 Severe speech disorders in adults and children can occur as a result of lesions of the central part and peripheral parts of the speech motor.
Severe speech disorders in adults and children can occur as a result of lesions of the central part and peripheral parts of the speech motor.
A similar phenomenon is observed in cases of pathological lesions of certain parts of the brain. Each separate type of speech defect directly depends on which area was damaged.
Contents of
- Characteristics of bulbar dysarthria
- Characteristic of bulbar dysarthria
- What causes
- Age features of
- pathology How does the pathology develop? Symptoms step by step
- What is the difference between bulbar and pseudobulbaria dysarthria
- Diagnosis
- Treatment and correction methods
Characteristics of bulbar dysarthria
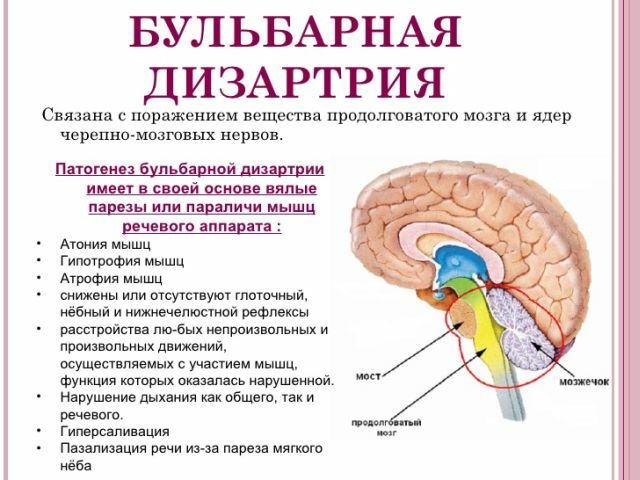
Bulbar dysarthria - violation of those responsible for speechorgans, which is caused by damage to peripheral motor neurons.
In this case, the cells are located in the medulla oblongata( in the Greek language this division is called bulbus, which determined the name of the disorder described), and their processes form motor nerves, the defeat of which leads to impairment of impulses and, as a consequence, to bulbar paralysis.
Bulbar type of lesion involves disruption of the hyoid and lumbosacral nerve, in some cases - facial and vagal.
Bulbar dysarthria is characterized by a violation of the innervation( connection of the organs) of the muscles of the departments of the speech apparatus with the central nervous system.
In particular, the muscles of the larynx, pharynx, palate and soft palate( palatal curtain) are weakened. The main articulation organ -  language - is also unable to perform the necessary movements. The same can be said about the lips.
language - is also unable to perform the necessary movements. The same can be said about the lips.
This type of speech impairment is also called "flaccid" because of the limited mobility of the speech and facial muscles.
Due to a decrease in the mobility of the vocal cords and the soft palate, there is a weakening of the voice;speech at the same time slows down, becomes indistinct and completely indistinct.
"Nasal shade" of speech( when a person speaks as if in a nose) appears due to the fact that the flow of exhaled air when loosening the muscles of the soft palate freely passes through the nose. A person suffering from bulbar dysarthria is not able to reproduce sonorous sounds, and when articulating the vowels "gets lost" to neutral sound. All the labial sounds are roughly distorted when spoken.
The intractability of speech is aggravated by the fact that the patient is not able to control the reproduction of sounds by phonetic trait, that is, to separate voiced and deaf, hard and soft, close and slit.
What causes
This deviation, such as bulbar dysarthria, results from:
- central nervous system lesions that occurred during the fetal development stage or early stage of the child's development, usually such lesions are the result of intoxication, oxygen deficiency, acute and chronicinfections transmitted during pregnancy, which also provoke birth trauma;
- abnormal development of the placenta;
- complications arising after infections affecting the central nervous system( encephalitis, meningitis);
- brain damage, having a mechanical nature;
- of cerebral vascular disease;
- stroke;
- development of a brain tumor - both malignant and benign;
- alcohol, narcotic, drug intoxication;
- carrying out neurosurgical operations.
A similar deviation can also occur in individuals with Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, against the background of the Cairns-Seir syndrome, myasthenia gravis, psychogenic dysphonia.
Age features of the pathology
Dysarthria bulbar can be observed at any age, both in adults and in children, including newborns.
Doctors say that such a disease is more dangerous for young children. Bulbar paralysis is expressed in newborns in problems with feeding.
Lean muscle does not allow them to fully eat: when milk enters the mouth, children choke and can not swallow it;often there is regurgitation due to the fact that the liquid penetrates into the nasopharynx.
To children of preschool age bulbar dysarthria prevents to develop, as they are not able to correctly pronounce sounds, syllables, words against the background of violation of articulation. In addition, a similar pathology makes a child quickly get tired of trying to talk.
To these symptoms, paralysis of the muscles of the extremities or other parts of the body can be added, which does not allow to perceive space and to orientate in it.
Adults with this disorder also have difficulty with speech, swallowing, a full chewing on food. In especially severe cases, such a deviation can lead to a disruption in the functioning of the cardiac and respiratory systems and, as a result, a lethal outcome.
What is Bulbar Syndrome:
And dysarthria as one of its manifestations:
How does the pathology develop? Symptoms Step by Step
The rates of development of bulbar dysarthria largely depend on the background of what disease or condition it develops.
Most often, initially there are difficulties associated with swallowing liquids and liquid food. Then there is a gradual weakening of the muscles of the tongue, and then of the chewing muscles and muscles of the face. The next stage is manifestation of attacks of muscle weakness, speech and breathing disorders.
What distinguishes bulbar and pseudobulbar dysarthria
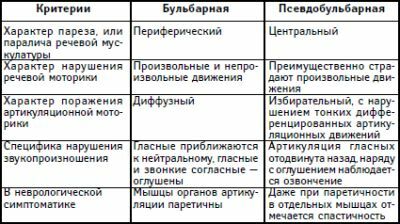 There are several types of dysarthria. At first, it is necessary to note such varieties as bulbar and pseudobulbar forms.
There are several types of dysarthria. At first, it is necessary to note such varieties as bulbar and pseudobulbar forms.
In both cases, there is an adverse effect on the same muscles.
However, bulbar dysarthria is a consequence of peripheral neuron disorder, and pseudobulbaria is central.
Bulbar dysarthria is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Disorder of the muscles responsible for the performance of the swallowing function, which is expressed in difficulty swallowing, and sometimes even in aphagia( inability to swallow).Under such conditions, there is a risk that food will get into the trachea and directly into the lungs, and this is fraught with choking and death.
- Speech disorder. At the same time, it becomes inaccessible to perception. A voice may vanish and the very opportunity to speak.
- The patient is tired of the strain experienced by the muscles of the speech device during the conversation.
- Weakening of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, which is due to the proximity of their location to the disturbed areas of the nerves;
- Deviation of the tongue to the side, not affected by paralysis.
- Hanging the soft palate.
- Absence of pharyngeal and palatine reflexes.
- Uncontrolled crying or laughter when carrying an object over the surface of the teeth.
With regard to pseudobulbar form of dysarthria, it is characterized by: 
- decreased motor activity;
- memory degradation;
- inability to concentrate;
- manifestation of a multitude of reflexes( proboscis reflex, Korzkian's nasolabial reflex, Bekhterev's reflex);
- violations of articulation and phonation, the function of swallowing( in this case, muscle degeneration, as in bulbar form, does not occur);
- involuntary contraction of perioral and chin muscles.
Subcortical( extrapyramidal) and cerebellar dysarthria are also distinguished. The first condition is characterized by a violation of the muscle tone, the manifestation of involuntary movements of facial muscles( hyperkinesis).Violations of speech are ambiguous: the same sounds and words can be pronounced correctly in different situations or vice versa.
Voice can be interrupted, its rhythm, tempo, intonation change.
The cerebellar form is characterized by nasalization of sounds, weakness of voice, tremor of the tongue, impaired coordination of movements, unsteadiness of gait.
Diagnosis of
Bulbar dysarthria diagnosed by such specialists as a speech therapist and neurologist. Speech therapist analyzes the state of the speech apparatus, checks the sound quality, determines the mobility of the facial muscles.
Additionally, to determine the exact cause of the pathology, the neurologist can prescribe the following diagnostic procedures:
- urine and blood tests;
- electromyography of the muscles of the tongue, sometimes also the muscles of the neck and limbs;
- conducted clinical trials on myasthenia gravis;
- investigation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment and correction methods
Therapy of such a deviation should be complex. The treatment process includes:
- Medication administration, in particular - nootropic drugs .They are appointed to stimulate the work of the brain,
 to improve mental performance. Usually recommend the use of Luccam, Carbamazepine, Piracetam.
to improve mental performance. Usually recommend the use of Luccam, Carbamazepine, Piracetam. - Taking medications that help reduce salivary secretion of ( eg, Atropine).This is a necessary measure, since the amount of saliva released during the day in individuals with bulbar dysarthria can reach 1 liter.
- Elimination of the underlying problem of , which triggered the development of a disorder( removal of the abscess or tumor, elimination of hemorrhage).
- Recovery of impaired body functions .For these purposes, the intake of vitamins is recommended.
- Improvement of disturbed respiratory functions of , for which an artificial ventilation is performed.
- Classes with the speech therapist for the development of articulation organs. They include massage of the tongue, work on the correctness of the pronunciation of sounds and on the expressiveness of speech, articulatory gymnastics).
- Therapeutic physical training and physiotherapeutic procedures .
- Reception of medical baths .
- Acupuncture .
It is impossible to make unambiguous conclusions regarding the prognosis of the disease, since bulbar dysarthria leads to disorders of the nervous system and the brain, some of which are irreversible.
Absolutely accurate preventive program does not exist, because the causes and the very essence of the disease are not fully understood. In order to avoid the development of such a deviation in a child, a pregnant woman is advised to give up bad habits, eat right, and when a threat of an infectious disease is immediately consult a doctor.
Adults should also visit a specialist immediately after finding the slightest speech impairment.



