Autoimmune thyroiditis is an inflammatory process in the cells of the thyroid gland, associated with the pathological destruction of the follicles of the organ itself. Often the disease occurs without obvious symptoms and is often diagnosed accidentally, when diagnosing other diseases.
Classification of
Autoimmune thyroiditis can have a variety of etiologies and flow patterns, as well as a clinical picture. Therefore, several types are distinguished:
- Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis is also called Hashimoto's goiter or lymphatic thyroiditis. It progresses due to the penetration of lymphocytes into the cells of the thyroid gland, increasing the concentration of antibodies, which gradually destroy the organ. Due to organic changes in the gland, hypothyroidism may occur. Chronic AIT is often a genetic disease.
- Thyroiditis of the postpartum period is considered the most studied. Due to weakening of the immune system during pregnancy, after the birth, an accelerated and often sharp increase in the activity of the immune system begins, which causes the disease.
- Cytokine-induced thyroiditis appears with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications against hepatitis C and blood or lymph pathologies.
- Bezbolovoy thyroiditis is also called silent. He is similar in symptomatology to the second type, but his etiology is not fully understood.
The last three types of thyroiditis are similar to the stages of development of changes in the thyroid gland. First, thyrotoxicosis develops, then hypothyroidism, which in many cases ends with the restoration of the natural function of the thyroid gland.
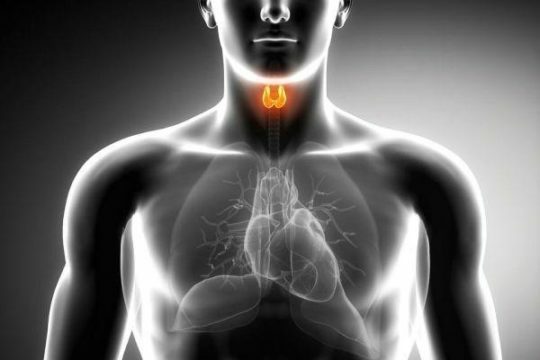
Phases of the disease
Any autoimmune thyroiditis can be divided into several stages of the development of the disease:
- The euthyroid phase - the functionality of the thyroid gland is not disturbed, and the stage itself can last several tens of years.
- Subclinical phase - with the progression of the first phase, mass attacks of lymphocytes on the gland begin to lead to its destruction and decrease in the amount of thyroid hormones produced.
- Thyrotoxic period - with the active growth of attacks of lymphocytes, the available amount of thyroid secret is released into the blood, which leads to poisoning of the body, which is called thyrotoxicosis. In the blood are also found the remains of the follicle of the gland, which also contribute to the active production of lymphocytes.
- Hypothyroidism is the last phase that most often ends with the normalization of thyroid function, but it can continue for a long time without adequate therapy.
Often autoimmune thyroiditis passes monophasically, lingering in the third or fourth stage.
Diagnosis
Unfortunately, until the last stage the diagnosis of autoimmune thyroiditis is difficult. Diagnosis of hypothyroidism occurs according to the patient's complaints, as well as the results of laboratory tests. If other family members find such diseases, the endocrinologist can make a diagnosis with confidence.
Laboratory diagnosis of autoimmune thyroiditis implies:
- A general blood test - is being investigated to determine elevated concentrations of lymphocytes.
- Immunogram - shows the presence of antibodies to thyroid hormones, thyroglobulin, thyroid peroxidase.
- Blood test for T4 and T3, TSH - determine the general and free hormones of T4 and T3, TSH is determined in serum. By the concentration and the ratio of these hormones, you can determine the stage of the disease. For example, elevated TSH and T4 normally corresponds to subclinical hypothyroidism, and the same TSH with reduced T4 corresponds to clinical hypothyroidism.
- One of the most important methods of research is ultrasound thyroid. Helps evaluate the parameters of the gland, pathological changes in the structure.
- Biopsy - examination is carried out by a thin needle method, allowing to find out large concentrations of lymphocytes. It is carried out if there is a possibility of degeneration of the nodes into malignant formations.
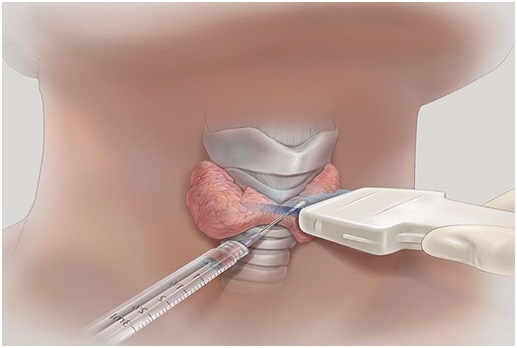
Diagnosis of autoimmune thyroiditis complex contains such components as increase of AT-TPO in the blood - circulating antibodies to the thyroid gland, as well as hypoechogenicity of the gland on ultrasound and clinical symptomatic signs of hypothyroidism.
The presence of only one of these indicators can only be indicative of the disease. Treatment is prescribed only in the hypothyroid phase, therefore at earlier stages the diagnosis of the disease does not make sense.
Symptoms of
In 85% of cases, autoimmune thyroiditis has been asymptomatic for several years. The organ does not change in size, palpation does not bring painful sensations, and hormonal changes do not cause obvious disorders to provoke a diagnosis.
Occasionally the patient complains of a slight increase in the thyroid gland, which is called goiter, it also causes a lumpy feeling in the throat and discomfort, squeezing. There is a slight weakness, joints can hurt.
Thyrotoxicosis is diagnosed in the first or second year after the onset of the disease. It is characterized by a fairly vivid symptomatology: a sharp weight loss for no apparent reason, emotional instability, weak nails, hair loss, pale skin.
Thyroiditis, which occurs after childbirth, may manifest as thyrotoxicosis in mild form. The reason for addressing the endocrinologist is fast fatigue, weakness, a sharp decrease in weight. In more pronounced forms arrythmia, tachycardia, tremor, sweating, a feeling of heat arises. Such symptoms can be seen at week 14 after childbirth.

Bezbolovoy thyroiditis in some cases manifests a slight thyrotoxicosis, and cytokine-induced can be completely not accompanied by thyrotoxicosis.
It is compulsory to undergo hormonal research during postpartum depression, as it often coincides with endocrine diseases, and sometimes even becomes their consequence due to emotional lability.
Causes of the disease
Even in cases where heredity occurs, only external or internal factors can cause active development of the disease. Factors of thyroiditis development can be:
- Postponed viral diseases or acute infectious, with complications.
- Presence of a chronic infection in the body, for example, caries, sinuses of the nose with infection, chronic tonsillitis.
- High concentration of halogens in food, water, environment, a special effect is iodine, chlorine, fluorine, which increase the activity of lymphocytes.
- Constant influence of radiation radiation, or excessive exposure to the scorching sun.
- The use of hormonal drugs and iodine containing drugs with an inadequate treatment regimen.
- Circumstances with severe psychological trauma. These can be loss of loved ones, loss of housing, work, disappointment.

Any of these factors can provoke reactivity of lymphocytes against the thyroid gland, especially if there is an effect of hereditary factors.
Forms of autoimmune thyroiditis
Depending on the intensity of clinical manifestations, changes in the body of the gland and its size, several forms of autoimmune thyroiditis are divided:
- The latent form implies the presence of only immunological signs, without bright symptoms. The gland does not change in size, there may be only a slight increase, there are no nodal seals, the organ regularly performs its functions. Sometimes a patient may experience increased sweating or emotional instability.
- Hypertrophic form of thyroiditis - accompanied by an increase in the size of the gland, there are symptoms of mild thyrotoxicosis. The gland can be uniformly increased, which is called the diffuse form, or it is partially enlarged to form nodes. There can be a combination of these forms. The organ function remains stable, but begins to gradually decrease.
- The atrophic form indicates a change in the size of the organ with symptomatic hypothyroidism. The most severe form can be a sharp decrease in the function of the gland.
Any of these forms undergoes effective treatment. This may be hormone replacement therapy, which ends after several courses with a gradual decrease in the concentration of the hormone, or continue throughout life, which, in general, does not reduce the quality of life of the patient.