Hypoparathyroidism is a pathology that arises from the insufficiency of parathyrin. It is a hormone produced by the parathyroid glands. Sometimes it is also called parathyroid hormone. Also, the disease can occur against a background of impaired receptivity of tissue receptors to this hormone, and the result will be a decrease in its functional activity. The main sign of hypoparathyroidism is tonic convulsions.
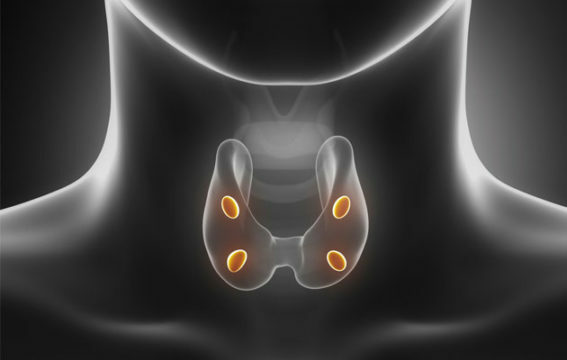
This is a fairly rare pathology that occurs in 0.3% of the population. Postoperatively, it is even less common. It can occur in any age group and lead to a violation of the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus.
Etiology
This disease usually develops for the following reasons:
- Surgical treatment of the thyroid gland or any other adjacent organ located in close proximity to the parathyroid glands. The trigger factor is their traumatic injury, in which case the disease is called postoperative hypoparathyroidism;
- Injury of the anterior surface of the neck, at which a hemorrhage appeared in the parathyroid gland;
- Inflammatory organ processes;
- Oncological processes characterized by metastatic screenings into the thyroid or parathyroid glands;
- Violation of the formation, development of the organ;
- Exposure to active iodine to correct diffuse toxic goiter;
- Comorbid pathology in other endocrinological diseases in the form of polyendocrine syndrome( for example, with adrenal, thyroid or pancreatic gland disorders);
- Consequence of autoimmune processes - amyloidosis, allergies to iodine.
Pathogenesis of
The regulation of the metabolism of phosphorus and potassium in the human body occurs under the influence of parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, a product of the thyroid gland, vitamin D. When there is a deficit of parathyroid hormone, the equilibrium between these elements is disturbed, which leads to a violation of the permeability of cell membranes. The end result of the pathogenetic chain is the excessive excitability of the nerve and muscle fibers, manifested by the development of seizures. The second important manifestation of the disease is the deposition of calcium salts in internal organs, on the endothelium of the vascular walls.

Classification of
Clinical forms of the disease differ in the course of the nature of the process. To date, the classification includes the following:
- Acute. This condition is difficult to treat. It is manifested by frequent and severe convulsive attacks;
- Chronic. Attacks are rare, arise due to various provoking factors - infectious diseases, excessive physical stress, stressful situations, psychological traumas, menstrual disorders in women. Exacerbations occur in the spring-summer period. With the appointment of the right therapy, a long and persistent remission is achieved;
- Hidden or latent. It is characterized by the absence of any external signs, but it is diagnosed fairly well during the examination.
Classification can also be based on the etiologic factor:
- Postoperative hypoparathyroidism;
- Idiopathic;
- Autoimmune;
- Congenital;
- Post-traumatic.
Clinical picture
The disease is characterized by the fact that all the main symptoms are combined into symptom-complexes, called syndromes. Each of them develops approximately by the same mechanisms and displays the state of the organism. There are four syndromes:
- Convulsive or tetanic. It includes excessive nervous and muscular excitability and spasmophilia;
- Disturbance of sensitivity and autonomic functions. Developed pathologies of internal organs work;
- The defeat of the nervous system is manifested by cerebral and spinal dysfunction;
- Trophic disorders. There is a decrease in trophism of the skin, manifested by ulcerative defects.
The most important symptomatic complex of this disease is tetany, which manifests itself in the form of tonic convulsions. Nervous and muscular excitability is usually associated with a deficiency or functional inability of parathyroid hormone for various reasons. As a result, strong muscle contractions develop, which proceed with pronounced pain sensations.
Quite often before the onset of an attack, there may be harbingers. These may include muscle stiffness, the presence of a sensation of numbness and creeps on the fingers of all limbs and in the region of the nasolabial triangle. After these precursors have passed, convulsions develop, which are characterized by symmetry. In this case, the upper and lower limbs may contract alternately - first alone, then others. Very rarely such phenomena develop in the facial muscles or muscles of the internal organs.
It should be noted that convulsive syndrome is always combined with muscle pain. The mild form of the disease provokes such a condition several times a week, they rarely last more than five minutes. But, if a serious form of pathology has developed, the tetany phenomena can accompany the patient not only daily, but also 5-7 times a day, and their duration can reach several hours. Perhaps their spontaneous appearance, as well as their development is possible on the background of various stimuli.
Spasms pass with fluctuations in blood pressure, they are always accompanied by tachycardia and pallor of the skin, digestion can be severely impaired. With prolonged attacks, patients experience episodes of loss of consciousness.
Postoperative hypoparathyroidism
Postoperative hypothyroidism today is one of the most controversial issues. This is due to a decrease in blood calcium levels in patients after surgical interventions for the pathological conditions of the thyroid and parathyroid glands in the postoperative period. Such a condition arises from their possible resection or total removal.
Sometimes these organs are damaged, which leads to hemorrhage in the tissues of the parathyroid glands. The consequence of this often develops fibrosis of the gland. It should be noted that this pathology can sometimes be transient in nature, especially in cases where the glands were not severely damaged and the process of fibrosis did not affect the functional areas of the tissues. Constant character develops with severe organ damage.
Treatment of
The therapy of this pathology is controlled by an endocrinologist. The same specialist is involved in the prevention of convulsions. Treatment includes a diet with a high content of trace elements such as potassium and magnesium, limited to dishes containing phosphorus.

Advantage is given to lactic acid foods, fresh fruits and vegetables. Exacerbation of chronic hypoparathyroidism implies a restriction, and with a severe degree of severity of the process - the rejection of meat. It is extremely important to include in the diet those products that contain ergocalciferol. These include egg yolk, fish oil and liver.
Drug therapy is aimed at replenishing calcium deficiency by prescribing drugs containing it. It is also necessary to prescribe to the patient medications that improve the absorption processes in the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the fact that calcium is not always well absorbed. To achieve maximum results, he needs vitamin D.
For the purpose of producing endogenous vitamin D, the patient is recommended to use solar baths and physiotherapeutic treatment with UFO apparatus. In order to determine the restoration of the level of essential trace elements, the patient must regularly take a blood test.
The fight against tetanus attacks is carried out by the appointment of anticonvulsant and sedative drugs. They may include narcotic drugs. In order to relieve the hypocalcemic crisis, patients are given calcium gluconate as an emergency aid.
Forecast
The prognosis for hypoparathyroidism is favorable if the patient complies with all medical recommendations. Pathology is monitored quarterly, and twice a year it is necessary to undergo an oculist to detect cataracts at an early stage.