Mitral valve prolapse( PMC) - this diagnosis can often be seen in the results of an ultrasound of the heart. However, one should not immediately worry: this type of valvular blemish is often diagnosed in quite healthy people and requires only periodic observation from a cardiologist.
Therapeutic tactics directly depends not only on the severity of the prolapse( deflection) of the valve, but also on the degree of regurgitation( the volume of the reverse blood flow).
Contents
- 1 Mitral valve prolapse - what is it?
- 2 Mitral valve prolapse 0 grade
- 3 mitral valve prolapse 1 degree
- 4 mitral valve prolapse 2 degree - mitral insufficiency
- 5 mitral valve prolapse 3 degree
- 6 mitral valve prolapse during pregnancy
- 7 Treatment of mitral valve prolapse
- 7.1 Elimination of severe regurgitation with bivalve valve prolapse
- 7.2 Forecast
Mitral valve prolapse - what is it?

The mitral( bivalve) valve divides the chambers of the left part of the heart: the atrium and the ventricle. The prolapse of the mitral valve is the deflection of the valve flaps at the time of contraction( systole) of the left ventricle.
Pathology is caused by a violation of the structure of the valve( its fibrous layer, less often of the tendon chords) due to connective tissue dysplasia. Valve flaps do not only bend, but can also be loosely closed.
When the left ventricle contracts through the remaining lumen of the valve, the blood rushes back to the atrium. This process is called regurgitation.
PMC is most often diagnosed in young people 20-35 years of age. Very rarely a deviation in the structure and work of the mitral valve is found in young children. Among adults, the frequency of pathology varies between 10-25%, and in the elderly, 50%.
The main causes of forming a valvular defect:
- Hereditary connective tissue dysplasia( Marfan and Ehlers-Danlo syndromes) - primary valve prolapse develops;
- Incorrectly flowing osteogenesis, leading to deformation of the chest;
- Rheumatic heart damage, inflammatory processes in its membranes, infarction, chronic ischemia of the heart, atherosclerosis / calcification of the valve ring - secondary prolapse is formed.
As for the deflection of , mitral prolapse is distinguished:
- of 1 degree - the height of the dome-shaped deflection of the valves does not exceed 0.6 cm( norm 1-2 mm);
- 2 degrees - bulging up to 0.9 cm;
- 3 degrees - dome of the valve with a height of more than 0.9 cm.
Symptoms of prolapse in regurgitation degrees
The classification of PMC in terms of the degree of deflection of valve flaps is rather arbitrary. The most important factor influencing the general state of a person and medical tactics is the degree of regurgitation( 1 to 3 degree), which causes a symptomatic picture of mitral insufficiency.
Mitral valve prolapse 0 degree
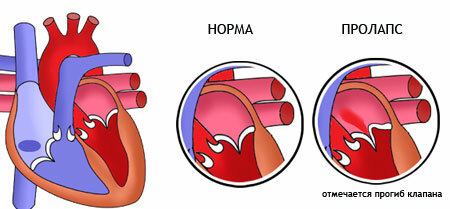
Even with a fairly pronounced deflection the valves close tightly, and the volume of blood from the left ventricle is fully flowing into the aorta( there is no reverse flow to the left atrium).
At the same time, regurgitation of grade 0 does not give any painful symptoms: a person feels completely healthy and does not complain about heart function.
Mitral valve prolapse 1 degree

pain with
The prolapse of the mitral valve and 1 regurgitation is diagnosed with the minimum volume of blood returned to the atrium. There are no complaints indicating a violation of blood circulation, the patient does not present.
Some patients note the occurrence of pain in the right hypochondrium during running. This is due to insufficient right ventricular functionality to increase the amount of blood flow in the heart. The deviation is fixed at the examination:
- Auscultation - listening to noise at the apex of the heart and a specific click caused by the sharp tension of the relaxed chords during the systole of the ventricle. Clicks are more audible in the vertical position, can completely disappear in the prone position. Sometimes( not necessarily!) The "meow"( squeaks) arising from the vibration of the chords or the valve flaps are heard.
- Echocardiography( heart ultrasound) is a small lumen between the closed valve flaps and a fixed volume of blood returned to the atrium.
Mitral valve prolapse 2 degree - mitral insufficiency
With bivalve valve prolapse and 2 regurgitation regimens, ultrasound( heart doppler) shows more pronounced signs of mitral insufficiency. The blood stream, returning through the partially closed valve, reaches the middle of the atrial chamber.
Atrium from the ventricle returns more than 25% of the blood. Symptoms characteristic of stagnation in a small circle of circulation are observed:
- Heart pain - weak or moderate, not having close connection with physical activity or emotional reaction to stress( can arise spontaneously).Admission Nitroglycerin does not have a particular effect in eliminating such pain.
- Headache - tense, often bilateral( only sometimes imitates migraine).Headache often occurs against a background of sharp weather changes, after emotional overstrain.
- Shortness of breath - often triggered by hyperventilation syndrome( deep or frequent breaths, triggered by a sense of lack of air).Dyspnoea may occur even after minimal physical exertion.
- Vegetative dysfunction - manifested by a lump in the throat, excessive sweating, rapid fatigue and morning weakness, unreasonable rise in temperature to 37.0-37.5 ° C, nausea and dizziness. At the same time, vegetative crises are repeated at least once a week, unrelated to situations threatening the patient, and the emotional side of this state is somewhat muffled. Syncope is also extremely rare. Vegetative disorders provoke the development of depressive states and emotional instability( melancholy and gloominess in the morning, anxiety and irritability in the evening).Often, patients complain of specific bodily sensations, which are sometimes perceived as a symptom of another physical illness.
- Interruptions in the work of the heart - the patient periodically notes pushes or heartbeats. In this case, extrasystoles( extraordinary strokes of the heart) and tachycardia( frequency of heart rate increase) are not recorded permanently, but occur during emotional experience, physical exertion or even after drinking coffee.
Mitral valve prolapse 3 degree
Insufficiency in the small circle of the circulation leads to an increase in the load on the right side of the heart. Gradually aggravated already existing symptoms and there are severe signs of insufficiency of a large range: swelling, increased pressure, cyanosis of the skin, insuperable weakness, fibrillation of the atria and enlargement of the liver. Such patients usually receive 1 group of disability.
The prolapse of the mitral valve is dangerous for life at the 3 rd degree of regurgitation: it can develop paroxysmal tachycardia, pulmonary edema, endocarditis and other severe complications, up to sudden death.
Patients with prolapse of the bicuspid valve more often than others suffer from colds, they are often diagnosed with chronic tonsillitis.
- Congenital dysplastic pathology of connective tissue in childhood is indicated by dysplastic changes of the hip joints, flat feet, abdominal hernias.
Mitral valve prolapse during pregnancy
Slight prolapse of the bivalve valve and minor mitral failure is not a contraindication to pregnancy, the child's bearing in this case is normal.
In this case, there may even be a temporary decrease in the deflection of valve flaps due to a physiological increase in the size of the left ventricle. However, systolic murmur and clicks return 1 month after delivery.
Severe degree of regurgitation and prolapse of the mitral valve in pregnancy is more dangerous: the risk of developing paroxysmal tachycardia attacks is significantly increased. During childbirth, rupture of valvular chords is not excluded.
In women with PMK, premature detachment of amniotic fluid and the weakness of labor pains are often recorded. The baby is prone to intrauterine asphyxia and is often born with low weight( hypotrophy).
Treatment of mitral valve prolapse
 Treatment tactics are selected in strict accordance with the degree of prolapse of the bivalve valve, the presence / absence of signs of mitral insufficiency and the complications that have arisen.
Treatment tactics are selected in strict accordance with the degree of prolapse of the bivalve valve, the presence / absence of signs of mitral insufficiency and the complications that have arisen.
1 degree of mitral valve prolapse: restorative measures
With minor changes in the structure of the valves( mitral valve prolapse with regurgitation of 1 degree), absence of constant arrhythmia and other painful symptoms, treatment is not required. A person is recommended to be monitored by a cardiologist once a year and correction of vital principles:
- Refusal from smoking and alcohol, coffee and strong tea;
- Rational nutrition;
- Physical loads, commensurate with the capabilities of the body;
- Education of stress resistance;
- Rational work schedule - rest.
Treatment of PMC and 2 regurgitation regimens
The appearance of painful symptoms of mitral valve prolapse indicates the need for drug therapy. Treatment scheme includes:
- Elimination of heart pain - it is advisable to use sedatives( valerian, sage, hawthorn, St. John's wort, motherwort);
- Therapy of vegetative vascular dystonia - andidepressants( Amitriptyline, Azafen), neuroleptics( Sonopax, Triftazin), tranquilizers( Elenium, Seduxen, Grandaxin);
- Improved metabolism in the myocardium - Riboxin, Picture, coenzyme Q-10, Panangin, vitamins and magnesium preparations( especially effective in mitral prolapse!);
- Restoration of the heart rhythm - Obsidan and other blockers;
- Prophylaxis of infective endocarditis - wide-spectrum antibiotics for every surgical intervention( tooth extraction, tonsillectomy).
Elimination of severe regurgitation with
bivalve valve prolapse. To eliminate the progression of the disease and prevent severe consequences of mitral insufficiency, cardiac glycosides, diuretics, ACE inhibitors( non-hypotensive dose of Captopril - about 0.5 mg / kg of body weight per day - have cardioprotective effect).Simultaneously with drug therapy, a surgical plastic of the bicuspid valve is performed.
Depending on the structural changes cardiosurgeons shorten the valve chords, suturing the valves and ablation of foci of pathological impulse( elimination of arrhythmia).In severe cases, the valve is completely replaced.
The possibilities of modern medicine allow many heart operations to be performed by endovascular( transcatheter) or endoscopic access. To an open operation, cardiac surgeons resort only in extreme cases, for example, with combined vices.
Forecast of
In the absence of mitral failure, the outcome of the disease is usually favorable. It is worth noting that a small deflection of valve flaps in lean people and adolescent children can disappear on their own, while observing a rest regime, adequate physical activity and adequate nutrition.
The patient's health with a severe degree of mitral prolapse and rapid progression of the disease directly depends on the timeliness and adequacy of medical care.