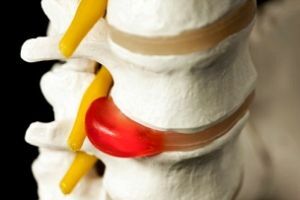
The deforming spinal spondylosis is a chronic disease caused by the degenerative-dystrophic changes of the in intervertebral discs , leading to their extrusion of vertebral bodies beyond the border and the growth of bone tissue.
The deforming spinal spondylosis is a chronic disease caused by the degenerative-dystrophic changes of the in intervertebral discs , leading to their extrusion of vertebral bodies beyond the border and the growth of bone tissue.
As a result, spondylophytes( or osteophytes) are formed, which significantly limit the mobility of the disk.
Specialists consider spondylosis to be the next stage of osteochondrosis.
Contents of the article
- The development of the disease
- The causes that trigger the development of the pathology
- General clinical picture
- Types and symptoms of the disease
- Cervical spondylosis
- Spondylosis of the thoracic department
- Lumbar type of deforming spondylosis
- Complex diagnosis of the disease
- Aims and methods of treatment of the disease
- A visual video about the changes of the spinewith the development of spondylosis
Development of the disease
Deforming spondylosis is the result of a violation of the processes ofmena in the fibrous ring of intervertebral discs( it surrounds the pulpous nucleus) and along the longitudinal spine along the spine.
At , the early stage of , spondylosis develops as a compensatory response of the body with increased stress on the vertebral bodies. Changes occur in the areas of maximum overload. Compensatory overgrowth of bone tissue helps to reduce the degree of adverse effects. At the same time, there is a spasm of muscle fibers surrounding the affected area.
Prolonged loads lead to the transition of the compensatory reaction to the pathological stage, as a result of which the area of contact gradually increases, the bone tissue turns into a kind of "skirt" - sometimes of enormous dimensions. At the of this stage , the longitudinal anterior ligament of the spine is often involved in the pathological process. Spondylophytes can squeeze the nerve roots that depart from a certain segment of the spinal cord, and even spread to the substance of the spinal cord or its membranes.
Simultaneously, the structure of the affected disc changes as a result of its dehydration( fluid loss), resulting in the disc's height decreasing, which leads to an increase in the severity of the clinic. Progression of the disease provokes the development of intervertebral hernia. At this stage, the disc is spread out between the vertebrae, and its cartilaginous tissue is squeezed out beyond the surface of the vertebral body.
 The more dangerous the most common deforming spondylosis of the cervical spine you can find out from our clarifying article.
The more dangerous the most common deforming spondylosis of the cervical spine you can find out from our clarifying article.
Worried about lumbar pain? One of the possible causes is spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine. Learn how to identify the disease here.
Reasons that trigger the development of
pathology The main difference between spondylosis and osteochondrosis is the defeat of the outer part of the disc. In osteochondrosis, dystrophic changes begin with the pulpous part.
The development of spine disease in spondylosis is associated with by a number of factors of ( internal and external):
- metabolic disorders;
- age-related changes;
- irrational load on the spinal column, which provokes persistent muscle spasms;
- direct and indirect injuries of a traumatic nature affecting the ligaments and muscles of the spine;
- with static load on the spinal column( for example, with prolonged stay in physiologically inappropriate position;
- with short-term stress of the surrounding spine of muscle fibers with pronounced hypodynamia;
- with genetic or constitutional predisposition;
- with infectious diseases;
- with the presence of tumors.
The general clinical picture of
The most common symptomspondylosis is pain :
- at an early stage, it is unstable, often appears during movement, increases during the day, can spontaneously disappear;
- the intensity of pain increases due to sudden movements or changes in the weather;
- , depending on the area of the lesion, it can irradiate into the lower or upper limbs;
- palpation of spinous processes and effleurage on them provoke an increase in pain( which distinguishes spondylosis from osteochondrosis).
As the pathological process progresses to a certain extent( depending on the severity of the disease), the mobility of the spine in a particular department is limited.
The types and symptoms of the disease
The specific localization of dystrophic changes is the basis for the division of pathology into three types of :
- spondylosis of the cervical spine;
- spondylosis of the thoracic spine;
- spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine.
The clinical picture varies to a certain extent depending on the particular species.
Cervical spondylosis
This variety is considered the most common. Its main symptoms of are:
- pains in the back of the neck and occiput, amplifying when the head moves;
- pain can spread to the shoulders, shoulder blades, hands;
- limited movement in the cervical region;
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- decreased vision and hearing;
- ringing and tinnitus;
- sleep disturbance( mainly due to the presence of pain syndrome).
Chest spondylosis
Breast infection is the most common type of this pathology. Its cause is most often a sedentary lifestyle, so the disease is mostly diagnosed in people of intellectual professions. Its main manifestations of :
- are unilateral pains with localization in the middle and lower divisions, often extending to the thorax;
- increased intensity of pain during extension, lateral inclinations;
- disruption of normal functioning of internal organs.
Lumbar type of deforming spondylosis 
This variety is second only to cervical in terms of its prevalence, which is caused by the considerable load to which the lumbar region is subjected. Basically, the fourth and fifth vertebrae are affected.
With simultaneous appearance with osteochondrosis, lumbar spondylosis often leads to pinching of the nerve roots and manifestation of sciatica in the lumbar region.
In this type of disease, the following clinical picture of develops:
- signs of nerve fiber damage and manifestation of radicular syndrome;
- symptoms of the inflammatory process in the lumbosacral plexus;
- weakness of the lower limbs;
- pain in the legs, leading to false intermittent claudication;
- pain does not disappear in a state of physical rest;
- often irradiates to the lower extremities( thigh and lower leg) or buttocks;
- may reduce sensitivity or numbness of the legs;
- pain syndrome is reduced with anterior tilt and climbing stairs, as in these cases the area of the affected disc is increased.
Integrated Diagnosis of
Disease Diagnosis is based on:
- Neurological comprehensive examination of patient.
- Radiography of the spine , with which it is possible to visualize osteophytes, assess the condition of the vertebrae, the degree of thickening of the joints and the reduction of the distance between adjacent vertebrae. And also to detect the displacement and pathological mobility of the parts of the spine, its individual elements with an extreme degree of extension and flexion.
- Computed tomography( CT) allows to obtain a detailed image of the spine, to detect narrowing( stenosis) of the canal, its degree, to determine the height of intervertebral discs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging( MRI) is the most informative method of research, as it allows visualization of soft tissues( discs, nerves, ligaments) and detection of compression of nerve fibers. In most cases, it is through this method that one can find the true cause of pain syndrome in spondylosis.
- Electroneuromyography( ENMG) - is assigned to confirm the presence of nerve damage. The method allows to determine the conduction disturbance and the specific degree of fiber damage.
- Radioisotope scanning - is based on the difference in the degree of absorption by tissues with different metabolic rate of radioactive material. In the case of an inflammatory process or a tumor, a larger quantity of isotope accumulates in a specific area of bone tissue.
Objectives and methods of treatment of the disease
 The spontaneous degenerative processes are irreversible, therefore the general goal of treating for all types of spondylosis( thoracic, cervical and lumbar spine):
The spontaneous degenerative processes are irreversible, therefore the general goal of treating for all types of spondylosis( thoracic, cervical and lumbar spine):
- elimination of pain and inflammation;
- removal of muscle spasm;
- improved local circulation and nutrition drives;
- normalization of metabolic processes and slowing of dystrophic changes in affected tissues.
The following methods of spinal spondylosis treatment are used:
1. Medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs( NSAIDs) for pain relief( novalis, ibuprofen, naproxen);
- muscle relaxants - to relieve muscle spasms( tizanidine, cyclobenzaprine);
- analgesics - to eliminate severe pain( tramadol or narcotic drugs);
- antidepressants - for the elimination of chronic pain( doxepin, amitriptyline, duloxetine, containing capsaicin ointment).
2. Physiotherapy reduces pain syndrome, improves conduction of nerve fibers, local metabolism and circulation. The following procedures are used:
- ultrasound effect on the affected spine;
- electrophoresis with novocaine;
- diadynamic currents;
- LFK for strengthening the muscular backbone.
3. Tibetan Medicine offers to treat spondylosis by:
- acupuncture;
- acupressure;
- of moxotherapy;
- Magnetic-Vacuum Therapy;
- massage;
- stone therapy.
4 . Introduction of steroids in trigger points , epidural space, joints significantly reduces pain.
5. The operation is assigned to :
- in the presence of spinal stenosis;
- with the development of horse tail syndrome;
- with a significant compression of the nerve root with an osteophyte.