The pancreas is an organ that participates in the digestive system and has a dual functional feature. The organ is divided into a head, body and tail. Pancreas located behind the stomach in the abdominal cavity, closely adjacent to the duodenum.
The length of the organ of an adult varies between 14-22 cm, and the mass is approximately 70-80 g. If we consider the structure, it can be noted that the gland has an alveolar-tubular characteristic. The connective tissue capsule covers the surface of the organ, and between the lobules of the basic substance there are connective tissue strands in which there are vessels, excretory ducts, lamellar bodies, nerves and nerve ganglia.
What role does the pancreas have in the human body?
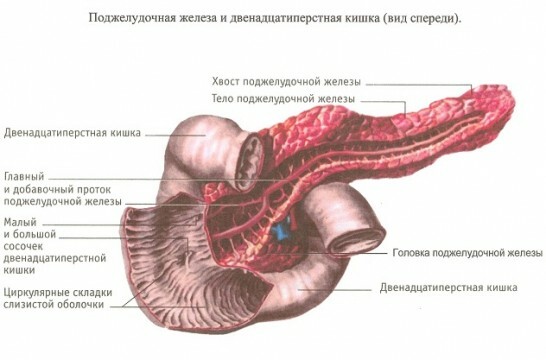
This body has the functions of internal and external secretion. For the body, the meaning of the gland is to provide the digestive tract with enzymes( enzymes) that can break down fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Every day it releases up to 1 liter of pancreatic juice, activating a chain of chemical reactions and thereby ensuring normal physiological functioning of the body.
Exocrine functions are important in that the beta-cell produces an important insulin hormone, as well as its antagonist - glucagon, which is produced by alpha cells. All this occurs in the pancreas between the lobules, which do not have excretory ducts, called in the islets of Langerhans.
Insulin is responsible for the regulation and normalization of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, causing the distribution of glucose across all tissues and muscles, thus ensuring stable blood sugar values. Glucagon, on the contrary, increases the level of sugar in a critical decline and participates in the production of liposin, which prevents fatty degeneration of the liver.
Diseases of the pancreas
As can be seen above, this organ occupies the most important place in the regulation of the vital activity of the body. Unfortunately, the stably adjusted work of the pancreas sometimes carries with it some malfunctions, in which pathological disturbances that are transformed into the development of various diseases are observed. For example, the destruction of beta cells leads to a reduction or complete cessation of insulin production and the development of diabetes mellitus. Unhealthy lifestyle, transferred operations, poisoning, etc.can cause disturbances in the development of enzymes, and as a consequence, the appearance of pancreatitis.
In addition, the cause may be and concomitant diseases. Here for a complete perception of the picture can be attributed to the diseases of the gallbladder, so to say "nearest neighbor" of the pancreas. In this case, problems with this organ, namely the presence of stones in combination with pancreatitis causes such complications as cholecystopancreatitis. Therefore, the appearance of stones should not be left without attention, since this is the first and main cause of this complication. Pancreatitis caused by gallbladder disease accounts for 50% of all pancreatic inflammation statistics. And if everything is clear with respect to the large gall bladder stones, they cause bedsores of tissues or organ rupture, then the small ones are "insidious by their nature".They can penetrate the bile ducts, causing severe attacks of cholecystopancreatitis.
In addition to the listed diseases of the pancreas, there are also such organ disorders as cystic fibrosis, pancreatic necrosis( complication of pancreatitis with possible organ atrophy) and tumor-like neoplasms.
Clinical picture of
Everyone has long known that the human body is, so to speak, a complex machine where everything is so interconnected that the violation of one function or its atrophy leads to another complication and so on along the chain. Suppose, with diabetes it is possible to disturb the digestive system and the occurrence of pancreatitis. Pancreatitis, in turn, gives a large percentage of statistics on the etiology of the formation of cancerous tumors.
Since acute or chronic pancreatitis is the most common inflammatory organ disorder, it would be prudent, by its example, to consider which first signs of pancreatic disease begin to determine pancreatitis in time and to prevent the most severe form of complication-oncology.
Symptoms of pancreatic disease are the same in both women and men. If we divide them according to the nature of the manifestation, then we can distinguish such groups:
- dyspepsia;
- painful manifestations;
- changes on the skin;
- "special" symptoms.
Dyspeptic signs

In adults and children, the very concept of dyspepsia is expressed in the disorder of the digestive system. The cause of impaired pancreatic function and the appearance of these symptoms may be improper nutrition or taking certain medications( sulfonamides, antibiotics, azathioprine, nirofurans, etc.).In addition, this group of clinical manifestations has the property to appear at the very beginning of the disease.
Pathology begins with a violation of appetite. The patient is disturbed by a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, even if a small portion is eaten. Further, a man or woman has a feeling of nausea. This is due to the irritation of the vagus nerve, which innervates the gland. In connection with the resulting intoxication, after vomiting begins vomiting, not bringing relief, and in the vomit masses there is a feeling of bitterness( vomiting of bile).
Nausea and vomiting can cause dehydration, in which there is rapid breathing and thirst. The severity of these symptoms will depend on the degree of dehydration. Further, because of a disturbance in water balance and inadequate production of enzymes, a disorder of the stool is seen in the patient. Here you can observe bloating, where a series of constipation is replaced by a manifestation of diarrhea.
Pain manifestations of
One of the leading signs of pancreatic disease is pain syndrome. It is associated with a dysfunction of the organ, which is characterized by dystrophic and inflammatory changes. Pain sensations can go far beyond the anatomical location of the gland and can be associated with the occurrence of gallstones.
The intensity of the pain syndrome may depend on the degree of inflammation, compression, the presence of swelling and the duration of the disease. The nature of manifestations is expressed in the development of severe pain localized in the upper abdomen with possible irradiation in the left hypochondrium. Pain cramps can be so severe that the patient takes a forced position with bent knees, with a marked palpitation and a release of cold sticky sweat. The appearance of these symptoms is usually accompanied by a meal, after which the pain syndrome begins in half an hour. It is worth noting that the disappearance of this group of clinical manifestations is a very bad phenomenon, becauseAt this stage, atrophy of most of the gland may have occurred.
Changes in the skin
The process of skin problems occurs most often with chronic pancreatitis. Especially if the manifestation is long and sluggish. In this case, there is a violation of the release of pancreatic juice into the duodenum, whose role is to neutralize the acidic gastric environment.
Further, there is a disruption in the activity of enzymes in the lumen of the intestine, the bactericidal properties of the intestinal flora are reduced, and as a result, the bacteria grow rapidly. These bacteria break the permeability of the protective barrier of the intestine and cause food or microbial allergies. These allergic reactions are expressed in the form of rashes on the skin, something similar to atopic dermatitis.
Because the edematous pancreas squeezes the bile ducts, the skin can become icteric or pale.
"Special" Symptoms of
| The name of the | symptom |
| expresses the Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom | During the test, a palpation and pressure is applied to the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. When you take your fingers from the skin of the patient, there is a symptom of irritation of the peritoneum( strengthening of the pain syndrome when the hand is pulled). |
| Gray-Turner symptom | Cyanosis is observed in the lateral abdomen on both sides, the development of which is due to abnormal circulation of the abdominal cavity. |
| symptom Lagerlof | As a result of intoxication of the respiratory tract, the patient has blue-toed nasolabial triangle and fingers. |
| symptom Mayo-Robson | When palpation of the vertebral-rib corner on the left side, its soreness is observed. |
| symptom of Grunwald | Appearance of bruises around and around the umbilical region. |
| symptom Chukhrienko | Tangent movements of the hand in the area of the epigastrium will cause soreness in the patient. |
| symptom Dudkevich | The meaning of the medical check is to install the doctor's arm 2 cm below the navel. When you move your hand as if inward and obliquely up the patient experiences painful sensations. |
Other diseases and their clinical manifestations
Not always a pancreatic function disorder is accompanied by the development of pancreatitis. The appearance of any other pathological organ disorders can be characterized by the presence of such symptoms:
- Cystic fibrosis. There are cramping pains resembling spasm and walking along the bowels, while the patient has an appetite, and the resulting diarrhea exceeds the norm of secrete diurnal stool several times. Also worth noting weakness in the muscles, dry mouth and salt deposition on the skin.
- Pancreatic necrosis. A toxic or pain shock is experienced, preceded by a loose stool and severe pain syndrome located behind the sternum or in the area of the epigastrium and radiating into the collarbone or back. The pain can be so strong that the patient can lose consciousness.
- Diabetes mellitus. For diabetes mellitus, clinical manifestations are characteristic of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. As a rule, there is no pain syndrome. And of dyspeptic symptoms, one can note a feeling of hunger and weakness in hypoglycemia, as well as nausea, vomiting, rapid heartbeat, loss of consciousness in the hyperglycemic state. And in that, and in another case at refusal of the help the patient can fall into a coma.
- Pancreatic tumor. The pain syndrome is unstable and can be localized in the area of the tumor location. The intensity depends on the stage of the cancer and can be similar to the pain manifestation of pancreatitis. The patient is characterized by a decrease in appetite, weight loss and bloating. With the transition to the later stages of cancer, dyspepsia symptoms intensify.



