 Japanese encephalitis is an infectious disease that has a transmissible transmission pathway. The disease is also called mosquito encephalitis.
Japanese encephalitis is an infectious disease that has a transmissible transmission pathway. The disease is also called mosquito encephalitis.
This name is not accidental: dangerous neurotropic viruses are transmitted by mosquitoes. When infected, the brain and its membranes are affected.
The disease is seasonal in nature. Its outbreaks are observed during the appearance of new individuals of mosquitoes. The disease affects not only people, but also some animals: white mice, monkeys, horses, cows, goats, sheep.
Contents of
- Contents of
- History of discovery and study of
- Causes and sources of disease occurrence
- Pathogenesis of disease
- Symptomatic and developmental stages of the disease
- From infection to stroke in the brain 4 days
- Disease and exacerbation
- Reconvalence period
- Diagnosis methods
- Treatment of disease
- Vaccination of population
- Forecast disappointing
The history of discovery and study of
The disease has a century-long history of origin. It was first discovered in Japan in 1924, when a large number of people died from an infectious outbreak. Of the 7,000 infected, only 20% were able to survive.
After the studies conducted by Japanese scientists, the diagnosis was approved - Japanese encephalitis. Later it was called summer, encephalitis B, mosquito and autumn mosquito encephalitis. 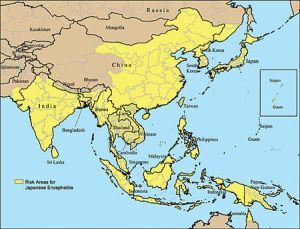
The final name for a complex neuroinfection was fixed in the form of the term "Japanese encephalitis".
After revealing the ability of encephalitis to arise in different foci of nature, the scientists concluded that it spread not only in Japan, but also in the Pacific countries.
Also in the risk zone were residents of Russia: in 1938 it was described by Russian researchers in the territory of the Southern Primorye.
Causes and sources of the disease
In the 30 years of the 20th century, the causative agent of Japanese encephalitis was first detected. The virus is included in group B of filtering neurotropic arboviruses. It has special properties.
- , despite its small size( no more than 22 mmK), it has an increased degree of resistance to environmental influences;
- at boiling the virus dies not earlier than after 2 hours;
- when exposed to alcohol, ether and acetone, the effect of oppression of the virus is observed after 3 days;
- cold has no effect, the virus can stay in a state of negative temperatures up to 395 days.
Among the sources of infection can be identified:
- waterfowl - the main source;
- rodents;
- pigs and horses - in anthropurgical foci;
- of domesticated birds;
- of bats is a reservoir in the interepidemic period.
Children under the age of 10 fall into the main risk group for the onset of the disease. The virus for pregnant women is especially dangerous. It can lead to miscarriage in the 1st and 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
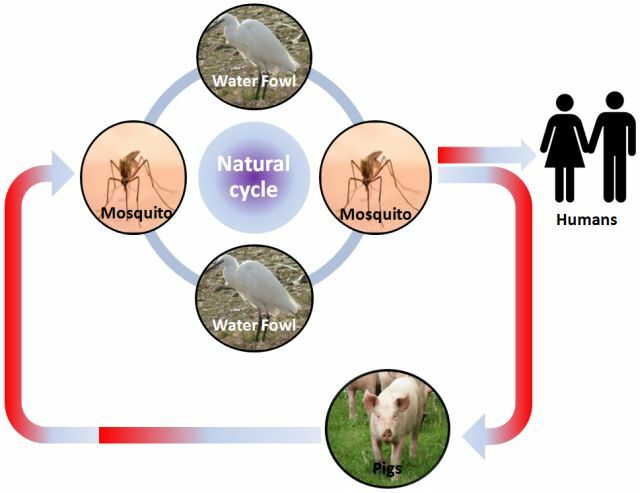
Transmission of encephalitis virus
Pathogenesis of disease
A person is infected with encephalitis by biting mosquito species Culex pipiens, Culex trithaeniorhynchus, Aedes togoi, Aedes japonicus. Insects can keep the virus in their body for about 3 months. The exacerbation of the disease occurs at the time of the fertility period of the insect females.
Infection occurs mainly in places where moisture is increased. Most often these are wetlands. Also, there is an infection of the body in the evening in parks, in open areas with a large crowd of people. The development of the disease can be affected by:
- general human condition;
- the rate of occurrence of the reaction of resistance of the organism;
- the amount of the virus caught in the blood;
- virulence and strain properties of the virus.
 The causative agent can spread during the hematogenous and neural path. At an elevated body temperature, the virus can attack more strongly.
The causative agent can spread during the hematogenous and neural path. At an elevated body temperature, the virus can attack more strongly.
Crossing the blood-brain barrier, a viral infection affects the parenchyma of the brain. In this area, it is actively multiplying.
During severe manifestations of the disease, the virus reproduces in the nervous system, as well as outside it. At the time of its entry into the brain, the peak of the disease is noted. In the course of the lesion, neurons die, swelling of the vessels and proliferation of glia occur.
Symptoms and stages of the development of the disease
The development of the disease involves several periods. In the incubation period, which lasts from 4 to 21 days, the presence of a virus in the body is detected. Further, the disease has several stages of flow.
From infection to stroke in the brain 4 days
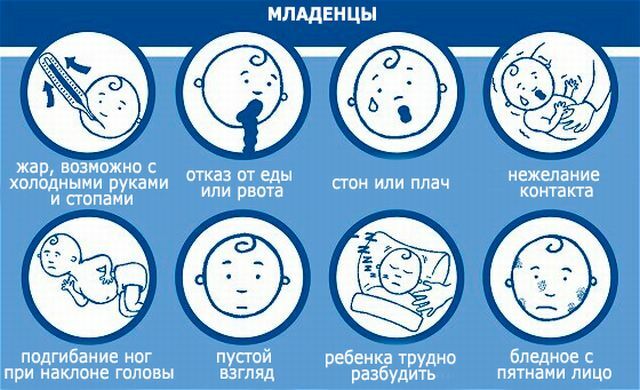
In the first 4 days a person experiences a sharp rise in body temperature( up to 39-41 ° C).The period of hyperthermia lasts about 10 days. There are also symptoms of acute development of the disease:
- chills;

- headache( especially in the frontal part);
- lumbar pain;
- pain in the abdomen, limbs;
- signs of nausea, vomiting.
There is hyperemia of the face, sclera, upper chest. Increases sweating rights. Pulse may increase to 140 beats per minute. The pressure in this case is significantly increased, and the peripheral capillaries may be narrowed.
Strengthened muscle tone of the whole body is noted. Oculomotor muscles work in an impaired mode.
Acceleration of the disease and exacerbation of
At the height of the disease, on day 4, foci of brain damage are detected. A man is diagnosed with a meningeal syndrome. Consciousness is broken, sometimes coma comes. Among mental disorders, there is a delirious status, delirium, hallucinations.
During this period the patient is forced to lie in a recumbent position due to the increased muscle tone, which is extrapyramidal and pyramidal in nature.
There are often postures on the back, on the side with the head thrown back, bending arms and legs. Hypertension of the muscles affects the chewing and occipital parts.
If a deep lesion of the pyramidal system is observed, then spastic hemiparesis, monoparesis, and paralysis appear.
 Choreiform hyperkinesis of facial muscles and upper limbs, paresis of the facial nerve in the central part with asymmetric arrangement of nasolabial folds may appear.
Choreiform hyperkinesis of facial muscles and upper limbs, paresis of the facial nerve in the central part with asymmetric arrangement of nasolabial folds may appear.
The acute period is characterized by hyperemia of the optic discs. Sometimes there may be a hemorrhage and swelling. The patient runs the risk of losing the ability to distinguish colors, respond to light. Also, the field of vision is significantly narrowed. During this period, symptoms of bronchitis, pneumonia may appear.
Reconvalescence period
The period of convalescence lasts from 4 to 7 weeks. The temperature is normalized or in the subfebrile stage. Residual lesions of the brain may persist.
Among them are:
- hemiparesis;
- coordination disorder;
- weakness in the muscles;
- is a mental disorder.
Methods for diagnosing
The first signal for the diagnosis should be to find a person during an epidemic in an area that is a zone of risk. If at that time a person was bitten by a mosquito, then the diagnosis should be carried out immediately.
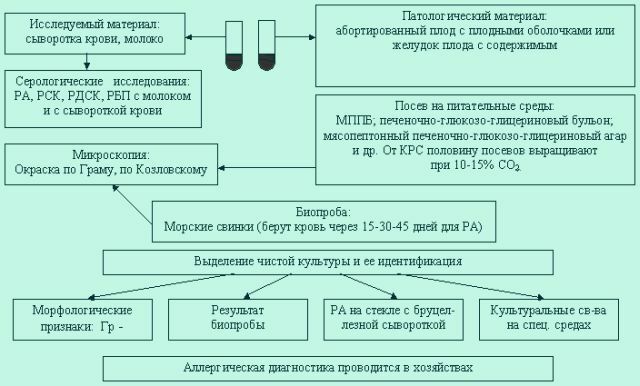
A reliable method of detecting infection is the analysis of blood serum. It notes the presence of specific antibodies. The most effective is the study of paired sera.
The first test is taken at the very beginning of the onset of the disease, and the second - 3-4 weeks later. By the end of the first week you can observe the reaction of the body. The titles increase with time. A positive result is an increase in titres by a factor of four.
In addition to this type of diagnosis, the hemagglutination suppression and neutralization reaction can be used. The PCR method is also used.
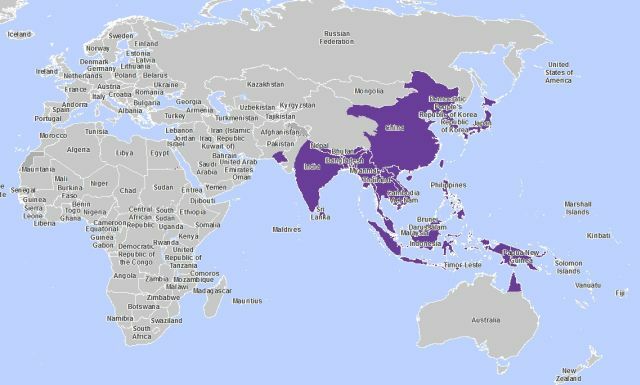
The area affected by Japanese mosquito encephalitis
Treatment of disease
In the course of specific therapy, which is carried out during the period of fever, the patient is injected with an immunoglobulin( 3-6 ml 3 times a day) or blood serum of recovolentents( 20-30 ml).
Also positive dynamics is observed with intramuscular or intravenous injection of hypermun horse serum  ( 15-20 ml) in the first week after infection.
( 15-20 ml) in the first week after infection.
In pathogenetic therapy, the patient is prescribed diuretics and detoxifying agents. Also, treatment involves the use of corticosteroids, sedatives and remedies for the elimination of convulsive syndrome.
If a patient has a violation of respiratory function, cardiovascular activity, then resuscitation is carried out. Treatment is conducted under the supervision of a neurologist and psychiatrist.
Vaccination of the population
The fight against the manifestations of Japanese encephalitis is possible through vaccination-vaccination of the population. It is shown mainly to residents of endemic areas, as well as to tourists traveling to regions where an outbreak is observed.

Vaccine
If an adult lives in a hazardous area, he is often not vaccinated. It is necessarily shown to children.
The vaccine lasts for 3 years. The vaccination is done from the moment of the onset of the one-year-old age. During the vaccination, 3 doses are administered on schedule 0-7-30.
With the accelerated regimen, the last inoculation can be done one week after the second. Revaccination should be carried out after 2-3 years.
When leaving for dangerous endemic areas, it is necessary to take care of vaccination in advance. It is necessary to vaccinate at least two weeks before departure. Vaccination against pregnant women and allergies is contraindicated.
Forecast disappointing
When infecting with mosquito encephalitis in 24-42% of children from 5 to 9 years and adults over 65 years there is a lethal outcome. The older the patient and the heavier form of the disease, the risk of fatal outcome increases.
With the transferred disease, a person may have mental disorders, mental and speech disorders, emotional lability, decreased motor ability, paresis, paralysis, hyperkinesia.