1 Features of intestinal dysbiosis
Intestinal dysbiosis is a pathological condition in which there is a disturbance of the balance between the useful and opportunistic microflora. This is a clinical and laboratory syndrome, and not an independent disease. Changes can be qualitative and quantitative. In the intestine live more than 500 species of various microorganisms. In the large intestine, their number is greatest. Microorganisms are constantly excreted with feces. Representatives of useful intestinal microflora are the following bacteria: enterococci, lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, E. coli, lactobacilli, bacteroides.
The share of opportunistic microbes is 1%.This group includes Clostridia, Proteus, Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and several others. The value of useful microflora is very high. It is involved in the digestion of nutrients, the digestion of minerals and vitamins. For example, bifidobacteria synthesize various acids( lactic, acetic), which take part in the assimilation of calcium. With the help of these bacteria, decomposition of alcohols, bile acids, and proteins takes place. Useful flora promotes normal metabolism of fats. The protective function is to suppress the growth and reproduction of dangerous microorganisms, to participate in the synthesis of class A immunoglobulins. Dysbacteriosis is diagnosed in 90% of the adult population.
Recommended to read
- Signs of bowel oncology
- Nutrition for intestinal dysbiosis in adults
- Tablets against intestinal dysbiosis
- Effective agent for gastritis and stomach ulcer
2 The main causes of
Symptoms of dysbiosis can be due to various reasons. The following etiological factors stand out:
- decreased immunity;
- presence of HIV infection;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- blood cancer;
- carrying out radiation or chemotherapy;
- systemic diseases;
- prolonged use of antibiotics;
- lack of enzymes;
- lactase insufficiency;
- infringement of intestinal motility;
- carrying out of surgical operations;
- presence of chronic pathology( pancreatitis, gastritis, ulcer, cholecystitis, enterocolitis);
- continued dietary compliance;
- fasting;
- parasitic diseases;
- food poisoning;
- acute intestinal infections( dysentery, salmonellosis).
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
Predisposing factors are the following: regular intake of alcohol, stress, poor ecology. In men and women, dysbiosis often develops against a background of stress. In this situation, the intestinal motility changes. At the same time, the food moves too fast, which affects the activity of the beneficial microflora.

3 Influence of antibiotics
Most infectious diseases are treated with antibacterial agents. Dysbacteriosis often develops when the treatment regimen prescribed by a doctor is not respected, or when antibiotics are used for a long time. Standard therapy regimens can lead to dysbacteriosis, but it is temporary. After a while, the state of the microflora normalizes itself. Especially often dysbacteriosis develops against the background of antibiotic treatment of a wide spectrum of action, which have a bactericidal effect. Such drugs kill both pathogenic and opportunistic and beneficial microflora.

The risk of this pathology is increased in the presence of chronic bowel diseases, inappropriate nutrition, taking medication in the form of tablets or capsules. Oral administration of antibiotics adversely affects the stomach and intestines. Each group of antibiotics acts on certain types of microorganisms. Against the background of tetracyclines, the growth of beneficial bacteria is suppressed, the content of clostridia, fungi of the genus Candida, and staphylococci are increasing. The use of aminopenicillin helps increase the number of staphylococci and streptococci. Recovery may take weeks or even months.
-
 Gastroenterologist VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
4 Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of dysbiosis can be different. There are no permanent signs. The most common symptoms are:
- bloating( flatulence);
- stool disorder by type of diarrhea;
- nausea;
- frequent burp;
- bad breath;
- pain in the abdomen.
With a combination of dysbacteriosis with inflammatory bowel diseases, a slight increase in body temperature is possible. Some patients develop allergic reactions. Dyspeptic disorders and diarrhea are a consequence of the failure of digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. With chronic dysbiosis, weight can decrease. The severity of symptoms is determined by the degree of microbial imbalance and the initial state of the body.

There are 4 stages of intestinal dysbacteriosis. Stage 1 is characterized by a slight disturbance in the composition of the microflora. This condition quickly disappears. At stage 2, there is a shortage of enzymes necessary for the digestion and assimilation of nutrients. At this stage, nausea, flatulence, constipation, or diarrhea may occur. At the 3rd stage of dysbacteriosis, the intestinal mucosa is damaged, which requires consultation of the doctor and the appointment of treatment. Often in patients in the stool, undigested food remains. Stage 4 is distinguished by the complete dominance of opportunistic microorganisms. Often this causes anemia, hypovitaminosis. With a severe form of dysbacteriosis, appetite may decrease. Often worried about headache, weakness, malaise.
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;
5 Diagnostic methods
How to determine a dysbacteriosis? The main method of diagnosis is the laboratory. It involves bacteriological analysis of feces, conducting a PCR test or determining in feces specific substances that are synthesized by a useful microflora( volatile fatty acids).Bacteriological method requires a long time. The material is the feces of man.
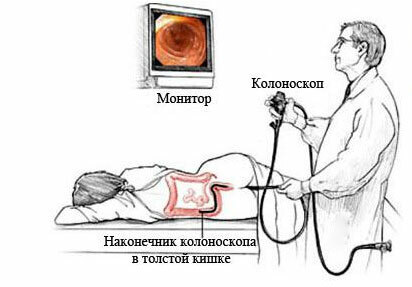
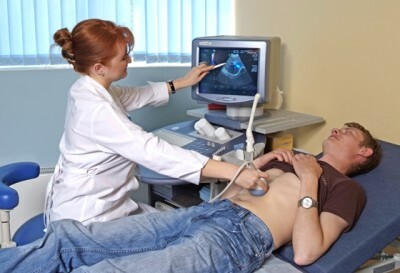
The metabolic test is widely used. It allows to estimate the amount of metabolites of beneficial bacteria. This method is more simple and convenient. An important place in diagnosis is the establishment of the exact cause of dysbiosis. To this end, the general and chemical blood analysis, urinalysis, endoscopy( FGDS, colonoscopy), ultrasound of the abdominal cavity are organized. Of no small importance is the questioning of the patient.
6 Methods of treatment
How to treat intestinal dysbacteriosis? The treatment has the following objectives:
- elimination of the main provoking factor;
- normalization of power;
- elimination of the main symptoms;
- strengthening of immunity.

Treatment of intestinal dysbacteriosis includes the use of probiotics and prebiotics, intake of vitamins, enzyme preparations, increased motor activity, elimination of stresses, avoidance of alcohol and cigarettes, normalization of nutrition.
The basis of treatment is the intake of medications and compliance with the diet.
To cure dysbacteriosis of the intestine, you need to eliminate the main cause of its appearance.
If a person has colon diseases, it is preferable to use those drugs that suppress the growth of opportunistic microbes with minimal impact on beneficial microorganisms. These include Furazolidone, Nitroxoline. If a severe dysbacteriosis of staphylococcal nature is detected, the following medicines can be used: Metronidazole, Biseptol. If feces are found in a large number of fungi, antifungal agents are indicated( Levorin, Nystatin).
7 Restoration of microflora
With dysbacteriosis treatment involves the use of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, enzyme preparations. Probiotics are the means containing living beneficial bacteria. They are indicated in case of detection of dysbiosis 2-4 degree. There are 4 generations of these funds. By 1 generation Bifidumbacterin belongs, the drug is taken orally. The drawback of 1 generation drugs is that bacteria die under the influence of gastric juice. The most effective drugs are 3 and 4 generations. These include Lineks, Bifikol, Biosorb-Bifidum. If necessary, prebiotics are prescribed - substances that promote the rapid growth and proliferation of beneficial microbes. The most commonly used are Dufalac, Hilak Fort.
Often, treatment involves the use of combined drugs( Bifidobac).At 4 degrees of a dysbacteriosis it is first necessary to clear an intestine from pathogenic microorganisms, and only then to apply probiotics and prebiotics. For the purification of the intestine, cephalosporins, penicillins, tetracyclines, metronidazole are used. With dyspepsia and impaired digestion of nutrients, enzyme preparations are prescribed( Creon, Festal).Treatment may include the use of enterosorbents and immunomodulators.

8 Diet
In the presence of a human intestinal dysbacteriosis, treatment involves the optimization of nutrition. This kind of food is called functional. It should be gentle. It is required for a while to refuse sharp, smoked and fat food, strong coffee and tea, alcohol. It is necessary to limit the intake of simple carbohydrates. They are rich in confectionery and bakery products. To reduce the process of fermentation in the intestine, it is advisable to abandon cabbage, grapes, beans, radishes. The food should be divided, carried out in small portions. The optimal frequency of food intake is 4-6 times a day.
There are a number of products that promote the activation of normal intestinal microflora. The list includes cereals( oats, buckwheat, wheat), sweet fruits, vegetables, lactic products( yogurt, yoghurt, kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese).Some products have a disastrous effect on a certain kind of opportunistic and pathogenic bacteria. The E. coli is adversely affected by onions and sweet peppers, on klebsiella - apples, garlic, dill. It is important to include in the diet products that improve intestinal motility. This is fruits, vegetables, juices. They contain dietary fiber and pectin. With dysbacteriosis, the following foods and dishes are prohibited: fresh bread, dough products, pancakes, confectionery, fatty meat and fish, milk soups, cabbage soup, borsch, pickles, canned food, honey, jam, animal fats, spices, fruit drinks, carbonatedwater, milk. In addition, vitamin complexes can be used.

9 Than the dysbacteriosis
is dangerous. Everyone should know not only how to cure dysbacteriosis, but also what this condition can lead to. With prolonged dysbiosis, the following diseases can develop:
- anemia;
- hypovitaminosis;
- chronic form of enterocolitis;
- acute infectious infection of blood( sepsis);
- Inflammation of the peritoneum;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- gastroduodenitis.
Against the backdrop of digestive disorders, the body does not receive the right amount of nutrients, minerals and vitamins, which can lead to weight loss and body exhaustion. To prevent dysbacteriosis, it is necessary to treat acute and chronic diseases of the digestive system in due time, follow the antibiotic treatment regimen, eat right( use lactic products, vegetables, fruits on a regular basis).If you suspect a dysbacteriosis, you need to contact a gastroenterologist and take a survey.
- 1 Features of intestinal dysbiosis
- 2 Main causes
- 3 Influence of antibiotics
- 4 Symptoms of the disease
- 5 Diagnostic methods
- 6 Treatment methods
- 7 Restoration of microflora
- 8 Diet
- 9 Than the dysbacteriosis
This condition, like the intestinal dysbacteriosis, occurs quite often. In a healthy person, the intestine is not sterile, it contains various microbes. Some of them are useful, and others are conditionally-pathogenic, that is, those that are present in the body in a small amount, but cause diseases only under certain conditions. Most often this occurs against the background of taking antibiotics, improper diet or lowering of immunity. Dysbacteriosis is a predisposing factor in the development of colitis and enteritis. What are the etiology, clinic and treatment of dysbiosis?
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method is to write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;