Epilepsy is a chronic pathology, which causes an increase in electrical excitability in the cerebral cortex. In this case, a person has spontaneous attacks, that is, nothing provoked.
Epilepsy is a chronic pathology, which causes an increase in electrical excitability in the cerebral cortex. In this case, a person has spontaneous attacks, that is, nothing provoked.
Focal epilepsy is a form of a disease characterized by a heterogeneous origin. It is distinguished by the fact that when developing it can accurately determine the cortical focus of excitation. This focus, in this case, is the so-called "rhythm driver".
This is where the hypersynchronous discharge occurs, which extends to the near parts of the brain. This impulse affects a fairly large number of neurons in the cerebral cortex.
Focal epilepsy occurs in children at an early age. To be more exact, in 75% of patients with epilepsy it manifests itself in childhood. And is one of the most frequent children's neurological pathologies.
Statistics show that 70-80% of patients with focal epilepsy exhibit partial symptomatology, since only part of the cerebral cortex is affected in this case. That is, a person's attacks happen much less often.
This disease has not been fully studied to date. Despite the fact that it is quite old, since even Hippocrates first described it.
Contents
- What causes a violation
- Symptomatic form
- Cryptogenic form
- Idiopathic form
- Complex of diagnostic measures
- Nature of therapy
- Complications and prognosis
- How not to aggravate the state of
What causes a violation of
The causes of focal epilepsy can be various factors:
- traumatic brain injuryconcussion, severe head injury);
- inflammation of the brain tissue( meningitis, encephalitis);
- birth injury in children;
- viral infections;
- hypertension;
- cervical osteochondrosis, or another type, in which there is an acute violation of the blood circulation of the brain;
- dysgenesis of nervous tissue;
- stroke, aneurysm, development of neoplasms;
- as well as diseases of internal organs.
Various diseases of the internal organs, as well as diseases of the viral and infectious nature, often provoke the onset of epilepsy if they have been transferred to the feet or not treated at all.
It can be concluded that the cause of the manifestation of focal epilepsy is metabolic disturbances in certain areas of the brain and then an epileptic focus is already forming. And the above factors are the causes of metabolic disorders.
Focal epilepsy has several types, namely:
- symptomatic;
- is cryptogenic;
- is idiopathic.
Symptomatic form of
Symptomatic focal epilepsy always occurs due to other diseases of the nervous system. These include metabolic encephalopathy, hemorrhagic-type strokes and impaired blood circulation in the main cerebral vessels.
 Often epilepsy of a symptomatic type is caused by various neoplasms of the brain, abscesses, cysts and dysgenesis. And also injuries, bruises of the head and broken heart work.
Often epilepsy of a symptomatic type is caused by various neoplasms of the brain, abscesses, cysts and dysgenesis. And also injuries, bruises of the head and broken heart work.
For the symptomatic form it is characteristic that convulsive attacks occur spontaneously, but their nature depends on which part of the brain is affected.
With frontal epilepsy, seizures often last up to 30 seconds. At this moment a person performs strange movements and can talk violently.
If the focus is located in the frontal part, then you can observe such violations:
- The muscle spasm of appears in the limbs, neck, face, body and entire body. And hypertension of the hands is also possible.
- The patient withdraws and / or rolls his eyes, can simulate chewing, smacking, while the saliva is abundantly salivating .And also can be a mahi's head.
- Possible manifestations of of autonomic symptoms, automatism and hallucinations .
For frontal epilepsy is characterized by the manifestation of night attacks, they pass in a mild form. Since this excitement passes precisely along the foci, and does not divide into other parts of the brain. This manifests itself as sleepwalking, parasomnia and enuresis.
If the focus is localized in the temporal region, then there are:
- Various hallucinations ( auditory, visual or olfactory).Visual hallucinations can be colorful and have a frightening effect on the patient. In this case, the patient may be frozen with wide eyes.
- The pronounced symptomatology from the vegetative system - heart palpitations, attacks of nausea, excessive sweating, a feeling of heat.
- Euphoria and constantly repetitive thoughts of an obsessive nature.
- Sleepwalking .
If the focus is in the occipital region, then the optic nerve is affected. Namely, there is a temporary loss of the focus, there are circles in front of the eyes and even the eyeballs are trembling. These are the initial symptoms. 
But more serious disorders can appear, such as blindness, narrowing of the field of vision, the eyeball can turn toward the lesion focus. And also all this is accompanied by such symptoms as nausea, vomiting, pallor of the face and headaches.
Attack, this may take several minutes. But since this species is classified as progressive, after a time of attacks, there are pronounced vegetative disorders and disturbances in the social adaptation of a person.
Epileptic lesions of the parietal lobe are diagnosed very rarely. In this case, there is a disturbed sensitivity. There is also a burning sensation, pain and discomfort that spread from the brush to the face. Sometimes the pain extends to the groin and hip area.
There may also be a hallucination and / or illusion. It may seem to a person that large objects have become small and vice versa. Perhaps the violation of speech, the loss of ability to count, but at the same time the consciousness remains. Such attacks can last up to 2 minutes and, as a rule, during the day.
Cryptogenic form of
Cryptogenic focal epilepsy is distinguished by the fact that the true causes of the disease are unknown. That is, when carrying out all possible diagnostic methods it is not possible to determine the cause of epileptic seizures. This form of epilepsy is considered invisible.
Seizures may occur due to such factors: 
- bad habits, namely, the use of drugs, alcohol;
- external factors: bright light, too loud sounds, temperature changes;
- head injury;
- viral infectious diseases;
- impaired liver and kidney function.
Cryptogenic epilepsy is drug-resistant. At the same time, rapid changes occur in the metabolism. The exchange of fats is stable, and the amount of water constantly increases and accumulates in the body. As a result, an epileptic seizure occurs.
A seizure of a cryptogenic type is accompanied by loss of consciousness, apathy, neurological disorders also appear. After regular seizures, a person begins to develop mental disorders.
Cryptogenic brain damage can also be manifested by prolonged seizures. Before them there are always certain precursors. For example:
- insomnia;
- tachycardia;
- headache;
- hallucinations are characterized by a vision of fire, sparks, etc.
Idiopathic form of
For idiopathic focal epilepsy, it is common that seizures happen, but there are no structural changes in the brain. The causes of this disease are the most often genetic predisposition, and also if there are congenital anomalies of brain development and diseases of the psychoneurological type.
Idiopathic form can also develop due to toxic effects on the body, it can be with alcohol,  drugs or certain medications.
drugs or certain medications.
In idiopathic focal epilepsy, the focus of excitation is formed in one of the cerebral hemispheres. But the body gives a protective reaction and a protective shaft is formed around the hearth, which is capable of retaining an excessive electrical discharge. For a long time this is not enough and the discharge still passes defensive boundaries. It is at this moment that the first epileptic attack occurs.
The peculiarity of this form of the disease is that it is easily curable. And with the right approach, taking medications is reduced to a minimum.
Complex of diagnostic measures
Diagnostics begins with examination of the patient by a neurologist. In this case, the expert studies the anamnesis. It is necessary to clarify the data on the nature of the seizures, their duration, the sensations that the patient is experiencing at the same time, which factors become the triggering mechanism for the attack, etc.
It is also important for the doctor to know exactly which drugs have eased the patient's condition. Sometimes relatives can respond to similar questions, because often a person is unconscious at the time of an attack, with confused consciousness, etc.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental methods of brain research are always assigned. These include: 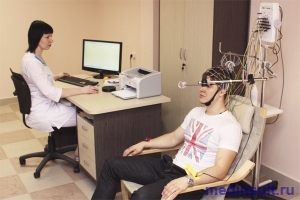
- magnetic resonance imaging( MRI);
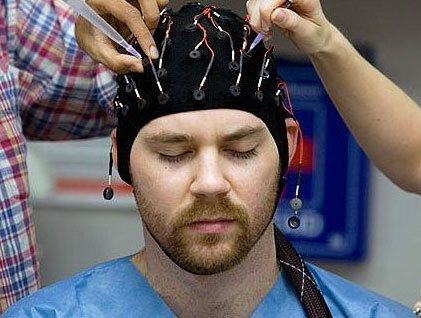
- electroencephalogram( EEG).
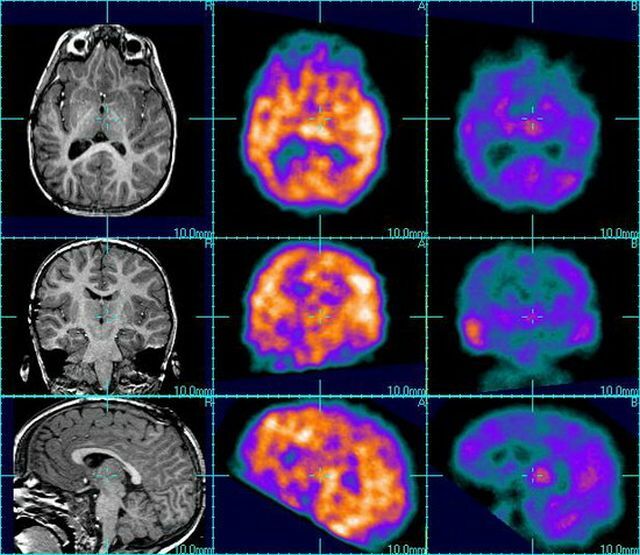
With the help of MRI it is possible to carry out all measurements of the brain, visualize it, which is very important in this case. A EEG will show the state of electrical impulses and violations in the process of their conduct.
Other studies are also being conducted. Namely, it is important to check the work of internal organs and to examine muscle tone.
The patient must pass a general blood test. With it, you can determine the presence of infections in the body, as well as learn the glucose, electrolytes, etc.
Additional instrumental methods are magnetic resonance spectroscopy and positron emission QD.
Nature of therapy
It should be understood that drug therapy in a patient with epilepsy will last a lifetime. In this regard, dosages are prescribed minimal( if possible) to reduce the likelihood of side effects, and then gradually increase them.
Antiepileptic drugs are prescribed. If the disease has arisen recently, then doctors prescribe monotherapy, that is, treatment with a single medicine.
Antiepileptic drugs include:
- Clobazam;
- Topiramate;
- Lacosamide;
- Zonisamide, etc.
Treatment of epilepsy can also be surgical. He is appointed if the patient's condition worsens and seizures become more and more frequent. And this has a very negative effect on the brain. 
The purpose of surgical treatment can be only if it is clearly diagnosed where the hearth is located. And while it does not affect the areas of the brain that are responsible for vital functions. During the operation, the affected areas are removed.
It is assumed that after this attacks are significantly reduced or even completely lost.
But the operation can also be performed on vital parts of the brain. In this case, the doctor makes incisions that prevent the spread of electrical discharges. These operations are called commissurotomy of the corpus callosum and functional hemisferectomy.
Complications and prognosis
Epilepsy can be complicated by such conditions:
- The epileptic status of is a series of seizures between which a person remains unconscious.
- Cerebral edema .
- Injuries to .A person is injured when a seizure occurs, as he can fall, hit, get into an accident when driving a car, etc. All this is fraught with fractures, concussion, traumas of the tongue, lips and even death.
- Mental disturbances of .
- Aspiration pneumonia and neurogenic pulmonary edema .
- Arrhythmia .
 With correctly selected medication, seizures are eliminated in 50% of cases. In 35% of patients, the number of seizures becomes less.
With correctly selected medication, seizures are eliminated in 50% of cases. In 35% of patients, the number of seizures becomes less.
With this disease, the prognosis can be favorable only if there is no organic brain damage.
In 70% of patients for whom no treatment is required in the hospital, there are no psychiatric abnormalities.20% of patients due to epilepsy have a slight decrease in intellectual abilities. Only 10% have severe mental health problems.
How not to aggravate the condition of
The main measures for the prevention of epilepsy are:
- not to consume alcohol, drugs;
- is not recommended to overheat, supercool, overeat, etc.;
- it is necessary to adhere to a diet and to observe a regimen of the day( a mode of rest and work);
- prohibits work at night;
People with epilepsy should always take medications prescribed by a doctor. And do not cancel them yourself, even if for a long time there were no seizures.