 Dischondroplasia, or Ollier's disease, is a congenital pathology of a systemic nature in which embryonic cartilage in the metadial and metaphyseal parts of the tubular bones is incapable of rebirth into bone tissue.
Dischondroplasia, or Ollier's disease, is a congenital pathology of a systemic nature in which embryonic cartilage in the metadial and metaphyseal parts of the tubular bones is incapable of rebirth into bone tissue.
Due to this process, the growth slows down and the size of bones decreases.
This fact suggests that the cartilaginous growth epiphyseal plate is inferior. As a rule, this disease is one-sided.
The risk of the disease is minimal, the pathology is rare, approximately 10 cases per 1000 inhabitants .
In the vast majority of cases, the disease of Olie is affecting the metaphysis of long tubular bones. This is a large tibia, femoral, humeral, forearm, tibia.
And in the first two there are the most serious and serious changes. Often it is possible to detect dyschondroplasia of pelvic bones.
When the disease extends to the metacarpal, metatarsal, foot and hand phalanges, pathological changes are observed throughout their entire length.
The only places for which the localization of the disease is not characteristic are the cranial vaults.
Contents of the article
- Contents of the article
- Content of the article
- Contents of the article
- Contents of the article
- The development stages
- Development stages
- Symptoms of violation
- Diagnostic methods
- Therapy of the disease
- Forecast
- Complications of the pathology
- Preventative measures
- Contents of the article
- Contents of the article
- Content of the article
Causes and risk factors
Today the disease remains unclear,.There are hypotheses about the transmission of pathology according to the autosomal dominant type of heredity.
Violations begin to be laid at the level of embryonic development.
When the disease is observed a cluster of cartilaginous tissue in the form of foci, protruding above the surface and resembling exostoses.
They are located in the depths of bones, specifically in diaphysis or metaphysis. At inspection it is possible to see, that they are similar to a hyaline cartilage.
Very rarely, the disease is accompanied by a violation of pigmentation or the formation of cavernous bodies. With this combination, they talk about the Muffucci syndrome.
Foci of cartilaginous tissue grow as the body grows up, as a result, deformation of the affected bones is observed. In some cases, a degeneration occurs in a malignant or benign tumor, chondrosarcoma or chondroma, respectively.
Stages of development of
Depending on the extent of the pathological process, the disease of the Olieu is divided into the following forms: 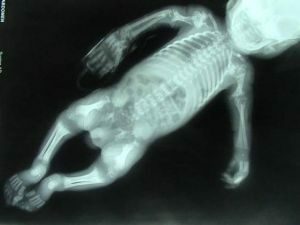
- Monoossal - one bone is affected.
- Oligossal - a violation of bone formation extends to 2-3 bones.
- Poliossal - pathology is observed in more than 4 tubular bones.
- Akroform - dyschondroplasia is localized only in the feet and hands.
In addition to this classification, the nature of the disease of the bone system is divided into:
- generalized;
- local;
- multiple;
- syndromes on the background of other pathologies.
Symptoms of a disorder
The clinical picture can appear at the age of 0 to 6, and sometimes up to 10 years. Such a long period of time is explained by the dependence of the localization of the process.
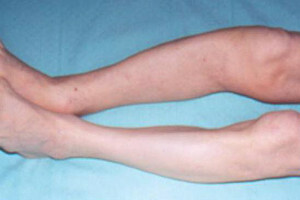
Earlier Olie's disease begins to manifest itself when leg injuries occur. When it comes time for the child to begin walking, there is a shortening and deformation of the limb, a curvature of its axis.
In case of lesion of the growth zone, the length of the diseased bone may be less by 20-30 cm in comparison with the healthy one.
If the pathological process spreads to the hands, thickening and deformation of the corresponding bones is observed. It can be phalanges of the fingers, shoulder, ray. The first symptoms in this case start to bother with 4-5 years of .
In some cases, tumor-like formations of a spherical shape may be present. Against the background of all these changes, no painful sensations are observed.
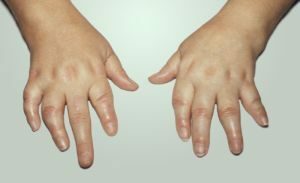 In addition to the above symptoms, valgus deformity of the affected joint( knee, hip, ankle) may develop. In this case, the movements are completely preserved.
In addition to the above symptoms, valgus deformity of the affected joint( knee, hip, ankle) may develop. In this case, the movements are completely preserved.
Also, a gait disorder in the form of lameness may develop. If the manifestations become severe, patients may be troubled by periodic pain. It is worth noting that the clinical picture is pronounced only in adults, children mark manifestations of the disease in a low degree.
Diagnostic methods
The final diagnosis is established after a visual examination and an X-ray examination method.
The latter shows a clear picture, typical for this pathology. The size of the affected long tubular bones is significantly less in comparison with the same healthy ones.
Metaphyses look bloated and thickened, visually resemble a mace. Diaphysis have curvatures, their degree depends on the progression of the disease.
In places of localization of chondromatous nodes, there is no bone tissue, light areas are located in its places. They are not homogeneous. Thickening of the epiphysis is caused by thinning and lifting the cortical layer above the foci. Periodic reaction is absent.
If dyschondroplasia affects the scapula, the cartilaginous foci are located closer to the periphery, the central part of the bone has a normal bone composition. When involved in the pathological process of ribs, there is localization in the anterior ends, swelling is not typical.
Therapy of
Disease You can get rid of this disease by such therapeutic methods:
- is conservative;
- orthopedic;
- operative.
Each of them requires the competent approach of an orthopedic physician, since the growth zone of the epiphyses is very difficult to influence.
It is necessary to combine these methods to obtain the desired result.
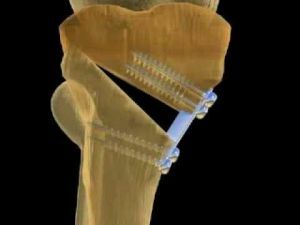
Most patients with this diagnosis need surgery.
Its purpose is to remove the foci of cartilaginous growths by resection or curettage, as well as the elimination of deformity phenomena and the conduct of bone plastic.
This method of treatment is shown with a significant shortening of the patient's limb and the presence of severe deformation. 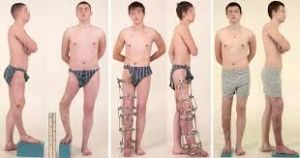
It is also necessary to carry out surgical intervention in severe forms of the disease, localized in the hands and feet, otherwise it will not be possible to avoid significant deformations in these areas.
The degeneration of the chondromatous nodes into a malignant tumor is also an absolute indication for surgical intervention.
Forecast
For dischondroplasia, the prognosis is favorable. If time to spend the necessary methods of treatment, it will be possible to prevent even residual phenomena. In severe forms, minor lameness may remain.
Complications of pathology
Concomitant complications are very rare. This may be the degeneration of the chondromatous nodes into a tumor of a benign or malignant nature.
With prolonged absence of treatment against the background of a shortened limb, the curvature of the spine may develop.
Signs of this process are gradually increasing painful sensations, as well as swelling in the area of the affected bone.
At X-ray examination, it is possible to detect sites of destruction. They increase in size in a short time and destroy the cortical layer.
Preventative measures
Since the cause of the disease is not precisely established, specific advice that helps to prevent the formation of cartilaginous foci is difficult to give.
 But in connection with the hypothesis of a violation in the process of embryogenesis, it is worth to observe during the pregnancy all the doctor's recommendations, to lead a healthy lifestyle, to avoid the influence of harmful environmental factors that can cause the violation of the laying of organs and fetal systems.
But in connection with the hypothesis of a violation in the process of embryogenesis, it is worth to observe during the pregnancy all the doctor's recommendations, to lead a healthy lifestyle, to avoid the influence of harmful environmental factors that can cause the violation of the laying of organs and fetal systems.
Thus, it can be argued that a disease such as dyschondroplasia, is a serious congenital pathology, which is difficult to get rid of .
Therefore, it is better to try in every possible way to prevent the development of this pathology, and if it is still diagnosed, it is necessary to immediately start treatment.