Epidemiology and prevalence of
Acute cystitis is mainly caused by women due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure of the urinary tract( smaller urethra with respect to the male). Acute cystitis in women usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Acute cystitis in men occurs hundreds of times less. For a year in Russia an acute cystitis is ill about 30 million people.
Acute cystitis is not a contagious disease.
Causes of acute cystitis
Acute and chronic cystitis in the vast majority of cases cause microorganisms, which in large numbers normally live in the human intestine( intestinal infection).Due to poor hygiene, over-cooling, various medical manipulations, this infection enters the urinary tract.
From the intestinal microflora of acute cystitis most often cause:
- E. coli;
- staphylococci;
- protey;
- klibsiel and others.
In addition, some pathogens of specific diseases can lead to acute and chronic cystitis:
- mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- pale treponema( syphilis).
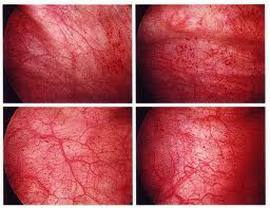 Cystitis can also cause some parasites( eg, schistosomiasis of the bladder).
Cystitis can also cause some parasites( eg, schistosomiasis of the bladder).
Etiology of cystitis can be not only bacterial and parasitic infections. Also to this pathological condition may result:
- thermal damage;
- chemical( toxic, medicinal) substances;
- bladder injury, including when performing various medical procedures, such as cystoscopy and bladder catheterization.
- bladder stones can form bedsores and lead to cyst;
- tumor of the bladder;
- any stasis of urine in the bladder due to prostate adenoma, prostatitis, polyp, etc.;
- , radioactive radiation leads to the death of epithelial cells and the sloughing of the epithelium, which leads to this pathology( radiation cystitis).
In addition to the causes of cystitis, there are also predisposing factors to it:
- poor hygiene of the pelvic organs;
- factors of fashion, among which one can distinguish the wearing of light and open clothes in the cool or cold time( short skirts, bare stomach contribute to the reduction of local immunity in the genitourinary system, which contributes to the development of not only cystitis, but also pyelonephritis);
- pregnancy;
- excessive sexual activity;
- use of spermicidal drugs as contraceptives;
- diabetes mellitus and other metabolic diseases.
Classification of cystitis
For the cause of cystitis:
- is infectious( including acute bacterial cystitis);
- is parasitic;
- chemical;
- beam;
- is traumatic;
- thermal;
- toxic;
- medicinal;
- exchange;
- is allergic;
- is neurogenic.
 Downstream, cystitis can be:
Downstream, cystitis can be:
- acute;
- chronic( more than 2 exacerbations in 6 months).
According to the primacy, cystitis is divided into:
- primary( arise independently without regard to other diseases);
- secondary( arise due to another disease).
According to the morphological changes in the mucosa of the bladder, there are:
- acute catarrhal cystitis;
- acute hemorrhagic cystitis;
- acute ulcerative cystitis.
In acute catarrhal cystitis, the lesion of the mucosal wall of the bladder is in its upper layers .Outwardly it looks hyperemic( full-blooded, reddened) and edematous. This is the easiest and most frequent variant of acute cystitis.
With hemorrhagic cystitis, there is further damage to the mucosa to the depth of the vessels that supply the bladder to the .As a result, blood appears in the urine, and in the body, anemia can develop sooner or later. Such an acute cystitis with blood in the urine requires more serious treatment.
Acute ulcerative( or necrotic) cystitis is characterized by the presence of ulcers in the wall of the bladder. Ulcers with this cystitis look like a deep mucosal damage up to the muscle layer of the bladder.
Also in a separate group are:
- acute cystitis in children;
- acute cystitis in pregnancy.
Symptoms of acute cystitis
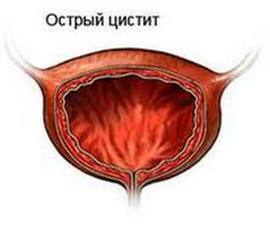 Symptoms of acute cystitis may be as follows:
Symptoms of acute cystitis may be as follows:
- dysuric phenomena( frequent, painful and difficult urination);
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- high body temperature;
- changes the color of urine( blood or pus in urine).
With an acute attack of cystitis, these symptoms are present for 6-8 days, after which they should disappear. If within 6 months acute cystitis occurs 2 or more times, the question arises of conducting additional diagnostics to identify chronic cystitis.
Treatment of acute cystitis
Treatment of acute cystitis is a complex and demanding task. The goal of this treatment is early relief of all symptoms, prevention of complications and the transition of acute cystitis to chronic. Therefore, one should not treat this problem negligently and try to cure yourself. On how to cure acute cystitis by all the rules and international recommendations, the attending physician with extensive experience in the treatment of this and other pathologies knows.
What should I do for acute cystitis?
First and foremost, you need to see a doctor. Acute cystitis is treated by a urologist or gynecologist. It is in his competence to treat this disease. Other doctors can be consultants and "advisers", but the last word is always for the attending physician.
Your doctor should find out the information you need for further diagnosis and treatment. He will ask you when the first symptoms of the disease appeared, for the first time whether there was such a disease, what were and are the symptoms, what were treated and much more.
After finding out the necessary information that is entered in the medical history, acute cystitis must be diagnosed in order to determine treatment and exclude other diseases.
Diagnosis of acute cystitis
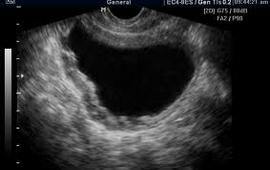 For the diagnosis of acute cystitis, a number of laboratory and instrumental examination methods are needed:
For the diagnosis of acute cystitis, a number of laboratory and instrumental examination methods are needed:
- total blood test;
- general urinalysis;
- bacteriological analysis of urine( urine culture) with the determination of the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibacterial drugs;
- ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- excretory urography and cystography;
- in some cases it is necessary to perform cystoscopy.
After diagnosis of acute cystitis, the doctor issues a complete and detailed diagnosis of the disease and approves a particular treatment strategy.
How to treat acute cystitis?
Treatment of acute cystitis depends on its cause, shape, clinical manifestations and other features of the disease and the patient himself. Treatment of acute cystitis in women and men has no fundamental differences.
Diet for acute cystitis
Any treatment will begin with a diet. Proper nutrition provides the necessary body resources( proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals) for better and complete regeneration of damaged epithelial tissues. Diet in acute cystitis is especially important in the presence of metabolic disorders in the body( diabetes, urolithiasis, gout, etc.)
But there are some general rules for the treatment of all types of cystitis.
Abundant drink. You need to drink at least 2-2.5 liters of fluid per day. Thus, the urine will wash out the excessive concentration of harmful substances from the bladder. However, do not drink any drinks. Alcohol is contraindicated in any quantities, as well as sweet drinks and various lemonades. It is best to drink black or green tea, fruit and vegetable juices, and berries. Juicy cowberry juice is very useful because it is a natural uroseptic that destroys bacteria in the urinary tract.
Vegetable products. Vegetables and fruits have the property of alkalinizing urine, thus changing the habitual acidic environment of pathogenic bacteria in an unfavorable direction. In parallel with this, it is necessary to exclude from the diet acute, salty, smoked food, which can lead to an increase in the specific gravity of urine( concentration).
Etiotropic treatment of acute cystitis
 This type of treatment implies an immediate impact on the cause of the disease. Without the elimination of the cause, other types of treatment will be ineffective.
This type of treatment implies an immediate impact on the cause of the disease. Without the elimination of the cause, other types of treatment will be ineffective.
In the case of bacterial acute cystitis, etiotropic treatment will be treated with antibacterial drugs. For this purpose, use special antibiotics, acting primarily on the organs of the urinary system( ie, which are excreted by the kidneys, and not through the liver and intestines).
The main representatives of these antibiotics are:
- 5-NOC;
- fluoroquinolones( ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, etc.);
- is monastic.
In radiation cystitis, it is necessary to eliminate radiation( radioactive) effects on the bladder, for allergic - allergen, toxic - toxin and so on. All this will be etiotropic treatment.
Symptomatic treatment
First aid for acute cystitis may be required in the event of intense pain in the lower abdomen. Fight this pain should be with the help of painkillers, which in recent years is becoming more and more. In the case of acute cystitis, preference is given to the analgesics of the antispasmodic group, since the pain itself arises from the spasm of the smooth muscles of the bladder.
Help with acute cystitis in this situation is possible with the help of the following drugs:
- papaverine;
- drotaverin( no-shpa);
- atropine ( being holinolitikom, it indirectly removes the spasm of smooth muscles due to impaired transmission of the nerve impulse at the level of the myoneural synapses).
But before you remove an acute attack of cystitis with these drugs, you should read the instructions for their use( contraindications ).
Treatment of acute hemorrhagic cystitis
Treatment of acute hemorrhagic cystitis should be performed in a hospital, since with this type of cystitis complications in the form of iron-deficiency anemia and urinary tract obstruction with a blood clot with acute urinary retention are possible. In addition, blood in the urine may appear in other diseases, such as:
- trauma to the organs of the urination;
- tumor of the kidney, ureter and bladder;
- stones kidney and bladder.
All this requires additional observation, diagnosis and more complex treatment, which can be obtained only in a hospital.
After passing all the additional examination methods, the patient is treated.
If hemorrhagic cystitis is caused by bacteria, then antibiotics are prescribed( eg monomial once or ciprofloxacin 400 mg twice a day for 3 days).
With pains in the lower abdomen using antispasmodics.
In iron-deficient anemia, is an iron supplement( Ferum-Lek, Sorbifer, etc., 100 mg per day).
To reduce blood loss, use drugs that reduce bleeding:
- vitamins C and K( Vikasol, Askarutin, etc.);
- calcium supporates( calcium gluconate, calcium chloride);
- etamzilate;
- alpha-aminocaproic acid 5%;
- tranexamic acid.
Prevention of acute cystitis
The following recommendations can serve as measures for both primary and secondary prevention:
- careful observance of personal hygiene;
- avoidance of over-cooling of the pelvic organs;
- timely treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease;
- prevention of urolithiasis;
- optimum water load( to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day);
- Milk and vegetable diet.
Video: Cystitis in women. Prevention and treatment of cystitis
 Acute cystitis is a disease characterized by the appearance of inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
Acute cystitis is a disease characterized by the appearance of inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane of the bladder.



