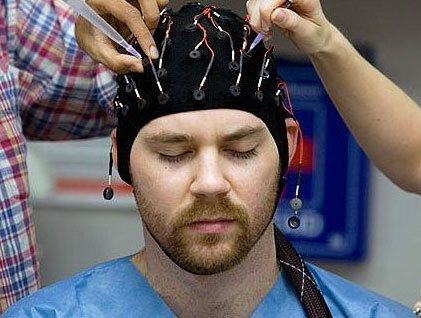
 In 2001, this syndrome was included in the list of diseases for which epileptic activity and epileptiform disorders in electroencephalography are characteristic.
In 2001, this syndrome was included in the list of diseases for which epileptic activity and epileptiform disorders in electroencephalography are characteristic.
These disorders cause developing deterioration of the brain. Also, Otahara's hypothesis was adopted that this disease in 80% of situations develops into another - Vest syndrome. And after a while there were situations with the transformation of the disease into the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Otahar syndrome is the initial stage of epileptic encephalopathy, which is detected in children in the first 3 months after birth. Acute seizures are characteristic of the disease, which appear throughout the 10-day life of the child, in rare cases after birth.
Infringements in a metabolism of the baby speak about family diseases. It is exacerbated against the background of ideal health.
Causes and etiology of
The most popular prerequisite is the formation of brain defects - unilateral megalencephalus, portentsefalia and others. Sometimes as a source can act as a mapping violation, failures associated with the exchange of substances.
In personal studies, Otahar considered 10 situations. As a result, 2 had a cyst in the cerebral hemispheres - portentsefalia,  also in 2 Aikardi syndrome and subacute mixed encephalopathy - a dystrophic change in the brain tissue, which causes disturbances in its functions. In the other 6 children the origin of the disease was not revealed.
also in 2 Aikardi syndrome and subacute mixed encephalopathy - a dystrophic change in the brain tissue, which causes disturbances in its functions. In the other 6 children the origin of the disease was not revealed.
In another survey of 11 infants, the 1st had asphyxia at birth, the 1st with congenital pathology, an important value in the development and distribution of which is played by genetics( agenesis of the corpus callosum).
In the first non-ketone hyperglycinemia, the other bases of the disease are not found. Only 1 was with similar symptoms of epilepsy as that of his relatives.
Schlumberger in his experiment in 8 out of 8 situations diagnosed with the defects of the brain.6 of which - unilateral megalencephaly and one Aikardi syndrome. Unilateral megalencephaly as a cause was encountered in the research work of Martin, Ohtsuka.
In 1995, in an article devoted to childhood epilepsy, it was written that the sources of Otahar syndrome are brain malformation.

As a result, after a multitude of studies, it was generally agreed that structural disorders of the cerebral hemispheres are provocateurs of the disease.
Pathophysiology
Otahara, Vesta and Lennox-Gastaut syndromes are very closely related, it is accepted that these syndromes show the age-related reactions of the brain in different periods of its formation.
With this kind of epilepsy, one had to face another patient with hemispheric or focal malformations, which produce severe partial seizures that precede, but mostly follow immediately after Otahar syndrome.
Clinical manifestations of
In 2002, Aicardi and Ohtahara presented the following main features of Otahar's disease:
- is usually affected by infants immediately after birth or at 10 days of age;
- different types of seizures, the main one is an excitatory spasm, seizures with excessive muscle tension can manifest themselves both during the day and at night;
- severe slowdown in psychotropic formation, often ends in death in infancy;
- possible transformation of the disease into other syndromes;
- basically, all cases are associated with brain disorders.
For Otahara syndrome, there is a progressive deterioration in health with an increase in the number of seizures, a visible slowdown in the psychomotor formation of the body. Basically, babies with this diagnosis remain disabled.
The disease is characterized by different types of seizures. As a rule, excitatory spasms, which can spread throughout the body, are symmetrical and lateralized relative to the cerebral hemispheres. The average length of the attack is on average 10 seconds, with an interval of 10-15 seconds. There is also a small chance of developing other seizures.
Because of the disease, infants are less active, hypotension is manifested. In Vesta syndrome, the disease can be transformed in 2-6 months of life of children, according to the results of the study, the percentage of the transition is about 75%.In the future, the disease has every chance to grow into the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.

Diagnostic procedures
Neuroimaging is a combination of ways in which you can visualize the structure, functions and biochemical properties of the brain. These methods are necessary to determine the causes and purpose of treatment therapies. As a rule, they show significant deviations from the norm and malformation.
 If the results of neuroimaging are normal, metabolic screening should be performed.
If the results of neuroimaging are normal, metabolic screening should be performed.
The first symptoms of the disease are interictal electroencephalography, which is a flash-suppression pattern with high amplitude paroxysmal discharges, which are separated from each other by a flat curve with a duration of about 18 seconds.
The pattern of "flash-suppression" may be asymmetric or predominate in one of the brain's hemispheres, and also worsen at the moment of sleep.
If the pattern of "flash-suppression" is replaced in places by gypsarhythmy( abnormal chaotic activity) in the 3-5 months, this indicates a different disease - Vest syndrome.
If the slow spike-wave activity, it is typical for the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. In all other situations it develops into a severe partial epilepsy with high activity of nerve cells in one of the hemispheres.
Since the main cause of the disease is brain damage, it is necessary to perform a neuroimaging test. All structural changes can be seen with MRI and CT.
With normal results of neuroimaging, diagnostics of metabolism is prescribed. Some disorders in the process of metabolism of orgasm can lead to lesions of the cerebral hemispheres.
The effectiveness of the therapy is practically zero
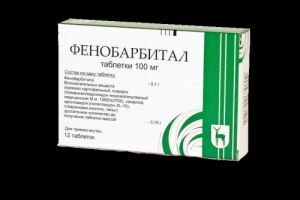 Antiepileptic drug Phenobarbital, also known as Luminal, is capable of reducing the number of seizures, but anticonvulsants are unable to stop the slowing down of the psychomotor formation.
Antiepileptic drug Phenobarbital, also known as Luminal, is capable of reducing the number of seizures, but anticonvulsants are unable to stop the slowing down of the psychomotor formation.
None of the known cases had a positive reaction to treatment with adrenocorticotropic hormone and calcium antagonists. In 2001, Fusco demonstrated favorable therapy with vitamin B6.
Ohno presented a situation with a good result on the way Zonisamide treatment. In variants with hemimegalencephaly or cortical dysplasia, neurosurgical interventions can help.
Unfortunately, currently there is no effective drug treatment of the disease, half of the patients die as early as the infancy from several weeks to a month, the rest develop a stable neurological and psychological defect.
Often attacks in Otahar syndrome are unrecoverable and can not be treated with antiepileptic drugs. With time, transformation into other diseases is possible.
If the transition has not been implemented, then the psychomotor development will be better. However, the forecast is unfavorable, in most cases a lethal outcome was observed.