 Kinbeck's disease is commonly referred to as the defeat of the wrist's semilunar bone, which is characterized by its deformation and destruction due to circulatory disorders and nutrient intake.
Kinbeck's disease is commonly referred to as the defeat of the wrist's semilunar bone, which is characterized by its deformation and destruction due to circulatory disorders and nutrient intake.
This disease can also be referred to as osteonecrosis of the semilunar bone, carpal osteochondritis, avascular necrosis, traumatic osteoporosis, aseptic necrosis of the wrist.
However, in our time this ailment is usually called "osteonecrosis" - the death of bone tissue.
Contents of the article
The causes of the disease and the risk group
Causes of the disease and risk groups
Pathology can develop due to constant loads on the upper limbshuman, in particular the wrist joint.
This fact is explained by the anatomical location of the semilunar bone: it is located in the central part of the wrist between the radial and capitate bone, therefore, it is subjected to mechanical stress most under any load on the wrist.
The disease progresses gradually and is most often diagnosed in athletes, as well as people of the following occupations:
- crane operator;
- locksmith;
- ruber;
- carpenter;
- loader;
- sinker in the mine or mine.
Pathogenesis of pathology
Regular minor injuries and damage lead to blood flow disorders in the affected area of bone tissue and are accompanied by minor hemorrhages.
A consequence of this is a violation of bone nutrition, the loss of minerals that give it strength. If the wrist rest continues, it can lead to fractures of the semilunar bone and as a result - its deformation and decay.
Stages of the disease
In modern medical literature, several stages of this disease are distinguished:
- Disruption of intake of nutrients and trace elements to bone tissues. The shape of the semilunar bone remains without the
 changes.
changes. - Minor change in shape with a violation of its integrity.
- In the field of necrosis, bone substance decays and its replacement by fibrous tissues.
- Enhanced deformation and fragmentation of the semilunar bone.
- Damage to a number of located bones, which leads to arthrosis of the wrist joint.
A gradual transition from one stage to another can not always happen.
Often the process ends at the stage of minor deformations.
Characteristic features of
The first signs of this ailment are a feeling of discomfort, periodic pains in the wrist with sudden movements or heavy loads.
When the hand is at rest, there is no pain. Over time, you can visually determine the swelling in the wrist area, the movements of the hand become limited, the hand gradually weakens, and atrophy of the muscles of the forearm. In the late stages of the disease a person feels a crunch during the movement.
Sometimes this disease occurs without any symptoms and is diagnosed absolutely by accident.
Diagnosis: Complexities and capabilities of
In the initial stages, it is quite difficult to establish the correct diagnosis. The attending physician should familiarize himself with the history of the disease, conduct an examination of the patient, and examine the radiograph.
Most patients have complaints of severe pain in the wrist area, which is aggravated during stress and extreme flexion of the wrist. When palpation is determined by soreness, as well as swelling in the area of the semilunar bone.
Often the decisive factor for establishing this diagnosis is radiography. However, this study has a significant drawback: changes in the semilunar bone are determined only 60 to 90 days after the onset of the disease.
The X-ray diffraction diagram gives a clear idea of the shape change and the increase in shadow density of the painful area. The shadow of the bone has an irregular shape of the triangle, its height is slightly reduced, and the edges become wavy and uneven.
The fragmentation stage is confirmed by dividing the bone into separate parts of different sizes with uneven outlines.
In the 3rd and 4th stages of the disease, the flattening of the bone is visible, and the sections of the joint cracks have insignificant extensions. At the fifth stage, bone growths are seen at the edges of the damaged area, as well as adjacent articular surfaces.
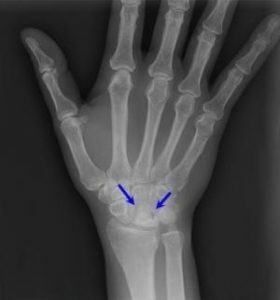 In some cases( mainly at the initial stages of the development of the disease), additional studies are needed, the most useful of which is magnetic resonance imaging.
In some cases( mainly at the initial stages of the development of the disease), additional studies are needed, the most useful of which is magnetic resonance imaging.
With the help of MRI, it is possible to establish a violation in the blood supply of the semilunar bone at that stage of the disease, when its signs can not yet be determined using radiography.
In addition, skeletal scintigraphy or computed tomography can be used.
Methods of treatment
If a disease is detected in its early stages, it is necessary to impose a plaster bandage limiting the mobility of the arm for a period of 60 to 90 days.
At the end of this period, the patient is recommended:
- , the course of the massage;
- exercise therapy;
- mud treatment;
- physiotherapy.
If these measures do not lead to better health, surgical treatment is prescribed, the purpose of which is to reduce pressure on the semilunar bone by elongation of the ulnar or shortening of the radius.
There are other alternatives: restoration of the blood vessels of the semilunar bone by implantation, fixation of the joints in a certain position or removal of a number of bones of the wrist.
At an easy stage of disease the difference in length of bones of a forearm is eliminated. This makes it possible to reduce the pressure on the semilunar bone and to avoid its deformation.
This method allows you not to apply surgery on the wrist itself and prevents the formation of joints after the operation.
If this operation is not possible, the wrist bones are bonded together. A consequence of such an operation can become joint densification and immobility of the brush for some time.
Application of each of these methods leads to the elimination of pain in the future.
Later stages of the disease will require the removal of damaged fragments or total fixation of the bones of the wrist. The first option can lead to partial restrictions on the functioning of the brush, and the second completely excludes its movement.
Most of the operations associated with osteochondropathy of the half-moon bone of the hand are performed under local anesthesia. The first 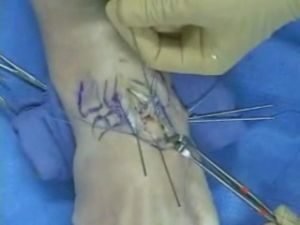 should be applied a few days after surgery with cold compresses, and the hand should be kept above the level of the heart.
should be applied a few days after surgery with cold compresses, and the hand should be kept above the level of the heart.
This will help to significantly reduce pain. After this, a tire or plaster bandage is applied, reaching the level of the elbow joint. In this position, the hand should be between 20 and 90 days, depending on the complexity and mode of surgery.
Possible complications of
In connection with deformation of the semilunar bone and untimely treatment, subluxation of other bones of the wrist may develop.
For example, the scaphoid bone moves from its place, which subsequently leads to arthrosis and functional restriction of the hand.
It is not uncommon for cases in which nerve compression or damage to tendons occurs.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
For the purpose of the fastest possible recovery of health after surgery, a number of rehabilitation measures can be carried out:
- Drug therapy , which includes taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as tools that improve blood circulation and stimulate regeneration.
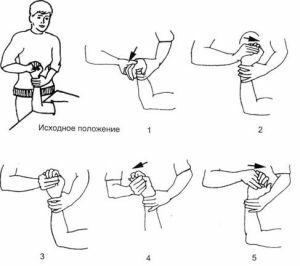
- Therapeutic gymnastics allow to develop a brush and strengthen muscles.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures by ultrasound, electrostimulation, phonophoresis with application of medicinal herbs.
- The course of recovery in specialized sanatoria.
It should be remembered that the treatment of Keenbek's disease is a complex process that can last several months. In the case of progression of the disease, there is sometimes a need for a re-surgical operation.
Early diagnosis, treatment and prevention, the change of work and the restriction of physical activity on the hands - will be the key to success in the fight against this serious occupational disease.