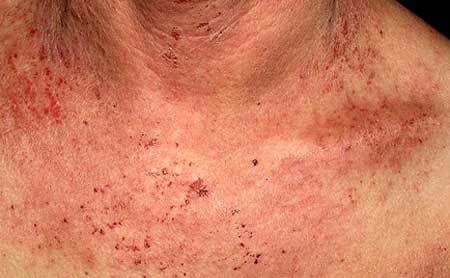
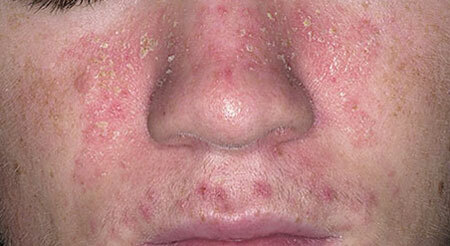
Microsporia, called folk ringworm, is an infectious disease transmitted from sick animals. That is why the characteristic spots on the skin most often appear in children who like to mess with cats and dogs( especially homeless people).
To prevent the spread of pathological spots in a patient and to infect healthy people, the first signs characteristic of the initial stage of microsporia and the compulsory medical measures should be known.
Contents of
- 1 Microsporia - what is it?
- 1.1 Microsporia in children - features of
- 2 Symptoms of microsporia in humans, photos
- 2.1 Microsporia of smooth skin
- 2.2 Microsporia of the scalp
- 2.3 Atypical forms
- 3 Treatment of microsporia in humans, preparations
- 4 Microsporia prophylaxis
Microsporia - what is it??
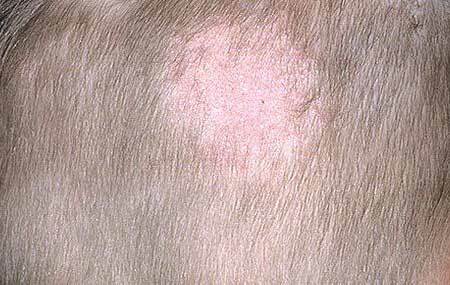
Microsporia is a skin disease from a group of mycoses, provoked by infection with the fungus Microsporum. Manifestations( signs) occur both on the smooth and the scalp of the skin( see photo).
Intruding into the skin, the fungus forms colonies in the hair follicles of the scalp or hair follicles covering almost the entire body. However, the foci of microsporia, although extremely rare, can also occur in areas completely devoid of hair - palms, soles, nails.
Microsporia is highly contagious( contagious), with the source of infection are sick animals.
Dogs and cats, rabbits, large domestic animals( pigs, goats, horses, sheep), as well as wild animals( monkeys, foxes, tigers, arctic foxes) can be infected with microspores in nature. Infection occurs not only in direct contact with the diseased animal, but also when it comes to human hands, wool and scales with items of care and food, through bedding and other equipment.
In animals, the disease often occurs secretly: lesions are detected only when the fluorescent lamp is illuminated( green glow).Only sometimes on the head, paws or tail can be seen foci with protruding fragments of hairs and scales.
It is possible to transfer the fungus from a sick person to a healthy one. You can get infected even by contact with the untreated clothes of a person who has been ill for some time. Fungus microsporium, thanks to a six-layered shell and ribs in the form of a spider web, is fairly stable in the external environment and retains viability for up to 3 months outside the human or animal body.
Microsporia in children - features of
The prevalence of skin microsporia in children is explained by the following facts:
- Special "love" to mess around with homeless kittens and puppies.
- Non-observance of strict hygiene rules - unwashed hands.
- Insufficient immune protection, weakening of immunity by frequent colds.
- In sebum in adults, there are organic acids that adversely affect the reproduction of the fungus. Skin immunity in children is less developed.
- Frequent skin trauma( cuts, abrasions, scratching and small wounds), which contribute to the spread of the disease when the fungus hits.
- Unexplained from a medical point of view, red-haired children are almost free of ringworm.
Symptoms of microsporia in humans, photo
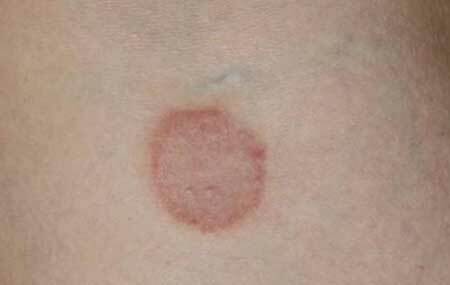
microsporia of smooth skin, photo
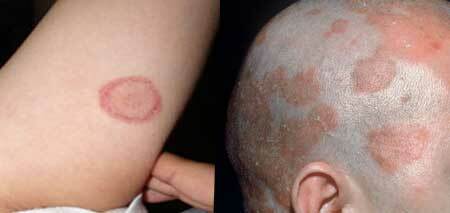
microsporia photo in human
The incubation period for microsporia is 5-7 days when infected from an animal and up to 4-6 weeks - when infected from a sick person.
The external manifestations of microsporia depend on the localization of the pathological focus.
Smooth skin microsporia

Initially appears a red patch of rounded shape, with clear boundaries, slightly rising above the skin. Very quickly, the periphery forms a roller with the smallest bubbles and crusts, and the fungal spot grows to 3 cm.
The central part of the pathological focus turns pale and is covered with fairly large otrepid scales. Most often found 1 - 3 focus on the face, neck, upper limbs.
Itching in microsporia is present, but not as intense as, for example, in allergic rashes.
Microsporia of the scalp
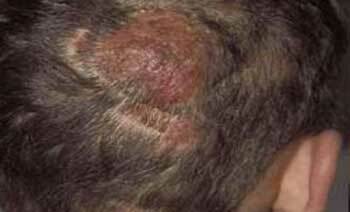
Most often occurs in the head and temples, as well as on the vertex. The fungus colony looks like this: a central large spot reaching 5 cm, and smaller( up to 1.5 cm) screenings along the circumference. With growth, the central spot can absorb nearby small foci.
Microsporia on the head of a person in the initial stage forms focal peeling. On closer examination, one can see a whitish "cuff" around the hairs growing inside the stain. This indicates the reproduction of the fungus at the mouth of the hair, which already after a week leads to their disruption.
It looks like a spot trimmed at the level of 4-6 cm. Broken, with a grayish touch of hairs are a haven for fungal spores. The changed position of the hair "hemp" during stroking is preserved, in contrast to healthy hair.
Actually, the scalp in the lesions is somewhat hyperemic, edematous and covered with small scales of white or grayish color.
Atypical forms
- Microsporia of nails - a dull spot is formed closer to the edge of the nail cut, later acquiring a white color. The nail plate in the lesion becomes soft and crumbles easily.
- Festering microsporia is the result of improper treatment. Against the background of the focus are formed purple-cyanotic nodules and pustules. Possible an increase in temperature and an increase in nearby lymph nodes.
- Weighed microsporia - proceeds chronically against a background of serious internal diseases( tuberculosis, arthritis, etc.).In this case, on the background of focal or diffuse peeling, the areas of alopecia are formed( bald spots), and the general sparsity of the hair cover is noticeable. Hair fragments reach a length of 10-15 mm and do not have gray cases of fungal spores.
- Microsporia pubis - is fraught with infection of the sexual partner. The branched blood system of this region leads to a rapid growth of spots on the labia, the inner thighs and the lower abdomen. Also, a bacterial infection quickly merges with the formation of infiltrates covered with purulent crusts.
Treatment of microsporia in humans, preparations
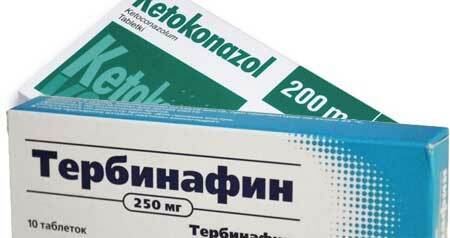
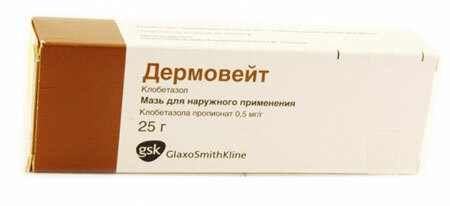
photo preparations
The earlier the microsporia is recognized and its full treatment is prescribed, the sooner the recovery will come. The main direction in the treatment of microsporia in humans is the destruction of the fungus. Given the high stability of the microsporium, local antifungal treatment is supplemented by high doses of systemic antimycotics, especially with a massive lesion of smooth skin or long hair.
Drugs for topical treatment of microspores:
- Clotrimazole is a non-toxic but not highly effective ointment that is the drug of choice for the treatment of microsporia in children under 3 years of age and pregnant.
- Isoconazole, Bifonazole - give a high percentage of allergic reaction.
- Ketoconazole is highly effective, but has a high toxicity.
- Terbinafine is the best preparation for microsporia for nontoxicity, efficacy and price. This is the most inexpensive and effective remedy for ringworm, a more expensive analog - Lamisil.
- Ointments containing sulfur( sulfuric-salicylic, sulfur-tar, sulfuric) and iodine solution - in the treatment of microspores are used in combination with antifungal external agents.
- Combined remedies( Triderm, Mycosolone, Travocort), which have corticosteroids, are suitable only with microscopy complicated by suppuration. It should be remembered: hormonal ointments with prolonged use provoke skin atrophy.
The complex treatment of microsporia of the scalp includes:
- Antimycotic antibiotic Griseofulvin is the drug of choice, it is toxic enough. For children under 3 years of age is available as a suspension.
- High doses of the drug are needed - 22 mg / kg body weight. Do not take with penicillins( simultaneous reception causes an allergic reaction).
- Hepatoprotectors( Karsil, Liv-52 and others) - to reduce the toxicity of Griseofulvin and protect the liver.
- Anti-worm drugs( Decaris) - degelmentization is necessary to increase the effectiveness of antimycotics and reduce the immunosupressive effect of Griseofulvin.
- Terbinafine in tablets( Lamizil) - a less toxic alternative to Griseofulvin, not inferior to it in effectiveness.
Obligatory measures in detecting microsporia in humans:
- Removal of damaged hairs( hair removal, daily shaving).
- Wash your head twice a week.
- Regular change of linen.
- Restriction of contact with a sick person. Isolation of the child from the pre-school, school in the treatment of microsporia in children.
- Inspection of people who have been in contact with a sick person.
- Inspection of pets by a veterinarian.
- Disinfection of articles of care( towels, combs), clothes, children's toys with the help of disinfectants. Spring-cleaning.
All treatment takes 3-6 weeks. Recovery is established with a negative analysis of scrapings from the injury site.
Do not rely on folk remedies. Microsporia is a fungal disease, and it must be treated with antimycotics. Home methods( rubbing with vinegar, etc.) often have a cauterizing effect, and additional irritation can trigger the spread of infection. It is possible to get burns.
Prevention of microsporia
To avoid microsporia, the following rules should be observed:
Avoid contact with stray animals.
Buy pets only after inspection by a veterinarian. Periodically carry out preventive inspections of pets.
Quarantine measures in the detection of microsporia in a child: isolation from a kindergarten / school, disinfection measures, observation of contacts with the patient.