In medicine, there are various names for diagnoses. And at their end, as on shoulder straps on a military uniform, you can accurately understand which category the disease belongs to. So, all inflammatory diseases have the suffix "-it".
These are hepatitis( inflammation of the liver), encephalitis( inflammation of the brain), periostitis, myositis and many other diagnoses. Tumors and tumors end with "-oma"( sarcoma, chondroblastoma, meningioma).
And those diagnoses that manifest excessive growth or change of a specific type of tissue, their configuration, or a violation of the structure, in general, its abnormal development and the formation of nonviable structures, end in "-oz."
These diseases include, of course, osteochondrosis, amyloidosis( which is characterized by the accumulation of pathological protein - amyloid), a serious congenital disease - cystic fibrosis. Such diseases include spondylosis. What does it mean and how does it develop?
Contents of
- 1 Spondylosis - what is it?
- 2 Causes of spondylosis
- 3 Spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine
- 4 Spondylosis of the cervical spine, symptoms
- 5 Complications of spondylosis
- 6 Treatment of spondylosis - drugs and techniques
Spondylosis - what is it?
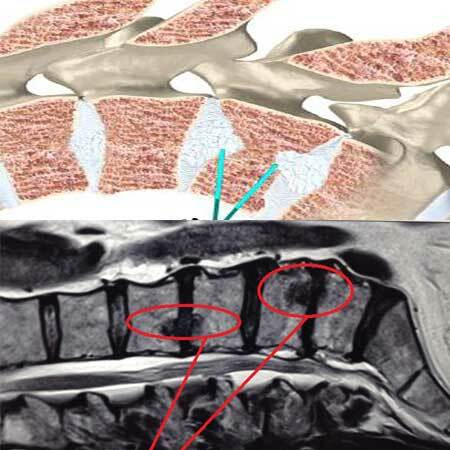
In Greek, "spondylon" refers to the vertebra. Therefore, spondylosis is an overgrowth of the vertebrae with a violation of their configuration. But the vertebra can not turn into a formless bone mass, and grow, wherever it pleases. After all, all vertebrae are connected by special facet joints and ligaments, and through their central orifices passes the spinal cord.
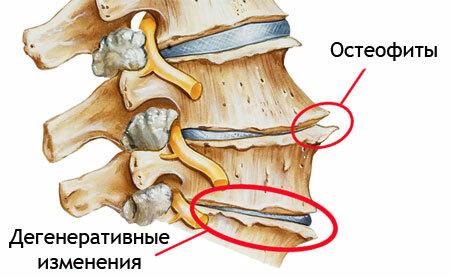
Therefore, only their free edges can grow in the vertebrae, which contact other vertebrae due to abnormally high pressure, or other reasons. These marginal bony expansions are called osteophytes, or bone spines.
It is possible to draw parallels: osteochondrosis is degeneration of cartilaginous tissue with deformation of intervertebral discs, and spondylosis is the same process, but not with a cartilaginous disc-tab, but from the side of bone tissue.
Spondylosis can lead to several important manifestations:
- Vertebra deformation;
- Violation of the internal structure of the bone tissue of the vertebra, which is accompanied by a decrease in its strength;
- Narrowing of the spinal canal;
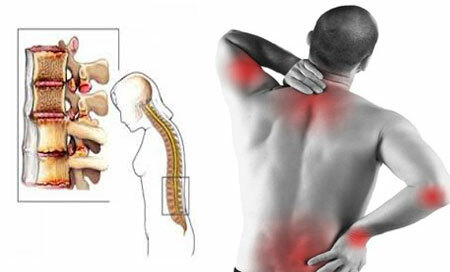
- Limitation of mobility, and the appearance of crunch and pain in the back, neck;
- Periodic irritation of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine, especially the anterior longitudinal ligament. This ligament is quite densely attached to the vertebrae, and the appearance under it of bony growths, in the form of thorns, can have a long and painful effect.
Causes of spondylosis
As with any dystrophic degenerative lesion of the musculoskeletal system, spondylosis never appears suddenly. It does not happen that a person went to bed with a completely healthy back, and the next morning he had in all departments of the spine expressed osteophytes, which would manifest themselves with the corresponding symptoms.
Spondylosis, like osteochondrosis, occurs slowly, for a number of years. The most important reasons for the formation of spondylosis are:
- Chronic, permanent injuries of the ligamentous apparatus of the spine. This may be due to edema of the ligaments, which are reacted deeper by the located vertebrae;
- Long sedentary work and uncomfortable body position, with considerable vertical load. It is shown that office employees who during the working day did not break away from computers and did not do preventive gymnastics, after the first three years of this regime, the first signs of spondylosis appear, and after five years of operation, its occurrence may reach 25-35%;
- Not only immobility, but also strong, short-term loads, which can dramatically increase pressure on the vertebrae, lead to the development of spondylosis. Typically, this occurs when the Sunday load in the country and the potato "potato" of those individuals who sat all week long motionless at the desk, and on weekends allowed themselves a pronounced strain on the back;
- Unfavorable heredity. It is shown that the development of spondylosis in parents increases the risk of children becoming infected;
- Age changes. In the elderly, bone tissue contains fewer organic compounds, and is more fragile;
- Osteoporosis, especially in postmenopausal women, also applies to a significant risk factor;
- Overweight. Simple reasoning shows that in this case there are the greatest chances for the development of spondylosis of the lumbosacral department as the most exposed to stress;
- In some cases infectious diseases can cause the spondylosis with tropicity( affinity) of pathogens to the musculoskeletal tissue( brucellosis, tuberculosis).Most often as a result, there is a complex inflammatory-degenerative lesion, which is called spondylose spondylitis;
- Of course, aggravating diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, irrational nutrition, deficiency of certain substances in the diet can also lead to bone tissue weakness, and as a result - the development of spondylosis.
Below we consider the variants of the most common lesion of the spine, in the cervical and sacral parts of the spine.
Spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine
What is spondylosis of the lumbar spine, we found out before. Now it remains to describe its symptoms and preferential localization. As in the case of osteochondrosis, the most frequent is the localization of osteophytes in the area of 4, 5 of the lumbar vertebra and the upper sacral bone, on which the entire human spinal column rests. So, the symptoms of spondylosis in this localization will be:
- Pains during movement, torso of the trunk, especially in the anteroposterior direction. But, since the irritation of the longitudinal ligament is a constant process, the pain does not disappear at rest, but has a constant and noisy character;
- A characteristic feature that helps diagnosis is the disappearance of pain, or significant relief when the body tilts forward. If you stand or sit like this, "crouching," then the pressure of the osteophytes on the compacted ligament weakens, which leads to a reduction in the pain syndrome;
- If the disease is started, then the radicular symptoms are attached to the constant pains, due to the involvement of the lumbar roots. There are phenomena of lumbosacral radiculitis, with a sharp increase in pain during coughing, sneezing, straining;
- With these phenomena, conductive sensory disorders, such as numbness or "crawling crawling," the appearance of paresthesias, are possible. There may be periodic weakness in the legs, lameness, weakness in the foot due to disruption of the motor nerve root.
Spondylosis of the cervical spine, symptoms of
 Because the spine is a homologous structure, cervical spondylosis is the same pain and impaired function.
Because the spine is a homologous structure, cervical spondylosis is the same pain and impaired function.
Only the proximity of the head allows us to make the correct assumption that spondylosis can not only cause pain in the cervical region, but also headaches, which leads to a general deterioration in well-being and working capacity. In addition to these pains, spondylosis of the cervical spine is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The expressed restriction and a crunch at attempt to turn a head aside, sometimes this crunch is heard by associates, and even at a long distance;
- In case of neglected cases, in full analogy with the lumbar spine, radicular cervical syndromes may occur. They manifest discomfort in the corresponding hand on the side of the lesion. There may be tingling, paresthesia, decreased sensitivity. In the case of defeat of the motor roots, there is a feeling of weakness in the fingers of the hand. Possible development of hypotrophy in the muscles of the wrist when the osteophytes are damaged by the motor roots, and even the development of paralysis;
- Everyone knows the "vertebral artery syndrome" can also develop due to severe spondylosis. Thus there are such signs, as transient disturbances of sight, a giddiness, a nausea, there can be a vomiting.
Complications of spondylosis
If all of the above is not enough to create a complete picture, here are two complications that can result from spinal spondylosis:
1) The development of a hernia in the corresponding spine department. It is difficult to say if spondylosis causes a hernia. But in the event that osteophytes adhere to the intervertebral disc, this complication is only a matter of time;
2) Compression of blood vessels and the central canal, with the development of the myelitis pattern. These complications, as a rule, are a consequence of a deep-seated process. With the compression of blood vessels, the picture of the syndrome of the vertebral artery, with violation of the blood supply to the brain regions, is most common. But sometimes an occlusion syndrome of the anterior spinal artery, which is called the Adamkiewic artery, can develop.
This vessel feeds most of the spinal cord below the lumbar thickening. With significant compression, a spinal cord infarction, sometimes called spinal syndrome of Preobrazhensky, may develop. For him, the following pattern is typical:
- flaccid, peripheral paralysis at the level of lesion( lower back), and below - spastic symptomatology with hypertension of the muscles of the extremities and lively reflexes;
- disturbed pain sensitivity, as well as temperature below the level of occlusion;
- disorder of urination and defecation.
Treatment of spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine with this complication in conservative ways is ineffective, the patient needs operational methods of decompression of the spinal cord and restoration of spinal blood flow. Therefore, when such symptoms of spondylosis appear, urgent hospitalization in a neurosurgical or vertebrological hospital is needed.
Such a stationary institution, for example, can be CITO in Moscow and NIITO( Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, where the outstanding surgeon Ya. L. Tsivyan, who is considered to be the founder of Russian vertebrology and spinal surgery) worked.
But this is an emergency. How to treat spondylosis with therapeutic methods?
Treatment of spondylosis - drugs and techniques
 Like any long-lasting disease, not prone to exacerbations dangerous to life, around spondylosis, as well as around the osteochondrosis of the spine, there are many frankly charlatan techniques that promise a "complete cure".
Like any long-lasting disease, not prone to exacerbations dangerous to life, around spondylosis, as well as around the osteochondrosis of the spine, there are many frankly charlatan techniques that promise a "complete cure".
Actually, the bony growths that have arisen on the body of the vertebra can be removed only in one way - by boring them with special bone nippers, which are part of the arsenal of instruments of traumatologists and neurosurgeons. All other ways and promises to "remove outgrowths", except for operational ones, are ineffective.
The only thing that can be done is using a complex of exercise therapy, unloading the spine, wearing special corsets and reklinators to change the load on the vertebrae and prevent further growth of osteophytes. It is also possible, with the help of medications and non-medicinal techniques, to remove the pain syndrome, which is expressed in the lesion of the longitudinal ligament.
So, the spondylosis of the spine, the treatment of which is carried out by the central muscle relaxants "Midokalm", "Sirdalud", non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can be transferred to the inactive form.
But the main treatment for spondylosis is physical therapy, swimming, and such, for example, techniques like acupuncture, which immediately relieves pain.
- Treatment of cervical spondylosis is reduced to wearing a collar of Shantz, improving cerebral blood flow and preventing the formation of cervical hernias.
- Lumbar osteochondrosis and spondylosis are sometimes offered to cure with UHT, or shock wave therapy. But if in the case of protrusion the elastic cartilage can be put in place, then a dense bone can only be broken. A breakaway osteophyte can cause serious complications, causing compression of large vessels and spinal cord.
Especially it is necessary to be attentive at development of process in a cervical department of a backbone as the affinity of a brain and an opportunity of a compression of large vessels is the raised risk of development of a stroke.
Therefore, it is necessary to know the reserves of the main blood flow of the arteries of the head and neck, and to undergo extracranial dopplerography in a timely manner, as well as to perform x-ray examination of the cervical spine with rotary samples in order to be sure of stabilization of the process.