 Diffuse axonal brain damage( hereinafter referred to as DAP) is a craniocerebral trauma that results in the rupture or damage of axons( nerve cord processes) that impart nerve impulses to the cells of the central nervous system, organs and tissues.
Diffuse axonal brain damage( hereinafter referred to as DAP) is a craniocerebral trauma that results in the rupture or damage of axons( nerve cord processes) that impart nerve impulses to the cells of the central nervous system, organs and tissues.
DAP, often leads to a coma, as a result of which a person can go into a vegetative state.
Brain diffusion occurs more often with young people who fall into traffic accidents, become victims of fights and beatings with brain damage, as well as children who have a much deeper coma, and neurological disorders are more coarse.
The variant of this CCT was first described in 1956 abroad, and the name itself appeared in 1982.The condition in the WCT is severe, occurring in a prolonged coma, which immediately occurs after trauma and is characterized by a prolonged course.
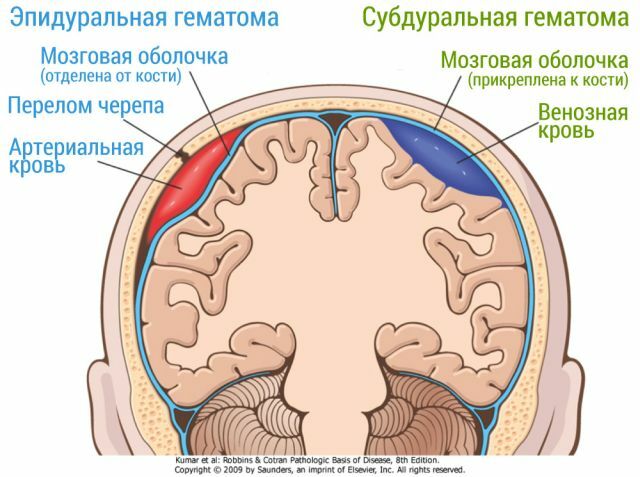
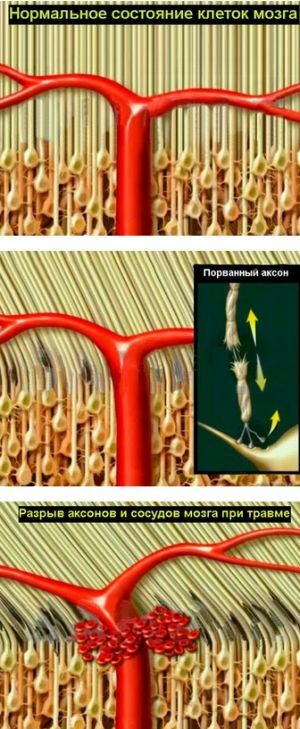
Axons damaged or ruptured as a result of CCT, and small hemorrhages are evenly distributed across the cerebral structures, and the innervation of all dependent organs is impaired. The most common injury sites:
- brain stem;
- is a white substance;
- corn body;
- fibers periventricular.
Diffuse brain trauma is always a serious condition with the prospect of transition to the vegetative state, non-routine and fatal outcome.
Causes and morphology of DAP
The most common causes of TBI in WCT: 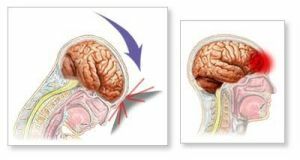
- severe bruise on windscreens in road accidents;
- drop;
- hit with a heavy object;
- syndrome of concussion in children, in which the brain is severely bruised afterwards by sharp shaking, as well as beatings, falls.
The DAP syndrome is the result of bruises caused by angular acceleration of the head. In this case, there may not be a direct collision with the object of injury.
Because of this, some patients do not have fractures of the skull and other visible wounds, which somewhat complicates the diagnosis. The statistics indicate that it is the oblique damage that leads to axonal damage and the emergence of the WCT.
Morphologically, this injury is characterized by the following three lesions:
- brain;
- corn body;
- brain stem and diffusely distributed tears.
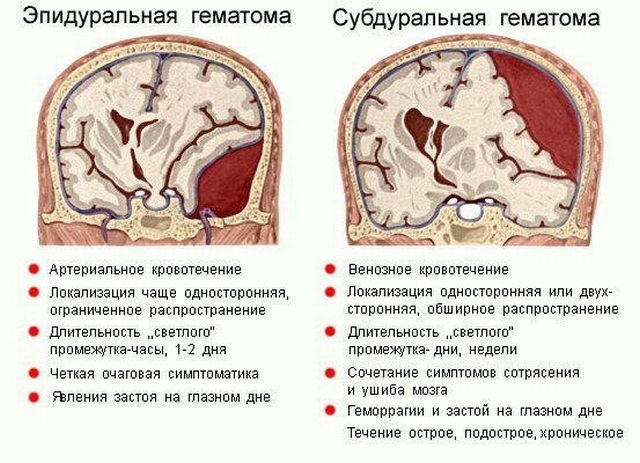
The first two focal features are macroscopic, which are arranged in the form of a hematoma up to five mm, looking like a torn tissue with bloody edges. A few days after TBI, the focus is pigmented and then scarred. The wound in the corpus callosum can be resolved by the formation of a vascular cyst.
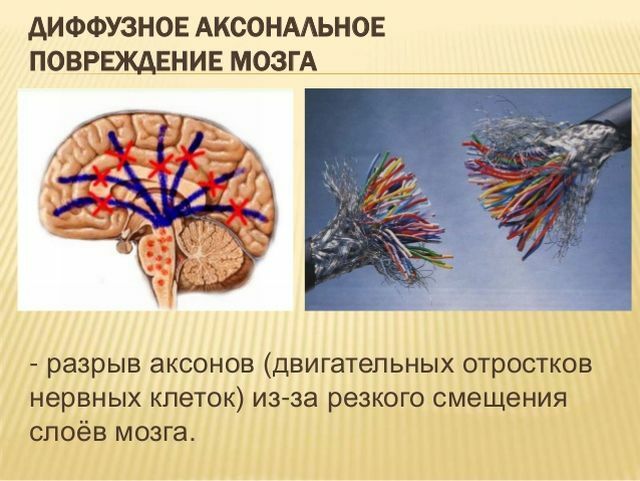
Axonal disorders in trauma
Features of clinical picture
Coma with diffuse brain damage lasts up to three weeks and manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- pupil reflex is broken;
- occurs paralysis of the eye;
- respiratory rhythm changes;
- increases muscle tone;
- appears paresis of the legs and hands;
- is diagnosed with hypertension;
- appears febrile or subfebrile temperature and other vegetative disorders.
When a patient with a WCL comes out of a coma, he is in a vegetative state with the following symptoms:
- eyes open to stimuli or independently;The
- view is not concentrated and does not follow moving objects.
The vegetative state, accompanied by reflex reflexes and symptoms of brain hemispheric separation, can last, on average, from several days to several years. The greater the presence in it, the sooner there are signs of polyneuropathy, such as:
- weakening of the hands;
- chaotic movement of muscles;
- disorders of neurotrophic;
- increased heart rate;
- edema;
- tachypnea, etc.
After leaving the vegetative state, the personality falls out. The main signs of violations after the release:
- extrapyramidal disorders;
- disorders of the psyche, manifested by a lack of interest in the patient's actual reality, aggression, amnesia, dementia.
Degrees of affection
Diffuse axonal brain injury occurs in three degrees of severity:
- of light - duration of coma from 6 to 24 hours, crash is insignificant;
- of the average - coma is more than 24 hours, but the craniocerebral trauma is moderate;
- severe - a prolonged coma, lesions are significant, there is a squeezing of the brain.
Severe degree is characterized by mass damage to axons, which lead to hemorrhages in the brain. The WCT can lead to a coma that lasts for years and is lethal.
The initial state of the brain after recovering from such a coma can not be restored, units returned to a more or less normal life after such damage.
Diagnosis of
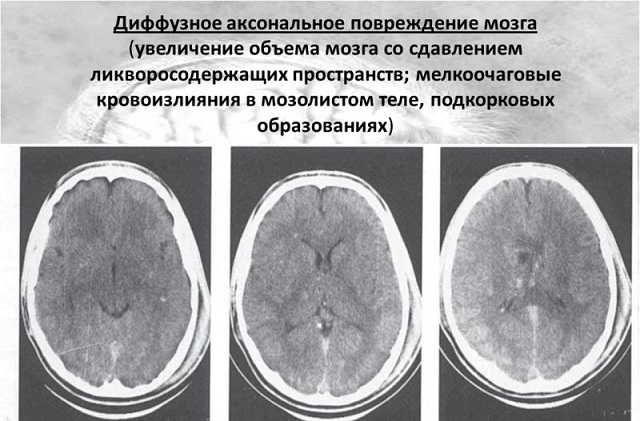
Diagnosis of diffuse brain damage is posed after computed tomography, the results of which in an acute period are characterized by an increase in the volume of the cerebral hemispheres, a decrease or squeezing of the lateral distances and the base of the brain. In white matter, the trunk and callosum body are small hemorrhages.
During the examination, a lightning-fast development of signs of DAP and degeneration is observed.
EEG in DAP syndrome reveals changes in the subcortex and brainstem, diencephalic syndrome. In the analysis of blood there is a sharp increase in serotonin, a significant decrease in dopamine and a jump in adrenaline, which involves therapy aimed at reducing sympathetic-adrenaline symptoms.
As a result, CT is determined to increase intracranial pressure or, conversely, reduced or absent. In this case, connect the sensor. If the outflow of CSF is normal, then intracranial pressure will be normal.
Support for the condition of the injured
After a diffuse brain injury, subdural liquor accumulations are often diagnosed over the large cerebral hemispheres, which subsequently dissolve, surgical removal is not necessary.
Axonal brain damage is most often treated conservatively. Neurosurgical operation is performed with a combination of gaps and axonal injuries with focal lesions that increase compression and provoke hydrocephalic syndrome.
In a coma patient connect to the ventilator, parenterally and inject the following medicines:
- to establish the correct acid-base and water-electrolyte balance;
- nootropic and vasoactive;
- eliminating hypertension or hypotension;
- antibiotics to exclude concomitant infections.
To resume the psycho-emotional sphere, the reception of psychostimulants is introduced.
After exiting coma: 
- is administered nootropics and vascular medications to normalize and improve the CNS, nootropics are also important for subsequent rehabilitation;
- prescribe drugs to improve metabolism and biostimulants;
- conducts exercise therapy to prevent paresis;The
- patient is engaged with a speech therapist.
Hormonal drugs in the WCT are not prescribed as needed. After the operation, if it still took place( there was a compression of the brain with concomitant injuries), drugs are introduced that prevent the formation of edema, vascular agents, nootropics, anticholinesterase, psychotropic( to avoid the development of aggression and depression) and neurotransmitters.
During the recovery period, the same therapy is carried out as after leaving the coma.
The outcome of severe trauma and its consequences
The prognosis and consequences of diffuse axonal injury depend on the extent of axonal lesions of the brain and the severity of secondary symptoms such as increased intracranial pressure, hyperhidrosis, swelling of the meninges, mental disorders, dementia development, etc.
Outcomealso depends on how the therapeutic methods aimed at eliminating the consequences of the WCT are helping - secondary damage and complications.
 But, it must be said that sometimes it is possible to recover completely or almost completely, to return the mental functions, to return to normal activity, all neurological disorders can be removed even if the person was in a coma of the third degree( severe), and after a long time stayed in the vegetative state. The tendency to self-healing is always present in the brain, and more severe disorders are also known, under which it was restored.
But, it must be said that sometimes it is possible to recover completely or almost completely, to return the mental functions, to return to normal activity, all neurological disorders can be removed even if the person was in a coma of the third degree( severe), and after a long time stayed in the vegetative state. The tendency to self-healing is always present in the brain, and more severe disorders are also known, under which it was restored.
But, unfortunately, more often in surviving people the subsequent course of the DAP syndrome can go according to two scenarios:
- output from a coma;
- transition to the vegetative state.
With the first option, the patient's eyes open, and the objects are tracked and the look at the object is fixed. It can have both a spontaneous output, and is guided by organized stimuli, sound and painful manipulations.
Then the patient regains consciousness, fulfills the requests addressed to him, the verbal baggage expands, he begins to communicate. Neurological pathologies slowly regress.
In patients who have left the vegetative state, extrapyramidal symptoms develop, accompanied by mental disorders( dementia, mood lability, aspontaneity, confusion).At the second variant the lethal outcome through certain time is inevitable because of depletion of neurotransmitters and somatic complications.
Modern studies confirm the regeneration of axons in children and young people whose brains have not yet completed formation. There is a restoration of neurological and mental processes. With prolonged coma, it is problematic, disability is guaranteed.