 Epilepsy is a neurological chronic brain disease. It is considered one of the most severe and most common diseases in the neurological profile.
Epilepsy is a neurological chronic brain disease. It is considered one of the most severe and most common diseases in the neurological profile.
Epilepsy is identified, usually at an early age. Spontaneous, short-term, convulsive, arising with an indeterminate frequency of seizures, and loss of consciousness can accompany the patient throughout his life.
Doctors classify the disease into primary and secondary epilepsy. The primary form of the disease is congenital, so seizures can appear already in childhood and adolescence.
Secondary( symptomatic) type of epileptic seizures develops after damage to the structure of the brain( as a result of trauma) or after a metabolic disorder in it( a metabolic abnormality can be triggered by a number of diseases: a tumor, a stroke, infectious diseases, drug and alcohol dependence).
The disease is not new, for the first time its description is found in ancient Egypt before BC.Falling disease, so called epilepsy in Russia. Epileptic seizures occur in every hundredth person in the world.
If, for the treatment of epileptic seizures, physicians can not select medications that adequately control repeated attacks of the patient, the only way out is surgical treatment.
Content
- When not do without surgery
- Lobectomy - resection of the temporal lobe
- Deleting pathological formation
- callosotomy - cut
- callosum Hemispherectomy functional
- Vagus nerve stimulation
- Preparation for surgery
- Conducting intervention
- Subpialnye dissection
- implantation of neurostimulator
- postoperative recovery
- Inside Lookand on the
- side Ask price
When the operation can not be avoided
BasicSpruce surgery - reducing the frequency of occurrence episindromnyh attacks. 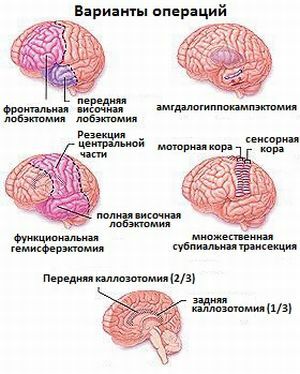
Surgery of epileptic seizures is an extreme measure, but effective. This is the most complicated neurosurgical operation on the patient's brain.
Before the doctors' council decides to localize the epileptic focus of the disease surgically, the patient undergoes a thorough and thorough preoperative examination.
The treatment for epilepsy is surgically prescribed in cases where:
- The main treatment method - antiepileptic therapy does not show positive dynamics. Pharmacotherapy worsens the condition of the patient.
- Drug treatment is effective, but intolerance of the individual components of the drug causes the patient side effects
- Seizures of epileptic seizures are diagnosed only in certain segments of the brain( during operation in certain parts of the brain the vital activity of the patient is not impaired).Additional studies allow you to determine which specific areas are provoked by seizures. In the operation, such areas of the brain are removed.
- Attacks have an atonic character( sudden drop in a patient without seizures)
- The patient has secondary generalization of partial seizures( the patient always loses consciousness) or partial seizures with an aura( before the attack the patient remains conscious).
As practice shows, only 20% of patients with a diagnosis of "epilepsy" for medical reasons are treated surgically.
The postoperative period is an equally important period, therefore it is always followed closely by the doctor.
Contraindications to the appointment of surgical intervention are severe concomitant diseases( for example, oncological and cardiovascular diseases).
To date, there are various surgical methods for treating episyndrome. Selects each of the methods based on the symptoms of the disease and the brain area, which provokes an attack.
Lobectomy - resection of the temporal lobe
 During the operation, the hemispheres of the brain are divided into four sections: the occipital, frontal, parietal, and temporal parts. In adolescents, the most common type of disease is when the epileptogenic focus is concentrated in the temporal lobe, it is extracted during surgery.
During the operation, the hemispheres of the brain are divided into four sections: the occipital, frontal, parietal, and temporal parts. In adolescents, the most common type of disease is when the epileptogenic focus is concentrated in the temporal lobe, it is extracted during surgery.
The focus is localized in the anterior and mesial parts. If you need to remove the brain tissue located outside the temporal lobe, resort to extramemporal resection.
Lobectomy is the most traditional method of treatment of an episodroma. This type of surgical intervention has high rates: in 85-90% of cases, the frequency of seizures in the first year of life after surgery is reduced by almost 95%.
Temporal resection is an open operation. Resection of neurosurgeons is performed using an operating microscope. The surgeon opens the skull, removes the part and opens the brain.
Eliminating the pathology, the possibility of preventing seizures further reaches 80%.The patient prescribes after a week in the absence of complications.
Removal of pathological formation of
Lesionectomy is based on the removal of defeated isolated areas of the brain, the occurrence of which is caused by trauma or pathology.
The patient is in the intensive care unit for the first 24 hours, postoperative follow-up is in the neurosurgical unit.
In most cases, after the lesionectomy, the symptoms of the disease disappear. The patient is discharged from the hospital for the sixth postoperative day.
Callosotomy - dissection of the corpus callosum
The operation prevents the propagation of electrical pathological impulses from one cerebral hemisphere to another. In the process of 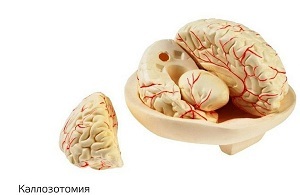 , operations partially or completely break the neural connections between both hemispheres.
, operations partially or completely break the neural connections between both hemispheres.
This method of surgical intervention prevents the spread of epileptogenic tumors and reduces the intensity of seizures.
Indication for surgery is a severe uncontrolled form of seizures, accompanied by severe convulsions, which, as a result, lead to fall and trauma.
Functional hemisferectomy
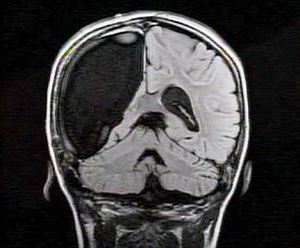 Hemisferectomy is a radical method of surgical intervention, as a result of which the hemisphere of the brain is removed. Indication for such an operation is a severe form of epilepsy( Rasmussen's encephalitis).This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of dozens or more seizures a day( epistatus).
Hemisferectomy is a radical method of surgical intervention, as a result of which the hemisphere of the brain is removed. Indication for such an operation is a severe form of epilepsy( Rasmussen's encephalitis).This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of dozens or more seizures a day( epistatus).
After both hemispheres are detached from each other, significant anatomical parts can be left.
The operation is prescribed for children under the age of 13 years, if one of the hemispheres in the patient is functioning abnormally. It is at this age that the chances of a full recovery are great. Home patient is discharged after 10 days.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve
The operation is prescribed when the patient has multiple foci of epilepsy scattered throughout the cerebral cortex. In the process of surgical intervention, doctors inject under the skin an electronic device that stimulates the vagus nerve.
Stimulator implantation combined with the vagus nerve controls and in some cases prevents the occurrence of seizures. The activity of the brain and the basic internal organs is also monitored.
50% of operations helps reduce convulsive activity and reduce seizures.
Preparation for operation
If a decision is made to perform an operation for the treatment of epilepsy, the patient must observe certain precautions before surgery:
- to avoid causes of seizures;
- continue to take daily medications;
- do not eat and drink 8 hours before surgery;
- to exclude insomnia( for this patient takes low doses of benzodiazepines);
- premedication for sedation is prescribed only by a doctor.
Intervention
Stimulation of the vagus nerve is one of the most common methods of treatment of an episodroma. To stimulate the vagus nerve, the 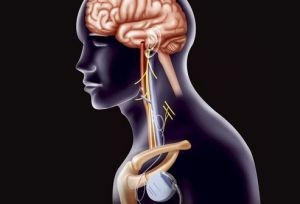 is implanted with a generator implantation. A neurosurgeon makes two small incisions. One under the clavicle in the left side of the thorax, and the second on the neck, also on the left side.
is implanted with a generator implantation. A neurosurgeon makes two small incisions. One under the clavicle in the left side of the thorax, and the second on the neck, also on the left side.
Further the system consisting of the generator of electropulse, electrode and cable is implanted under the skin. The surgeon inserts a generator under the skin on the chest, and the electrode fixes on the vagus nerve through a cut previously made on the neck.
The thin cable serves as a connecting element between the generator and the electrode. The duration of the procedure is 60 minutes. The patient is allowed to leave the hospital on the next postoperative day.
Subpial dissections
Subpial dissections - removal of epileptogenic foci that are located in the brain. Foci are located in the motor zone or in the speech center of the brain, so it is almost impossible to remove them without neurological damage.
Then the decision is made to conduct subpial dissections. The neurosurgeon doctor on the tissues around the hearth carries out many small transects.
Notches prevent the distribution of epileptic activity to other areas in the cerebral cortex. It is important that the functioning of the brain in this case is not violated. On the fifth day the patient can be discharged.
Implantation of neurostimulator
 The operation consists in implanting a neurostimulator under the scalp, connected to two electrodes. The neurostimulator is located directly in the part of the brain that promotes convulsive activity.
The operation consists in implanting a neurostimulator under the scalp, connected to two electrodes. The neurostimulator is located directly in the part of the brain that promotes convulsive activity.
The device captures the electrical activity of the brain and performs stimulation in these areas. Thanks to the implanted neurostimulator, brain activity normalizes earlier than the seizure develops.
All surgical procedures are performed in both adults and children.
Post-operative recovery of
After surgical intervention, the patient is under the supervision of the attending physician, who follows:
- neuropsychological development;
- neurological deficit;
- quality of life of the patient;
- psychological adaptation of the patient.
In the complex carried out control is the key to successful recovery and a barrier for the recurrence of the disease.
As for the patient himself, he must:
- observe the regime moments( correctly take medications);
- more rest, sleep should be full;
- eliminate overstress, stress;
- to abandon bad habits.
The rehabilitation period is 60-90 days.
A look inside and from
Reviews about the treatment of epilepsy surgically.
At the age of 20, as a result of a car accident, the doctors diagnosed "Eisindrom".Spontaneous seizures and convulsive attacks occurred three times a day. Life has become a constant fear of waiting for the manifestation of the disease.
The treating doctor after diagnosis advised surgery. It was necessary to remove the pathological formation. It was scary, because the operation is still on the brain. There was no choice, agreed. The lesionectomy was rapid, calm and without complications. Now I'm completely healthy. Thank the doctors.
Grigory, 21 year
For us - therapists, the main method of therapy for many patients with episodrome remains antiepileptic treatment. But, unfortunately, for most patients this method is unacceptable for medical reasons. Only after a long study of the medical history, diagnosis and analysis of the results of the survey is the decision - to treat epilepsy with the help of surgical intervention.
Alexey Sergeevich, doctor-neurosurgeon
Question price
 Operative treatment of epilepsy is a process not only laborious, but also not budgetary. Thus, the cost of surgery in Moscow for focal and extra-temporal resection varies in the range of 60000-100000 Russian rubles.
Operative treatment of epilepsy is a process not only laborious, but also not budgetary. Thus, the cost of surgery in Moscow for focal and extra-temporal resection varies in the range of 60000-100000 Russian rubles.
The operation by the method of temporal resection can be performed already starting from 40,000 rubles.
The most costly method is hemisferectomy. The price of the service is from 90,000 rubles.
In Israel, the cost of surgery to get rid of the episode is about 3000-12000 US dollars. The cost includes consultation of highly qualified doctors, diagnostics, examinations, preparation for the operation, the very process of surgical intervention, as well as postoperative supervision and care.


