Meningococcal meningitis is characterized as a generalized clinical form of one of the meningococcal infections.
Meningococcal meningitis is characterized as a generalized clinical form of one of the meningococcal infections.
Called, as a rule, because of meningococcus. Symptoms are considered to be toxemia, as well as some brain reactions.
The causative agent of this disease is Gram-negative meningococcus, which remains immobile, and also differs in that it often changes. He is unstable when he is in the external environment.
To be more precise: the virus is fond of moisture and rays of the sun, does not tolerate cold. The best habitat for him is a temperature above 37 degrees. A pathogenic factor is considered to be a capsule, which protects this microbe from being absorbed by phagocytes.
Contents of
- Routes of infection
- Difference in symptomatology in children and adults
- Diagnosis of
- Treatment of infection
- Folk methods of therapy
- Possible complications
- Prevention of spread of the disease
Pathways of infection
The main source of infection is considered to be a person who is already infected with this ailment. Also it can be a healthy person who only carries a virus.
Healthy meningococcal vectors are much more dangerous. At the time of sporadic incidence, their percentage of the total population is at least 1%.
The carrier keeps the infection in less than two weeks. Transmission is carried out by airborne droplets. While the person coughs, or sneezes, the causative agent of the disease is allocated to the surrounding world. It is almost impossible to get infected with a normal contact with a person.
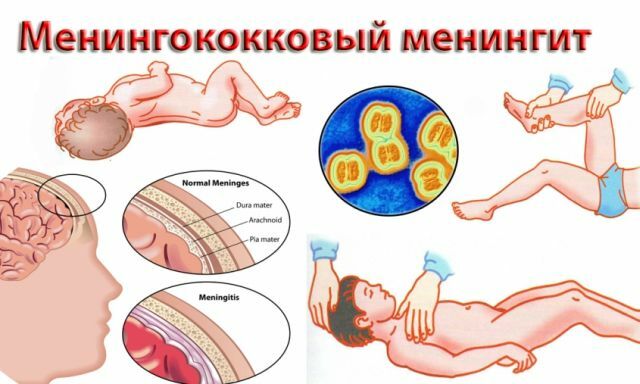
Difference in symptomatology in children and adults
Unlike adults, in children the form of meningococcal meningitis is clinical and is caused by meningococcus. The onset of such  is acute and manifests itself as general cerebral symptoms.
is acute and manifests itself as general cerebral symptoms.
Sometimes, as in adults, children develop toxemia. Toxemia is the poisoning of blood by certain bacteria. The presence of bacteria in the blood is always undesirable.
Like an adult or a child, a sudden outbreak of meningitis occurs suddenly, and the course of the disease is always acute. At first, the disease can be similar to an ordinary cold. They do have many similar ghosts regardless of age, namely:
- has a strong weakness throughout the body;
- prolonged fever;
- refusal to eat.
In children all of the above symptoms are also present. But they are added a few more, namely diarrhea, eructation and anxiety.
Diagnosis of
The diagnosis is based on the clinical findings. There are some clinical signs that are considered most important.
For example, the acute course of the disease, obvious symptoms and fever, a sharp decrease in appetite, poor sleep, unpleasant sensations under the eyelids, weakness in the whole body, excessive excitement or chills.
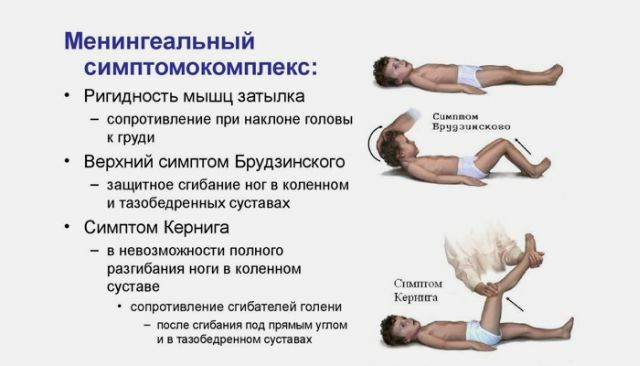
Meningeal syndrome, characterized by severe pain in the head, nausea, as well as rigidity of the muscles on the occiput, can also appear.

Treatment of infection
Timely therapy provides an opportunity to cure the disease quickly and painlessly and helps to avoid death. If the disease has reached its peak, complex treatment is required, in which antibiotics and pathogenetic agents are prescribed as soon as possible.
 Semisynthetic Penicillin is widely used and effective against meningococcal infections. As an initial therapy, this drug is most reliable, especially with purulent meningitis until the exact diagnosis is made.
Semisynthetic Penicillin is widely used and effective against meningococcal infections. As an initial therapy, this drug is most reliable, especially with purulent meningitis until the exact diagnosis is made.
Penicillin is administered within 24 hours, between receptions should take three hours. The dose may be increased at the doctor's discretion, but in such cases the drug is administered every four hours.
Similar therapy is established by doctors depending on the individual characteristics of the human body, as well as on the basis of clinical data. Such treatment lasts for a week, sometimes less. This is quite enough to get rid of the disease in its initial stage.
Pathogenetic therapy occurs at the same time as etiotropic therapy. Mostly, it cures of toxicosis.
Use solutions of 5% glucose, Ringer's solution and some other crystalloid and colloidal solutions( for example, Dextran or Gelatinol).Introduce up to fifty milligrams of fluid, depending on the weight of a person.
The procedure takes place once a day. If a person remains conscious, the solutions are removed by a preoral method.
The course of the disease, as in children and adults, is not much different. Symptoms are similar, but in children meningococcal meningitis in the early stages is most similar to a cold. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner so as not to miss when the infection becomes acute.
If you find signs of illness, regardless of age, a person is urgently hospitalized and given out medicines.
As such, treatment takes place solely under the supervision of doctors in the hospital. The main therapy is using antibiotics.
In the event of primary signs of infection, antibiotics with a wide spectrum are immediately administered. It can be Cephalosporin and Penicillin, as well as some others.
Traditional methods of therapy
 Treatment in a hospital under the careful supervision of doctors is a modern way of treating the disease. However, you can use the auxiliary people's ways.
Treatment in a hospital under the careful supervision of doctors is a modern way of treating the disease. However, you can use the auxiliary people's ways.
So, for example, the most popular method of treatment is poppy tincture. In the evening, poppy seeds, or rather its seeds, are grinded.
Then pour over pre-heated milk, put the mixture in a thermos bottle and leave it overnight. Since morning the medicine can be used. Take the medicine every day three times, one hour before eating. For children, one spoon will suffice, whereas for adults about 70 grams.
However, before taking this medication, it is worth consulting with a doctor.
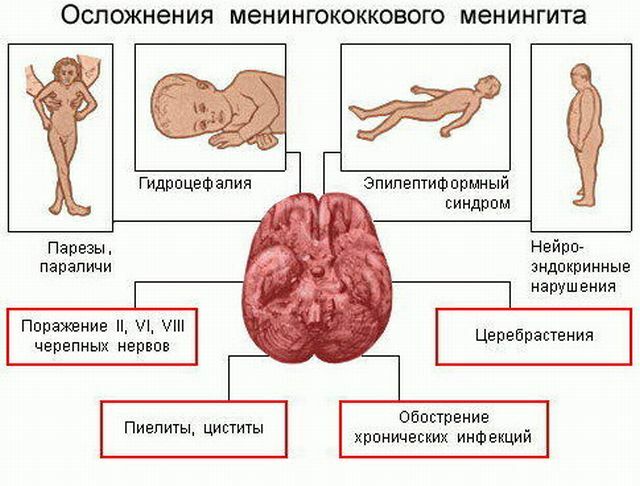
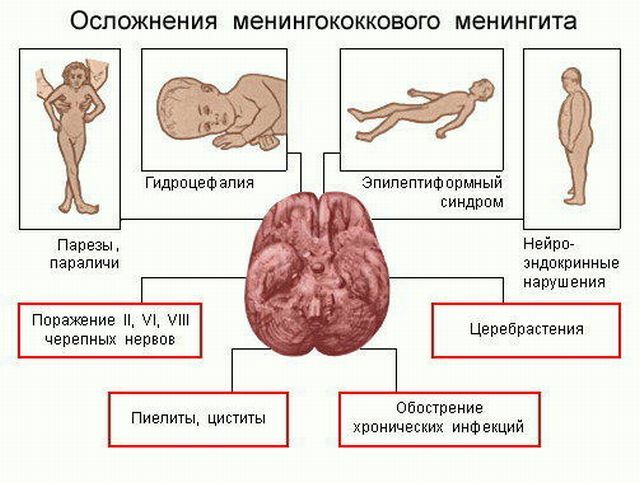
Possible complications of
Almost half of the total population who suffered meningitis may experience certain complications. As a rule, the following occurs:
- Hydrocephalus is characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which is in the brain of the head. Usually, it is observed in children. If the child has a hydrocephalus, an operation should be performed to remove the undesirable amount of fluid. The operation is recommended only at the time of increased intracranial pressure.
- The onset of stroke by due to impaired blood circulation in the brain. The main sign is the loss of normal speech, memory impairment. This suggests that you need to see a doctor immediately.
- The epilepsy of begins in the first days of the onset of the disease. Seizures do not say that treatment is useless. If epilepsy continues, then you should notify the attending physician.
There are some other complications. For example, the development of pneumonia, the onset of septic shock and some others. More details about the risk of complications should be consulted with a doctor.
Prevention of the spread of the disease
If the form of the disease is generalized, then patients are hospitalized. Other patients can also be hospitalized, but home isolation is also acceptable. Children in contact with sick people undergo a thorough medical examination and bacteriological examination of the nasopharynx.
Patients with convalescents freely enter educational and many other institutions, but only after the research of the nasopharynx has passed. It should be performed after discharge no more than a week or after the prescribed treatment.
Vaccination is possible. If there are indications, a serogroup A and C vaccine is administered.