 Dysarthria is a speech pathology that occurs as a result of impairment of impulse transmission in the area of the neural pathways of the speech device.
Dysarthria is a speech pathology that occurs as a result of impairment of impulse transmission in the area of the neural pathways of the speech device.
The severity of speech pathology depends on the localization and degree of damage to the peripheral and central nervous system, and also directly depends on the intrauterine development of the child and on the age at which the primary defect leading to the development of dysarthria was discovered.
Dysarthria is manifested primarily as a pathological disorder of the articular apparatus due to various lesions of brain structures and its departments. It manifests itself in the form of violations of the muscular tonus of the speech apparatus, voice and respiratory system, which leads to underdevelopment of the verbal means of communication and communication in general.
In dysarthria, a disorder of phonemic perception and lexico-grammatical speech is observed, as well as an underdevelopment of the VFR( higher mental functions).
Content of
- Factors affecting the development of a disorder
- Development of a disorder
- Early diagnosis of dysarthria in children
- Dysarthria in adulthood
- Bulbar disorder
- Pseudobulbar disorder
- Cerebrosis dysarthria
- Subcortical disorder
- Cortical form of disorder
- Diagnosis
- Basic methodscorrection of speech development
- Speech massage: basics and tips
- Articulatory gymnastics
- Development of articletranslational vibration motor
- gymnastics
- Setting proper breathing
- Extension diaphragmatic breathing
- Development of a disorder
Factors affecting the development of disorders
psychosomatic and psychomotor development of the child is a complex process, since any negative factor could affect its development adversely. To such unfavorable factors are:
- intrauterine infectious lesions;
- intrauterine oxygen deficiency;
- intoxication of the CNS;
- manifestations of toxicosis;
- birth before the due date;
- birth injury.
Together with fetal development and innate CNS features, the social environment that  is able to provide a supportive and stimulating function for the development of the child and, on the contrary, to exert a depressing, deprivating role, plays a significant role in development.
is able to provide a supportive and stimulating function for the development of the child and, on the contrary, to exert a depressing, deprivating role, plays a significant role in development.
So, after birth, a major role is played by the transmitted infections, head injuries, which lead to intoxication not only of the central nervous system, but also of the brain.
Such adverse factors cause organic damage to the peripheral and central nervous system, resulting in violations of cognitive processes, hearing, vision, and motor skills. Thus, dysarthria in children is observed in cases of cerebral palsy in more than 80% of cases.
Development of Childhood Disorder
In connection with numerous studies and studies of the dynamics of neurological development of the child in the postnatal period, experts argue that the dysarthria in children is of a mixed specific character, since lesions are characterized by localization in different parts of the brain.
The following are the most common forms of dysarthria in children:
- The spastic-parietal form of has all the signs of pseudobulbar dysarthria in adults. Main symptoms: phonetic speech is impaired;weak articulatory apparatus;complexity of reproduction of arbitrary movements;high tone of the muscles of the speech apparatus;presence of violent movements;constant stable tremor, the child is not able to open his mouth arbitrarily. The development of this form of violation is characterized by the late appearance of walking, babbling and sound reproduction. At later stages of development speech remains vague, passive, monotonous. Before the articulatory movement is carried out, the tone of the muscles sharply increases, leading to spasm - the tongue is pulled back and folded by a lump.
- Hyperkinetic form of is characterized by abrupt and unstable muscle tone of the articular apparatus, as a result of which it manifests itself in the form of dysarthria and dyskinesia. Subcortical lesions are observed, as a result of which there is a disorder of speech breathing, as well as manifestation of instability of speech sounds. This form of dysarthria is amenable to correction.
- Atonic-astatic form is observed most often in cerebral palsy. Symptomatology is characterized by mixed signs: violation of the speech apparatus - a thin sharp tongue, sluggishly located at the bottom of the oral cavity, the language is inactive;There is a sagging of the palate and loss of sensitivity of both cheeks;speech impetuous, it accelerates, then slows down. There is an unreasonable change in the modulations of the voice, the speech is chanted, chopped and accompanied by cries. In children with this type of dysarthria, there are violations of pronunciation of sounds from simple to complex. Training and correction is difficult, because such children are not critical of the situation.
Early diagnostics of dysarthria in children
Before performing such a diagnosis as a dysarthria of speech, specialists focus primarily on indicators that indicate a certain level of development of the child's motor skills, its functional features of the psyche and the speech device.
Coverage and consideration of the above indicators allows specialists to adequately assess the overall clinical picture and to identify disorders and abnormalities in the central nervous system of the child.
In the period from the newborn with the transition to infancy, three main stages of development of psychomotor activity are singled out:
- The first stage covers the age period from the first days of life to six months of .Characterized as a thalampopallar stage. The child at this stage is characterized by erratic movements with increased tone: the arms are tense, the hands are clenched into fists;legs bent at the knees, a step reflex is observed;grasping reflex. All these involuntary movements are under the control of the spinal cord. Closer to 6 months, the child gradually reflexes disappear, to replace which appear motor functions of an arbitrary nature. If involuntary movements persist for more than six months, specialists diagnose a motor disorder of a central character.
- The second stage covers the age range of the child from six months to 11 months of .This stage is called striopallidal. At this stage, the child noticeably normalizes active movements, the child holds a toy in his hands, independently sits, distinguishes sounds, recognizes his own and others'.The main sign that development corresponds to age characteristics is babbling. So, the child begins to form an articulatory apparatus, and with it the pronunciation of vowels and some of the front-language sounds. The child distinguishes between speech, begins to understand the meaning of words, characterizing objects and emotions.

- The third stage covers the age from one year to three years .At this stage, there is a development of cortical and subcortical structures. The child makes fine movements of the hands, creeps, then begins to walk. Distinguishes intonation, and by the year words accumulating meaningful and emotionally positive load accumulate. The child has his own speech, and thanks to auditory reverse afferent connections, the phonetics of the native language begins to form in the child. If the child's speech apparatus develops within the limits of the norm, then the speech breathing will be characterized as smooth, measured, without manifestations of pauses. At this stage, with proper development, the overlying parts of the brain begin to subordinate the underlying structures of the brain.
The generally accepted information on the step-by-step formation of the child's central nervous system and the child's VPF allows specialists to identify in a timely manner violations of speech development.
The crying of a child with organic lesions of the CNS and brain is qualitatively different from the crying of a healthy child, and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- short;
- uniformity, without intonation and voicing;
- for no apparent reason;
- by suddenness.
Symptoms of dysarthria include such signs, manifested in the process of breastfeeding:
- sluggish sucking;
- incomplete nipple grip;
- milk flows out of the mouth;
- milk flows from the sinuses of the nose;
- flooding.
Also, dysarthria in young children has the following symptoms:
- The signs of the walk are manifested in later periods, vocalization and babbling are characterized by a limited repertoire.

- The timing of all speech phases is late in comparison with the norm for 3-4 months. As soon as speech begins to appear, words are uttered indistinctly, blurred, inarticulate.
- The vocabulary of against the background of children with normal development is very poor.
- The sound and phonetic part of the speech is not sufficiently differentiated. The voice is quiet, hoarse, hoarse, the intonation is even, the rhythm is undulating. Such factors are associated with delay and impairment of respiratory function, as a result of oxygen deficiency, as well as with birth trauma.
- The phrasal speech of is delayed in development, the lexical part of speech is not formed.
- Speech device is often characterized by weakness or hardness of the sky, shortened frenum.
If a parent finds a child with more than the above two signs, you should contact a specialist.
Dysarthria in adulthood
Dysarthria in preschool children, adolescents and adults is caused by complex speech disorders, which are expressed in soundproofing. Disturbances are associated with the pathological processes of the neuromotor apparatus of the muscles responsible for the production of oral speech.
There are the following main clinical forms of adult dysarthria.
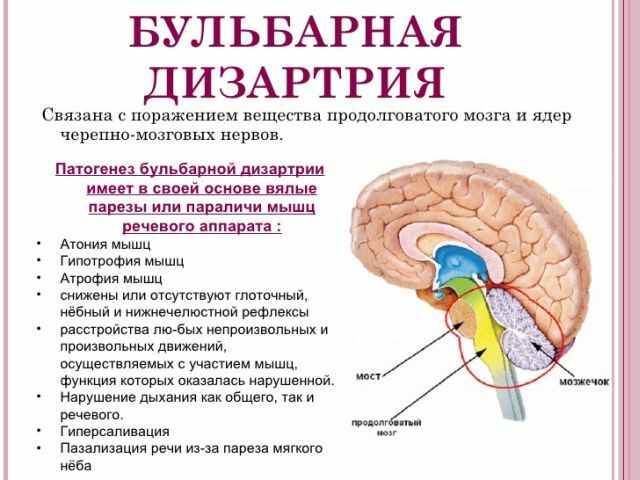
Bulbar disorder
Bulbar dysarthria is a disorder of the articulatory apparatus, as a result of neuronal damage in the medulla oblongata. Against this background, there is a decrease in the tone of the muscles of the nasopharynx, the palate, and the larynx. Speech is weak, nasal, blurred, indistinct, difficult to comprehend. People have an understanding of auditory and written speech, as well as reading to themselves.
Violated:
- speech articulation;
- grammatical structure;
- expression of one's own thought;
- use of the dictionary in its entirety.
Due to the blocking of nerve impulses coming along the peripheral nerve to the muscles of the speech device, the following speech disorders are observed in the patients:
- paresis of the backrest - the sound "l" gives out the sound "in", for example, "spoon "-" vozhka "-" okzhka ";
- paresis of muscles on the tip of the tongue distorts the pronunciation of the sound "p", the output is "frame" - "ama" - "lama".
- paresis of the muscles of the basal part of the tongue , the posterior pronunciation of sounds is disturbed, for example, "doll" - "tula" or "horn" - "vokha".
- paresis of labial and circular muscles of the mouth leads to the disturbance of explosive sounds, for example, "barrel" - "kidney" or "brush" - "mesh".
Pseudobulbar disorder
Pseudobulbar dysarthria is manifested as a result of nonspecific termination of motor neuron connection in the cortex of the cerebral hemispheres with the motor neuron of the spinal or medulla oblongata. The patient is not able to perform arbitrary movements, but the involuntary ones remain intact.
So, the patient at the request of a specialist can not stick his tongue out( arbitrary action), but is able to lick his lips while eating( involuntary movement).
The crying is accompanied by a voice, but when you try to say anything, there is no voice. When examining the patient, you can see that the muscles of the tongue are weakened, unable to hold the desired posture. When asked to show the language, the patient protrudes and quickly draws the tongue back.
All movements of the tongue are characterized by low amplitude, there is a moderate salivation in the process of speech, as well as by writing. Breathing and speech cycles are shortened, as a result of which clipping of phrases is observed.
Cerebrosis dysarthria
Cerebellar dysarthria develops as a result of damage to the nuclei and the conduction pathways of the cerebellum and is due to the weakness of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus and the weak tone of the soft palate, a sluggishness of the tongue is observed.
The face in patients is characterized as amygmous, sad, there are local lesions of the nasopharynx and respiratory processes.
When examining the oral cavity of the patient, a thin and sharp tongue is observed, pressed to the bottom of the oral cavity, the movement of the tongue is sluggish, the mobility is limited, the amplitude is reduced, the sky is saggy; speech is characterized as:
- slow;

- scanned;
- is indistinct;
- segmented;
- featureless;
- nuzzling.
In individuals with cerebellar involvement and its pathways, the following complex disorders are observed:
- muscle tone relaxation;
- speech attenuation, pauses or chants;
- breakdown of stressed syllables, which causes slurred speech;
- ataxia during breathing leads to a tremor in the voice.
Cerebrospinal disorder produces tension in speech, often the patient's speech is accompanied by such reactions as redness of the face.

Violation at subcortical level
Extrapyramidal dysarthria( subcortical) manifests itself in focal lesions of basal nuclei( lenticular, pale and caudate nucleus, thalamus and subthalamic structures of the brain).
Lesions result in the following:
- increases muscle tone;
- tonic activity;
- congenital oral automatisms.
Disorders associated with the extrapyramidal system lead to various muscle stereotypes, stamps, so in patients there is tremor and athetosis( freeze in a certain position).In the vast majority of cases, muscle tone rises with a slight attempt to say something or move, often this tone reaches a peak - muscle spasms.
Violation of tonic activity leads to respiratory disorders, as well as to disorders of voice formation and speech breath, against which there is a violent opening of the mouth or throwing the tongue forward, while the patient freezes in this position for several minutes.
When subcortical structures are affected, sudden involuntary movements in various muscle groups are observed. The patient may have uncontrolled manifestations of laughter or crying, as well as moaning and stopping speech.
Oral speech with subcortical lesions is characterized as intermittent and flowing, so the patient may be talking from acceleration to deceleration. Therefore, speech may be indistinct, blurred or vice versa, too legible, pronounced in syllables.
Voice modulation can vary from a monotonous pace to an impetuous nature of speech.
Cortical form of disorder
Cortic dysarthria is caused by damage to the secondary motor zones of the cerebral hemispheres. With this form of violation, there is a loss of arbitrary speech, while the understanding of words and phrases is preserved. Such disorders can appear - the patient, at the request, can not stretch his lips, cheat his cheeks, stick his tongue out. Although patients can perform all these actions with involuntary movement.
Similar dysarthria is characterized by the absence of such manifestations as involuntary salivation, lack of voice, fading in the pose, bouts of breathing.
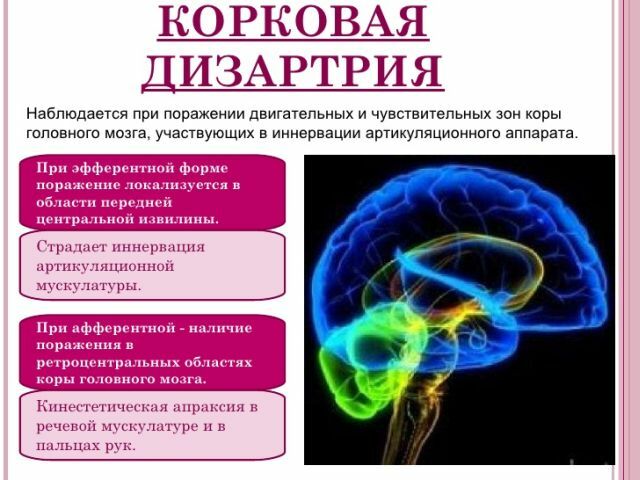
Depending on the lesion focus, there are two more types of this form of disorder:
- efferent cortical dysarthria;
- afferent cortical dysarthria.
The efferent( premotor) form of the disorder manifests itself against the background of the lesion of the anterior central gyrus, which is responsible for the transfer of momentum from the brain to the articulatory apparatus. In this regard, efferent cortical dysarthria is characterized by such manifestations in speech as:
- high frequency of pauses;
- is predominantly positional;
- speech is spasmodic;
- intonation varies from low voice to high.
So in a patient's speech one can hear an average change in vowel sounds, for example, "o" - "y".Elongation of vowels - "sszadi", "vvvede", etc., as well as the addition of sounds "beautiful" - "krasivy".Removing( skipping) sounds - "simple" - "postoy", "smart" - "wise."
Afferent( postcentral) cortical dysarthria is manifested mainly in neoplasms in the brain.
Violation is accompanied by intensified and sustained searches for correct articulation. So, the patient's speech during the search is constantly interrupted, disrupting the fluency of speech. Sometimes such searches are replaced by the type of stammering. General speech pattern:
- blurred;
- dissected;
- is indistinct.
In turn, in neurophysiology, according to the classification, 2 subtypes of afferent dysarthria are distinguished:
- Paresis of articulatory muscles .Disorders of movements of the tip of the tongue are observed, which violates the pronunciation of "ж", "ш", "р", with complex violations - "с", "з", "л".This or that position of the language is not remembered or held in the motor memory. In such situations, articulatory movements are performed only with visual control, in the absence of it, patients try to perform such movement with the help of hands, namely, they grope for the tongue, direct, lower and lift it.
- Articulatory apraxia .There is an increased tone of the muscles of the tip of the tongue, so the pronunciation of only the front-language sounds is disrupted. Often in the speech of the patient you can hear the difficulty of moving from one sound to another.
Diagnosis of
The examination for dysarthria is performed primarily by a neuropathologist, taking into account the conclusion of a speech therapist and a defectologist.
 Before you make a diagnosis, take into account the age and physiological characteristics of the child. The conclusion of the neurologist is based on the mother's history, the pattern of pregnancy and the presence of affected areas of the brain.
Before you make a diagnosis, take into account the age and physiological characteristics of the child. The conclusion of the neurologist is based on the mother's history, the pattern of pregnancy and the presence of affected areas of the brain.
The peculiarities of the articulatory apparatus violation, the state of speech and facial muscles, the nature of the course of breathing and its volume are studied. To make an accurate diagnosis, hardware diagnostics are carried out, namely, brain MRI, electroencephalography and electromyography.
Speech therapist builds conclusions based on the rhythm, speech rate of the child. Evaluates the clarity of pronunciation of sounds, as well as the synchronization of voice formation.
The defectologist evaluates the lexical structure of the child's speech and phonemic perception.
The main recommendations of specialists - timely access for help with the detection of signs of pronunciation disorders and in the work of the speech device.
Basic methods of correction of speech development
Prophylactic and therapeutic therapy begins after a deep diagnosis. Timely implementation of diagnosis and treatment will eliminate the unfavorable development of the child's psychomotor.
The corrective program for children with dysarthria is based on the results obtained through a comprehensive examination.
Speech massage: basics and tips
The main corrective method for dysarthria is a speech therapy massage, the purpose of which is the normalization of the muscular  tone of the peripheral articulatory apparatus.
tone of the peripheral articulatory apparatus.
For children with normal psychophysical development, as well as without pathological manifestations associated with the musculoskeletal system, but who have diagnosed dysarthria, a self-massage technique is performed.
For self-massage, a special speech-therapy brush is used, which is put on the index finger of the child. With the help of such a massager, the child is invited to do several exercises:
- stroking the cheeks, tongue, palate and gums in all directions;
- make circular motions brush in the mouth.
- hold the brush at the level of the lips at a distance of 2-3 cm and ask the child to reach the brush with the tongue;
- to try with a brush in the mouth to pronounce the words "cotton wool", "vase", "water".

Self-massage activates the motor and muscular sensitivity of the articulatory apparatus. Muscles of the speech apparatus during the above exercises are in a tone, which stabilizes the basic function of the speech apparatus - articulation.
How to do logopedic massage with dysarthria - master class with video:
Articulatory gymnastics
Articulatory gymnastics is prescribed for children who have violations of small and large motor skills along with dysarthria.
The correction is carried out with the help of a specialist and includes the following exercises:
- Passive hand massage - stroking the hands from the outer and inner sides, squeezing-opening of the jaws with resistance, rapid movement from the tip to the base of the finger.
- Active hand massage - brushing on the specialist's hand, circular movements of the brush with the brush away then to the right, then to the left, alternately flexing and extension of the fingers.
- Massage of the tongue .To relax the muscles of the tongue, the specialist asks the child to stick out his tongue, usually the tongue in children with dysarthria is characterized by high tension, a great similarity with the lump. Specialist with a special spatula starts to pat on the tongue, under the influence of which the tongue relaxes for a while, softens. This exercise is repeated 3-4 times, showing the tongue does not take a flattened position. After several sessions, this exercise is carried out to hold and fix the relaxation of the tongue, lips, cheeks.
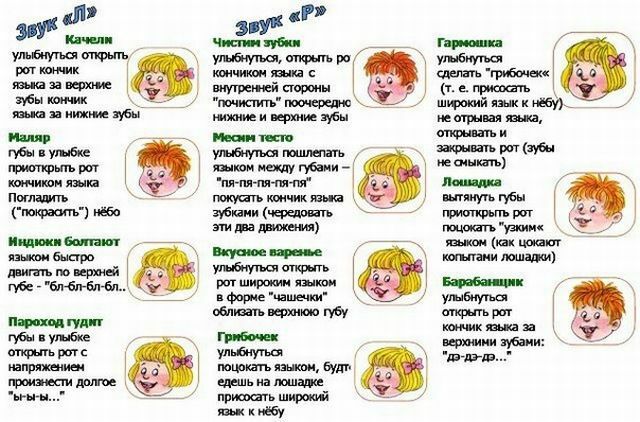
Sound setting "C" and "P" with dysarthria
Development of articulatory motility
This technique is aimed at activating the muscles of the speech device as a whole:
- passive language movements - pulling the tongue forward, back, top, bottom;
- circular movements of the tongue on the lips in a clockwise and counterclockwise direction;
- stretching the lips into a tube, stretching the lips into a smile;
- put your lips to the sounds of "a", "s", "e", "y";
- chewing movements, open and close your mouth, swallowing saliva;
- simultaneous and alternate inflation of cheeks.
Vibrating gymnastics
This technique is focused on the activation of vocal cords. For this, the child is asked to bring one hand to the larynx of the speech therapist, the other to his larynx. The specialist stretches out the sound "m" and asks the child to feel how the specialist's larynx starts to vibrate, then asks the child to repeat the sound and fix the vibrations of his larynx.
Next is a series of exercises for short sounds, for intonation through vowels, for raising and lowering the sound. Thanks to this technique, the child regains speech breathing, and also modulates the voice, the power of sound.
Setting the right breathing
Techniques for breathing are carried out to expand the capabilities of the respiratory apparatus. The work on development of speech breathing is conditioned by the following exercises:
- Formation of a long inhaled and exhaled through the mouth .Respiratory exercises are performed by a specialist, indicating that for this exercise, it is necessary to engage diaphragmatic rib breathing. Then the specialist helps the child to repeat the exercise.
- Expansion of the child's physiological capabilities for speech exhalation .This technique begins with relieving tension in the shoulder girdle, then setting the press in the abdominal cavity and only then a series of smooth speech is organized. A short sentence is chosen, and the child is asked to repeat it in the course of one continuous exhalation.
Extension of diaphragmatic breathing
This technique is performed in a prone position. At the first stage, the child needs to relax all muscles. Then connect the game tricks: 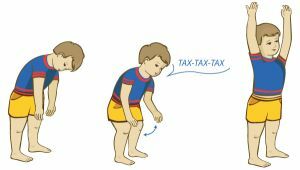
- Exercise "Breath-exhale" .Any playing activity is set, during which you should take a deep breath and a long exhalation.
- Exercise "Repeat Melody" .This technique should also be conducted in a game form. To do this, it is necessary to develop the melodic characteristics of the child's voice with the help of vowels. Then learn to intone, then form a voice. For example, when breathing out, it is time to pronounce the sound "a", the specialist should make sure that the sound is pronounced continuously during exhalation, and also that there is no additional exhalations.
- The voice of can be formed by changing the pitch of the voice. For example, with the help of sounds - "oh", "a", "y", "and" convey emotions, such as surprise, joy, regret, etc.
To prevent the development of dysarthria in a child, it is necessary to undergo examinations with a neuropathologist from the first days of a child's life.
Inspection of a specialist is very important even in cases when the child does not have disorders and lesions of the brain. For the development of dysarthria it is enough if the pregnancy has been severe or there has been frequent and persistent toxicosis.
Timely appeal to specialists, will help to level or completely eliminate signs of a violation in speech.



