If you do not pay proper attention to diabetes and do not take prescribed medications, then the course of the disease can become unpredictable. As a result of metabolic disorders and changes in vascular blood circulation, diabetic angiopathy may occur. This rather serious complication is manifested by acute pain in the lower extremities and tissue atrophy. Such a problem requires immediate treatment and preventive procedures to prevent negative consequences. In order to timely diagnose the disease, you need to understand the symptoms of angiopathy.
Symptoms of the disease
The development of angiopathy occurs against a background of narrowing of arterial vessels. Depending on the location of the source of the disease, diabetic angiopathy of the lower extremities( ICD code 10) can be diagnosed by the following symptoms:
- Reduced brain activity;
- Visual impairment;
- Problems in the work of the heart muscle.
It is very important to establish the right treatment in an accurate diagnosis. Otherwise, diabetic angiopathy of the vessels of the lower limbs can result in gangrene. The development of the disease can also indicate other factors:
- The presence of blood in the urine;
- Dryness and flaking of the skin of the feet;
- Quite frequent bleeding from the nose;
- Sudden pain, resulting from prolonged walking, which disappears after a short rest;
- Bloody discharge in sputum;
- Periodic itching of the lower limbs;
- On the skin of the legs appear fun.
If you find these symptoms, you need to see a doctor immediately for additional diagnosis of the disease.
Diagnosis methods
Primary diagnosis is based on the study of patient complaints. In the presence of serious symptoms, the doctor may order the following examinations:
- Tomographic examination of the problem area;
- Ultrasound Doppler study of blood flow and vascular walls;
- Blood test;
- X-ray examination of the permeability of vessels;
- Inspection of the choroid of the eyes for the detection of hemorrhages and the analysis of the number of newly formed vessels.
Treatment of diabetic angiopathy of the lower limbs is based on the data obtained during the diagnostic procedures. If the development of the disease has become a threatening character, then, first of all, the tactics of treatment should be based on the constant monitoring of glycemic parameters.
Mechanism of the development of the disease
Angiopathy of the lower limbs in diabetes mellitus is a consequence of damage to the vascular walls. As is known, the high content of sugar in the blood has a negative effect on the endothelial function of the tissues. In this regard, glucose begins to penetrate into the walls of the vessel and in the form of sorbitol and fructose accumulate there to menacing limits. In addition, such a violation leads to the accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues, which causes a thickening of the vessel. As a result, the body activates the formation of thrombi, worsens blood circulation and increases clotting.
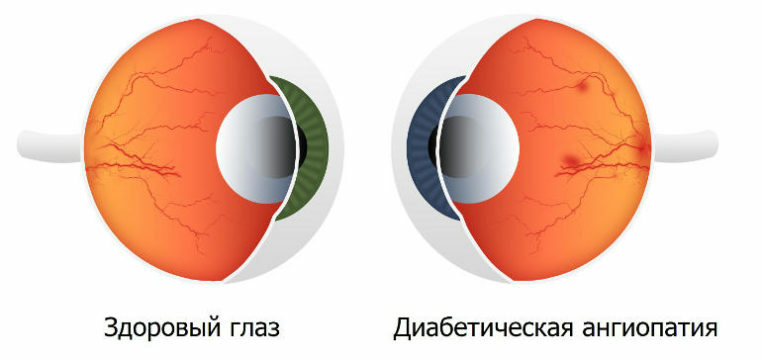
First of all, if there are disturbances in metabolic processes, small blood vessels of the legs suffer, as a result, negative symptoms of the disease become visible, such as swelling, convulsions, numbness and death of tissues. Quite often in some vessels, small aneurysms are formed, which lead to fragility of the walls and, as a result, to frequent hemorrhages that become noticeable on the retina of the eye and the surface of the skin of the legs.
Macroangiopathy
Diabetic macroangiopathy of the lower extremities is manifested by sclerotic lesions of medium and large vessels. Dangerous accumulation of cholesterol leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, which overlap the lumen of the vessel. With macroangiopathy, there is a high probability of angina pectoris, ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, and gangrene of the legs.
The increased risk of developing diabetic macroangiopathy can be caused by the following factors:
- Persistent hyperglycemia;
- By reducing the susceptibility of cells to insulin;
- Increased blood clotting;
- Obesity;
- Smoking, intoxication;
- Hereditary predisposition.
In addition, the development of the disease is accelerated after 55 years in women and 45 years in men. Diabetics with experience have the greatest probability of occurrence of negative consequences.
Development of macroangiopathy of legs occurs in stages:
- At the first stage the patient practically does not notice deviations from the norm. In some cases, after a long stay on the legs, there is a slight numbness and tingling of the feet.
- At the second stage of the development of the disease, leg fatigue increases, the patient experiences periodic weakness. Lower extremities often freeze or vice versa without cause sweat. Due to atrophy of the skin and fingers, lameness appears.
- The third stage is characterized by the appearance of acute pain along the entire length of the leg. A painful symptom is accompanied by a diabetic while in a lying position. At night, there are nocturnal cramps, the skin of the foot cracks and flakes.
- At the fourth stage, single or multiple ulcers caused by skin necrosis appear on the legs.
- The fifth stage is the heaviest. On the foot, fingers die, the body temperature rises, a febrile condition is observed, gangrene begins.
All stages of the development of the disease are quite pronounced, so doctors are rarely mistaken with a diagnosis.
Microangiopathy
Microangiopathy of the lower limbs is a pathological consequence of the lesion of small blood vessels. This disease can develop against a background of diabetes, oncological disorders, liver disease and kidney failure.
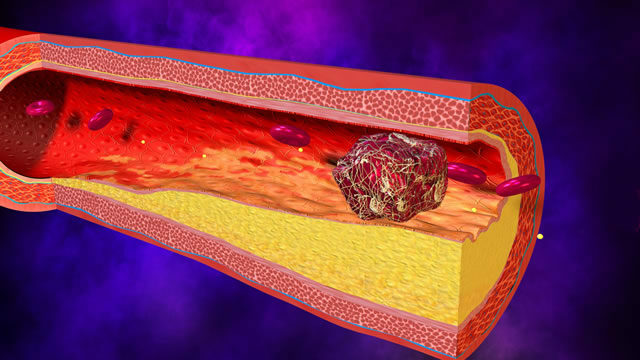
The most common causes of the disease are:
- Vascular thrombosis, blood flow disorders and high clotting;
- Necrosis of tissues and cells;
- Protein dystrophy( hyalinosis) resulting in the deposition of hyaline on the walls of the vessels;
- Fibroid increase in the permeability of the connective tissue of the vessels.
The clinical picture of diabetic microangiopathy of the legs depends on the degree of damage to the tissues of the body, as well as on the effects of external factors.
Stages of development of microangiopathy:
- The first symptoms may be the appearance of urolithiasis, hypertension, the presence of protein in the urine.
- In the second stage, one can notice the pallor of the skin of the legs and the appearance of reddish stars. Feet constantly freezes.
- During the third stage, painful sensations appear, ulcers become more pronounced.
- At the fourth stage, necrosis of the tissues and, as a consequence, blackening of the skin in the area of ulcers. Skin disorders can be accompanied by purulent phenomena.
- During the fifth stage the disease continues to progress, the ulcerative foci increase, this affects the nearby areas of the foot.
- At the sixth stage, foot necrosis occurs.
Methods of treatment
The tactics of treating diabetic angiopathy are built taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient. The greatest effect in solving this problem is achieved through conservative medical treatment. Selection of drugs is carried out by a doctor, taking into account their ability to restore blood circulation in tissues. Medicines should reduce its clotting, so that access to the vessels will improve. In addition, medications should help reduce sugar levels. In the first stage of diabetes, patients are prescribed insulin injections subcutaneously.
A good effect is also provided by accompanying activities. For example, in the treatment of diabetic angiopathy, physiotherapy sessions are used, which are aimed at cleansing the blood through plasmapheresis, as well as various baths that promote the restoration of blood circulation.
Quite often in the last stages of the disease, the patient needs surgery. In the course of a complex operation, surgeons restore microcirculation of the vessels and increase the clearance between the walls of the artery.
If the disease has reached the stage of gangrene, then in this case only amputation of the foot is possible. This measure does not mean a victory over diabetes mellitus, therefore the subsequent period of a life should pass under steadfast attention of doctors. The patient should regularly monitor the sugar content and adhere to a strict diet.
Prevention of
Disease The patient must change the whole way of life when diagnosing diabetes. In order to prevent the development and progression of angiopathy of the lower extremities, it is necessary to observe a number of preventive measures.
- First of all, it is necessary to follow all the instructions of the attending physician without fail.
- Monitor the blood sugar level and take insulin.
- Important role in the development of negative consequences is overweight, so you need to follow it closely.
- In addition, a strict diet should become a lifestyle diabetic.
- If the test results show high blood clotting, then you need to drink diluting drugs. This will prevent the risk of thrombosis. For the same reason, strict control of cholesterol and liver samples is required, since the liver is responsible for the production and processing of cholesterol and glycogen stores.
Timely prevention of diabetic angiopathy will help prevent many of the dire consequences of this insidious disease.