 Ventriculitis is an inflammation of the walls of the ventricles of the brain. This disease is also called ependymitis or periventricular purulent encephalitis. In most cases, this disease is the result of a transferred infection.
Ventriculitis is an inflammation of the walls of the ventricles of the brain. This disease is also called ependymitis or periventricular purulent encephalitis. In most cases, this disease is the result of a transferred infection.
This disease affects mainly newborn children. Very often the disease proceeds subacute in the form of serous inflammation and does not manifest itself as a characteristic clinical picture. Changes are visible in the region of the lateral ventricles of the brain and are expressed by spikes, cords in the lumen of the lateral ventricles, or bright condensed ependyma.
Features of the disease in newborns
Most often, ventriculitis occurs in newborn infants with low body weight( predominant in boys).The development of the disease is observed in 25% of cases of neonatal sepsis and only occasionally it can manifest itself as an individual lesion. The first symptoms of the disease are already observed in the first week of life and are often diagnosed as a lung disease.
The cause of the formation of cerebral abscesses is increased intracranial pressure, which may be an indication of an increased head size, bulging fontanel or vomiting. Suspicion of ependymitis in newborns occurs if the body does not respond to antimicrobial therapy.
Causes of the disease
The main provoking factors are three:
- Breakthrough pus from the abscess .In most cases, this is due to the compensated state of the patients. Thus suddenly
 there is a vomiting, a headache, frequent respiration, increase of pulse and sharp rise in temperature.
there is a vomiting, a headache, frequent respiration, increase of pulse and sharp rise in temperature. - Infections due to salmonella, fungi, enterobacteria and staphylococci .In this case, the infection has several ways of penetration. The first way is hematogenous, which is a consequence of the influence of a massive bacterium. Also, the infection can get into the brain with neurosurgical interventions, head injuries and infectious processes in the scalp. The source of such infections is primarily the mother. Also, it could be another sick child, staff taking birth, or ancillary tools used in delivering childbirth.
- Insertion into the microflora of the ventricles of the brain of foreign objects , wounding shells or bone fragments.
Newborn babies with neonatal sepsis are at risk. A high probability of the disease is present in people who have previously suffered craniocerebral trauma or surgical interventions on the brain.
Symptoms of
Symptoms of the disease are characteristic for purulent or serous ependymatitis. In this case, the clinical picture manifests itself as an acute and rapid regression of the general condition of the patient.
Tachycardia, hyperthermia, unbearable headache and vomiting appear. Against this background, a transition to a coma is possible. Observed pronounced changes in muscle tone. Often there are horizontal and vertical pareses of the gaze upward.
In case of taking a spinal puncture, a troubled cerebrospinal fluid with blood particles is observed. In the cerebrospinal fluid there are many cellular elements from the abscess. This content shows a high level of protein, about 18-20%.
Diagnostic methodologies
Diagnosis is based on the following diagnostic methods: 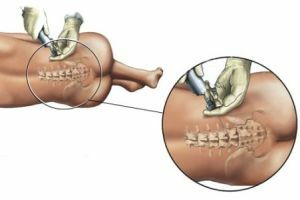
- Anamnesis and history of the clinical history.
- Taking a lumbar puncture .All the data that have been obtained complete the clinical picture and provide substantial reasons for the diagnosis.
- Comprehensive survey of .In this case, the following types of research are carried out: laboratory, clinical-neurological, computed tomography, ophthalmoscopy. If necessary, a study of ventricular cerebrospinal fluid using microscopy and bacteriological culture is carried out.
Methods of treatment
The essence of the treatment of ventriculitis is to eliminate the primary source of purulent infection and to increase the immunobiological protective forces of the body. First of all, antibiotic therapy is conducted. This treatment is used until the results of bacteriological studies. After this, correction of antimicrobial therapy is performed with replacement of medicines with less toxic ones.
The effectiveness of the therapy depends on the type of microbial pathogen and its susceptibility to antibiotics. The most harmful 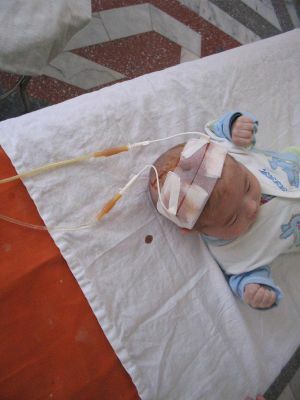 pathogens are gram negative microorganisms, which include enterobacteria, acinetobacter and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
pathogens are gram negative microorganisms, which include enterobacteria, acinetobacter and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The treatment also uses detoxification therapy with the connection of forced diuresis and glucocorticoids. The purpose of this therapy is to provide sufficient detoxification, rehydration and tissue perfusion. For this, 500 milliliters of sodium chloride solution with a parallel intake of 120 mg of prednisolone is intravenously administered.
In the development of occlusive phenomena, surgical intervention is performed. In this case, external ventricular drainage is established, through which the liquor is withdrawn and all the necessary medications are administered.
Consequences and prevention of
The following conditions are related to the consequences of the disease:
- asthenia and neurotic manifestations;
- hypothalamic and diencephalic syndrome;
- cerebrosthenic and asthenovegetative syndrome.
To prevent the onset of the disease, early surgical treatment of wounds, elimination of foreign bodies present in the brain should be performed. The basis for the prevention of posttraumatic ventriculitis is the activation of regenerative processes in the wound.