such manipulation. If possible, the procedure is replaced by fibrogastroscopy. X-ray of the stomach does not require special preparation. You should stop eating 7 hours before the procedure.
In the presence of abnormalities in the work of the intestines, stomach, and also to people of age, it is necessary to observe a diet( to reduce gas production).To do this, the following products are removed from the diet:
- flavored foods;
- is sweet;
- milk and dairy products;
- cabbage;
- all fizzy drinks.

Allow to eat lean meat, fish, porridge on the water, eggs. With propensity to constipation recommend the use of laxatives, staging an enema or rinsing the stomach.
4 How is the diagnosis?
Before the procedure, an overview radiograph is taken for the detection of gross pathologies and for assessing the condition of the body. Then give a contrast drink, make a series of pictures of the digestive system in different positions of the body( on the stomach, on the back, standing).It is extremely necessary in the diagnostic method under consideration, since hollow organs do not retard the flow of X-rays. Pictures without contrast will become completely uninformative. The following formations must be diagnosed:
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;
- larynx and its components;
- the first narrowing of the esophagus( passage of the pharynx into the esophagus);
- the second narrowing of the esophagus( broncho-aortic narrowing);
- third narrowing( diaphragmatic);
- itself diaphragm;
- cardiac part of the stomach, the place of passage of the esophagus into the stomach.
There are 2 types of procedure:
- Method with carrying out radiographs - the patient drinks contrast( 200 ml).After a while on the monitor, the condition and the filling of organs by contrast are assessed. Then the doctor conducts a series of roentgenograms for a detailed study of the morphological state of the digestive system. For clarity, pictures are taken in different positions of the patient.
- Technique with double contrast. It is used to assess the condition and elasticity of the walls of the stomach. For this purpose, use an aqueous solution of barium and air.
This study can identify the following problems:
- Changing the lumen of the digestive tract - often the cause of this manifestation is oncology. The cancer of the organ grows from within, so the constriction will also develop the same way. If the hollow organ( stomach, esophagus) compresses something from the outside, this indicates a cancerous neoplasm of neighboring organs - the liver, the pancreas. Then the narrowing of the lumen will come from the outside. In the pictures you can see the local narrowing of the lumen of the organ in comparison with the norm. The change in the shape of the stomach can be observed with congenital pathology. In this case, the organ has the form of an hourglass, a horn or a cochlea. Normally the form of the organ is represented in the form of a hook.
- Displacement of the digestive system - as a result of various injuries and the development of hernias, the abdominal organs can change their location. With the help of an X-ray, you can see the projection of the stomach, its displacement on the organs of the small pelvis. Developing gastric emptying - gastroptosis.
- Changes in the structure of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, its integrity.
5 Results of the study
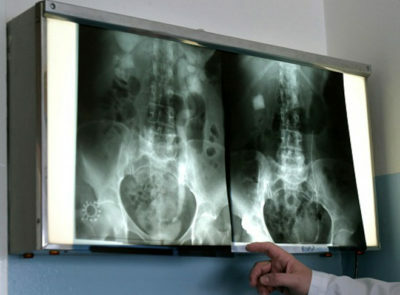
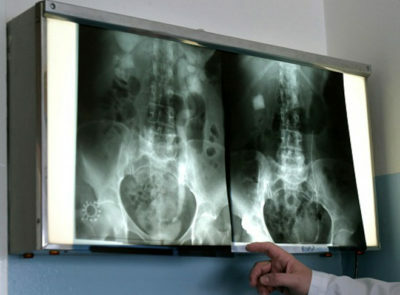
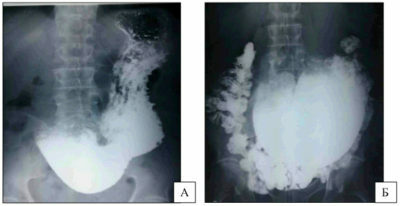
After the procedure, the photo is reviewed by a radiologist, gastroenterologist and surgeon. They are deciphering the pictures. At the site of the wall defect, the photographs clearly show darkening. Such a symptom is called a niche - it accurately indicates the development of an ulcer. In places where contrast could not reach, reveal dark areas. They indicate a tumor, foreign bodies, polyps.
In pictures of a healthy stomach, there are no kinks, filling defects, neoplasms. Chronic atrophic gastritis - in the pictures you can see the depletion of the mucous membrane, almost complete absence of folds on its surface.
With a stomach ulcer in the pictures, a niche is visible( darkening, which is pressed into the wall of the organ).From her in different directions the folds of the mucous membrane. Polyps of the stomach are presented in the form of dark defects of rounded shape with smooth contours. Destruction of the mucosa is not detected.
One conclusion of a fluoroscopy of the stomach is not the final diagnosis.
The physician draws attention to data from objective research, complaints, laboratory and instrumental results. Radiography of the stomach is not an investigation that should be assigned to oneself. It gives an extra radiation load to the body, which can harm your health.
- 1 Informative survey
- 2 Stepwise contrasting
- 3 Indications and contraindications for prescribing
- 4 How does the diagnosis go?
- 5 Results of the
X-ray examination of the stomach - X-ray examination, based on the study of contrasted organs with the help of X-ray photographs. With the help of this technique, it is possible to identify many pathologies and functional failures in the functioning of the stomach:
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer disease;
- neoplasm;
- diverticula;
- polyps.