Synostosis is the process of splicing one bone or two adjacent .
Synostosis is the process of splicing one bone or two adjacent .
Synostoses are spontaneous, i.e.congenital, post-traumatic or anatomical,
. Also, they are artificial, that is, they are specially created in an operative way.
Article Contents
- main pathologies
- metopic
- lambdoid isolated
- Pathology ribs
- Congenital radiocubital
- Pathology Klippel-Feil
- Fusion
- bones after injury
- Pathology artificial genesis
- Physiological
- Causes and risk factors
- The dangerous disease
main types of
pathology Considercharacteristic types of anomalies.
Metodic
Metopic synostosis - premature fusion of the frontal bones. Usually, the frontal suture does not overgrow in young children under the age of 24 months.
If the frontal bones are spliced before birth or immediately after it, in this case the frontal hillocks do not grow and develop. The skull subsequently acquires a triangular shape, creating an obtuse angle in the region of the frontal suture.
Very often it is combined with other developmental anomalies, being at the same time a composite element and a syndrome of many vices.
If there is a polished metopic synostosis, a full surgical intervention is shown within the first 2 months after the birth of the child.
Lambdoid insulated
This type of synostosis is rare and is accompanied by an increase in the thickness of the occiput and the expansion of the large fontanelle with an increase in the anterior part of the skull.
It is usually combined with the premature closure of the so-called sagittal suture.
Pathology of the ribs
Synostosis of the ribs- is the fusion of bones in the posterior or anterior part of the body .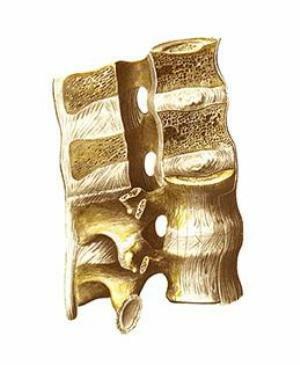
Very rarely, the fins are spliced completely.
It happens that round or oval, well-defined bone, holey defects appear along the length of the splice.
The space between the edges becomes asymmetric.
Toughening therapy is possible.
There are also surgical methods of treatment, but it is necessary to consider each situation separately.
Congenital radiobulange
This synostosis is rare, in just under 10% of all congenital deformities of the limbs. More often, a similar anomaly of development occurs in men and on the right side.
The disease is transmitted by inheritance. Such a synostosis can be from the distal( rarely enough) or proximal ends of human bones.
Clinically, the pronational location of the forearm can be noted in the absence of supination, often limiting the movements of bones in the elbow joint.
Typical radiograph - proximal bone ends are spliced by 3-4 centimeters. The head of the radius is in a dislocated state or atrophied.
If the patient has not managed to adapt to this defect, treatment is possible only by surgery - by implanting a new joint.
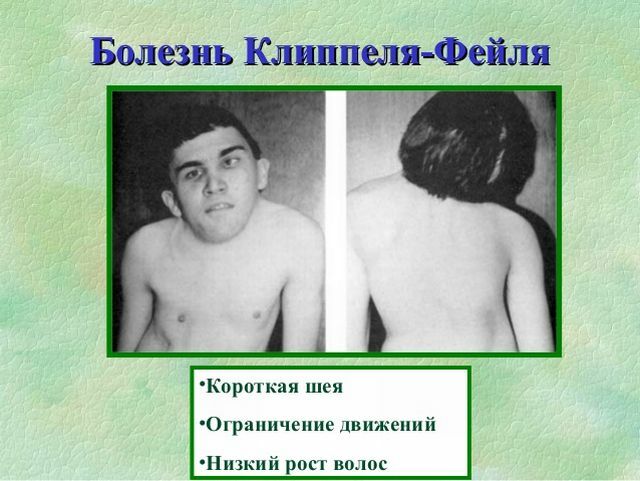
Klippel-Feil pathology
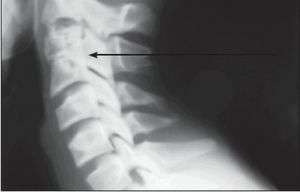 Klippel-Feil syndrome is a rare and rare congenital anomaly in the development of the spine bones, which is accompanied by a synostosis or a decrease in the number of cervical vertebrae.
Klippel-Feil syndrome is a rare and rare congenital anomaly in the development of the spine bones, which is accompanied by a synostosis or a decrease in the number of cervical vertebrae.
This disease was described by French doctors: Klippel and Feil more than 100 years ago. The main characteristic signs are such phenomena as a short neck, poor mobility of the upper parts of the spine and a decrease in hair growth at the nape.
Also, probably a combination with many other anomalies, including - with heart defects, spina bifida, wolf mouth and scoliosis.
Usually, the treatment of this type of synostosis is conservative, with a strong cosmetic defect, it is not uncommon to remove the ribs located on top.
To prevent future, secondary deformities and improve posture, patients are given a massage, prescribed physical therapy and physiotherapy.
With further appearance of radiculitis, analgesics are used. With a strong squeezing of the nerve roots, surgical intervention is performed.
Bone battle
Congenital synostosis is a pathological fusion of bones, which is caused by aplasia or hypoplasia of the connective tissue between them.
Often, an anomaly is formed between the radial and ulnar bone.
Less common is craniostenosis( premature fusion of two or more cephalic joints), a synostosis of the middle with a nail phalanx of the fifth toe, and a synostosis of the wrist.
The books describe cases of fusion of phalanges of neighboring fingers, synostosis of normally developed ribs and fusion of the first and cervical( additional) ribs.
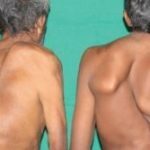 The extremely dangerous congenital disease of Sprengel originates in the womb of the mother. How to behave to a future mother, so as not to cause pathology.
The extremely dangerous congenital disease of Sprengel originates in the womb of the mother. How to behave to a future mother, so as not to cause pathology.
Abnormal finger development caused by a malfunction at the gene level of the syndacty toe of the legs and hands. What methods of surgical intervention exist?
After
trauma Post-traumatic synostosis is the splicing of bones located next to each other due to a defect in bone tissue, periosteum, or epiphyseal cartilage.
Most often, pathology is detected between the bones of the forearm, the bones of the lower leg and the adjacent vertebrae. The main cause of synostosis is the rapprochement of fragments of bones in the area of damage.
Postural diagnostic synostosis of vertebrae occurs as a result of ossification of the longitudinal anterior ligament after dislocation of the vertebra and marginal fractures of the body of the bone.
Artificial genesis pathology
An artificial synostosis is the creation of a fusion between the bones during the operation. It is used to eliminate strong bone defects and prevent the appearance of false joints, etc.
Often pathology appears between the tibia. The main load during walking after surgery presses on the fibula, which subsequently becomes compensatory and becomes like a tibia.
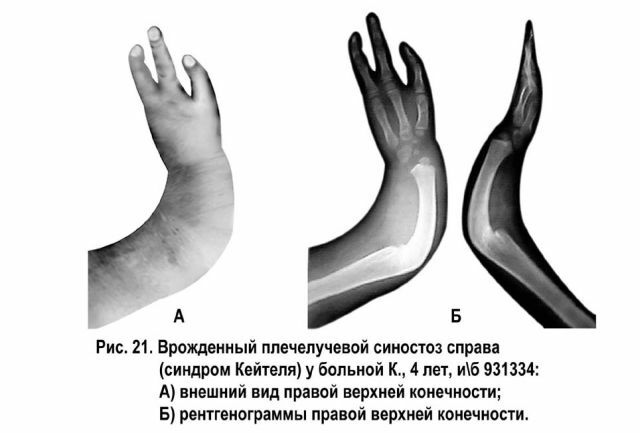
Physiological
This is a common bone connection that occurs during adulthood. In their norm, synostosis appears in adolescence and adolescence at the site of the cartilaginous joints between the sacral vertebrae, the pelvic bones and the base of the skull.
With eunuchoidism, hypergonadism, Kashin-Bek disease and many other diseases, this process is accelerated or slowed down, which can lead to disruption of the entire musculoskeletal system of the body.
Causes and Risk Factors of
All doctors and specialists distinguish hereditary factors that contribute to the onset of pathology. 
These include hereditary genetic defect. The child thus can observe a violation of the differentiation of growth, which is necessary for the proper further development of the entire skeleton( also for the formation between the bones and joints of the borders).
All this, over time, leads to disruption of the formation of the bones of the skeleton in the third to the ninth week of fetal development inside the womb of the mother.
With this form of inheritance in the family, where one of the parents has a synostosis, the chance of having a sick child varies from 50 to 100%.
This type of inheritance occurs mainly in the Klippel-Feil disease and is an autosomal recessive type of inheritance of the disease.
Than the disease is dangerous
The disease is especially dangerous because it is difficult to treat and has a lot of complications in the life process.
The disease, although unpleasant, but you can live with him comfortably, with timely access to a doctor, although much depends primarily on the strength of the damage to the bones.
Almost always the only correct one is the solution is operational. The prognosis for life, as a rule, is favorable in the majority of cases and under the condition of intensive training in physical therapy during the postoperative period, it is possible to restore the function of the skeleton to 100%.