Chlamydial infection is not a rare occurrence in men. Chlamydia develops due to the penetration into the body of the causative agent of infection - chlamydia trachomatis. This causative agent is an intracellular organism of the coccoid type, which most often affects the genital system, although it can be located in other tissues( lymph nodes, respiratory tract, joint and cardiovascular tissues, etc.).
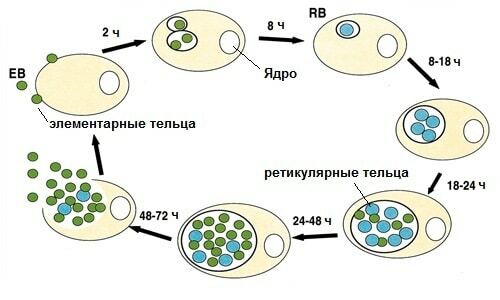
Symptomatic of chlamydiosis
The treachery of chlamydia is the often hidden course of the infectious process. A similar phenomenon is observed in 60% of cases. And sluggish pathology absolutely does not cause male anxiety, because patients do not hurry to a specialist. This is very dangerous, because the specialists managed to find out that the neglected chlamydia infection often becomes a decisive factor in the development of erectile dysfunction.
Characteristic manifestations of chlamydia usually occur within a week or a month after infection. They are as follows:
- Painful urination procedures;
- Sensations of itching, irritation, constant desire to scratch the intimate area;
- Characteristic changes in urine;
- Swelling of the genitals, exit urethra;
- Sensations of soreness in the rectal area;
- Unusual secretions from a hole in the urethra like a translucent substance or purulent mucus.
Gradually, the symptoms decrease, excretions appear only after a night's sleep. Such changes indicate chronicization of the chlamydial infectious process and its deeper penetration into the genitourinary system. When the lesions reach the prostate, there is pain in the perineum and in the anus, radiating into the lumbar region. Sometimes chlamydia penetrate into the testicles, then the scrotum tissues swell, the body temperature rises, the ovarian appendages swell appreciably.
 In addition to the genitourinary system, the lesion can spread to other organs: in the pharynx, rectum, bronchi, joints, pulmonary system, kidneys, etc. When the pathology is neglected, the lesion extends to the prostate gland and provokes spermatogenetic disorders that cause male infertility. That is why the infectious processes of chlamydial origin are very dangerous and require professional adjustment of a specialist.
In addition to the genitourinary system, the lesion can spread to other organs: in the pharynx, rectum, bronchi, joints, pulmonary system, kidneys, etc. When the pathology is neglected, the lesion extends to the prostate gland and provokes spermatogenetic disorders that cause male infertility. That is why the infectious processes of chlamydial origin are very dangerous and require professional adjustment of a specialist.
Approximately half of the cases of chlamydia do not cause any pathological symptoms in patients, which often causes the transmission of infectious agents to the sexual partner. And from the man himself, pathology progressively progresses, reaching erectile dysfunction and infertility. That is why timely diagnosis and therapeutic effects in the case of chlamydia are so important.
Ways of infection and causes of infection
Transmission of infection occurs predominantly through unprotected sex. But it is quite probable and extra-sex pathway of infection, when chlamydia penetrate the body through underwear, towels or hands, stained with infected secretions. Newborns in the presence of infection in the mother in half the cases become infected with chlamydia in the womb or when moving through the birth canal. Usually signs of lesions appear after the appropriate incubation period, which in chlamydial pathogens is on the order of a week or a month.
Chlamydia trachomatis most often penetrates the body through unprotected sexual contact, and the probability of infection from the type of contact is absolutely independent and does not decrease. In other words, infection with the same probability can occur with the traditional method of sexual intercourse, as well as anal or oral sexual contacts.
Usually chlamydia are populated in the urethra, provoking the development of urethritis of chlamydial etiology. This phenomenon is most often caused by casual sex without the use of barrier protection. Urethritis of chlamydial origin is usually accompanied by inflammation of the prostate gland, and in some patients there is also an inflammation of the testes.
Often, urogenital chlamydia manifests epididymitis of chlamydial origin, especially often this is the case with improper or insufficient treatment of chlamydial infection. At times, if the therapeutic measures were delayed or they were not effective enough and full, chlamydial infection leads to the emergence of chronic pyelonephritis.
Danger of the disease and its possible consequences
Chlamydial lesions are very dangerous, because the life of pathogens has many pathogenetic features. First, the infection is difficult to detect and recognize, because the pathogen differs intracellular nature of parasitism. Secondly, chlamydia exist due to the resources of the cell, which subsequently leads to its destruction. Gradually, the pathogens multiply, destroying an increasing number of the patient's cellular structures.
Often the consequences of chlamydial infection are nervous systemic lesions manifested by encephalitis, eye pathologies like conjunctivitis, rectal infection like chlamydial proctitis, as well as damage to the joint tissues, intra-ear structures, genitourinary pathologies, etc.
Approach to the treatment of chlamydial infection
If suspicious symptoms occur,an immediate reference to a specialist. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may need additional information, which he receives from the results of laboratory tests. For this, a scraping study, PCR and enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescence test, etc. are often prescribed.
The approach to the treatment of chlamydial infection is based on the use of drugs that have the ability to penetrate the cell membranes. In addition, antibiotic therapy with the administration of drugs such as Doxycycline or Azithromycin is used. If such agents do not exert the expected therapeutic effect, then antibiotic agents of the fluoroquinolone, tetracycline or macrolide group are administered. A more specific choice is determined by the degree of chlamydial damage. For some drugs, a single dose is enough, others must be taken within a week.
Since the immune defense of the organism is in a depressed state due to the harmful influence of pathogens, the treatment should be supplemented with preparations of immunomodulatory action, vitamins, probiotics or adaptogens. Physiotherapeutic procedures like iontophoresis or ultrasound have a good therapeutic effect. Usually, the full treatment is about a month, after which it is recommended to take repeated tests.
In order to maximize the effectiveness of treatment, several simple rules should be observed:
- Self-treatment is absolutely unacceptable. The therapeutic course should be appointed by a graduate after a thorough diagnosis;
- While the course of therapy lasts, it is necessary to abandon sexual relations;
- The therapeutic effect must be provided simultaneously to two sexual partners;
- There is no single curative program, each drug is prescribed individually to the patient.
If after the course of therapy the chlamydia is again found, then they resort to an additional therapeutic effect. After that, the patient will again have to take control tests for the presence of the pathogen.
Prognosis and preventive measures
In the early stages of infection, treatment predictions are positive. The patient is considered fully recovered, if after a lapse of a month or two from the end of the treatment the tests showed the absence of chlamydia. A neglected disease or self-medication leads to less favorable predictions, since such amateur activity often results in impotence and infertility. The best prevention of chlamydia will be the exclusion of casual sexual intercourse, as well as the observance of intimate hygiene.