1 Causes of development of pathology
Bleeding can occur in any part of the digestive tract: stomach, intestines, esophagus. Diseases that are capable of provoking bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract are many, and therefore they are usually grouped into groups:
- Pathologies associated directly with the damage to the digestive tract. It can be peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, tumors, diverticula.
- Bleeding caused by portal hypertension. This includes liver disease - hepatitis and cirrhosis.
- Pathological changes in the walls of the vessels, characteristic of varicose veins of the esophagus, scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, atherosclerosis.
- Blood diseases, such as hemophilia, leukemia, anaplastic anemia, thrombocythemia.
There are certain factors that can directly cause gastrointestinal bleeding, in particular, the intake of medicines( aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, some hormonal drugs).As such factors can be alcohol intoxication, exposure to chemicals, excessive physical stress, severe stress.
2 Types and symptoms of the disease
The classification of gastrointestinal bleeding is very extensive:
- By the nature of the course: acute and chronic.
- For etiological reasons: ulcerative and non-ulcerative.
- Localization: from the upper or lower esophagus.
- According to clinical manifestations: profuse, torpid, stop, continue.
- By severity: light, medium and heavy.
- By volume of blood loss: insignificant, moderate, abundant.
- Intensity: explicit and hidden.
Recommended to consult
- Characteristic symptoms of intestinal bleeding
- Code of chronic pancreatitis according to ICD-10
- Classification of intestinal colic in ICD-10
- Effective agent for gastritis and gastric ulcer
Symptoms and signs of the disease under consideration directly depend on the type of pathology and degree of its severity. In general, it is accompanied by severe weakness, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, pallor, lowering of blood pressure. The patient may have a cold sweat, cut or palsy heartbeat.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
If the bleeding is weak, then its manifestations will be insignificant. Thus, a patient can have tachycardia without changing blood pressure. Chronic gastrointestinal bleeding also does not have pronounced symptoms. By its nature, it resembles a greater degree of iron deficiency anemia. Symptoms are increased fatigue, reduced efficiency, general weakness, pale skin, frequent dizziness. In a patient with chronic HCC, stomatitis and glossitis often develop.
Bloody vomiting and the same stool are the most prominent signs of the onset of HCC.In this case, the unchanged blood type in the vomit suggests that bleeding has occurred in the upper gastrointestinal tract. If the source of blood flow is the stomach or duodenum, the blood will have the colors of the coffee grounds. With a profuse type of pathology, the blood in the vomit will be bright red.

With regard to the stool, with large blood loss from the lower part of the GFR, the blood will be there in its pure form. If such an episode was repeated, the feces will be black and resemble tar. If there is less than 100 ml of blood in the gastrointestinal tract, a possible change in stool color may be unnoticed.
-
 Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
3 Diagnosis, treatment and prognosis
If you suspect a gastrointestinal bleeding, you need to determine exactly which department is damaged. For this, the patient is given fibrogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy. With the help of these methods, any defects on the mucosa of the digestive tract and, accordingly, the true source of bleeding are detected.
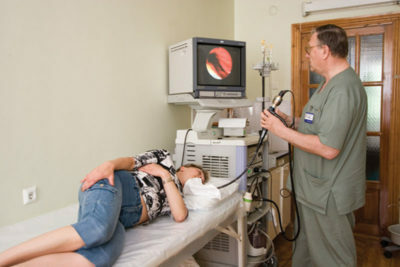
To correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment, you need to be able to assess the severity of blood loss. It is also necessary to distinguish between gastrointestinal bleeding from the pulmonary and nasopharyngeal. To do this, endoscopy of the nasopharynx and bronchi is performed.
Primary treatment measures should be aimed at stopping bleeding. In some cases, surgical methods of action may be required for this. At 1 and 2 degrees of severity of the pathology treatment is carried out using conservative methods, by introducing special medicines. At 3 and 4 degrees, as well as with profuse and recurrent bleeding, which can not be stopped by medication, an operation is performed. Emergency surgery is required and with a perforated ulcer. Various surgical techniques are applied depending on the specific situation. In most cases, treatment is limited to conservative methods.
TIP FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;
During an acute period it is important to follow a special diet. The patient is not allowed to eat for several days, until the bleeding ceases completely. After this, it is recommended to take food in liquid or semi-liquid form( mashed potatoes and porridges, yogurts and kissels, rubbed soups).Categorically not allowed to receive hot food, only in a cooled form.
The prognosis of the disease depends on many factors, among them the following are important:
- causes that caused bleeding;
- degree of blood loss;
- the age of the patient;
- concomitant diseases.
In the absence or untimely provision of qualified care, the risk of complications and death of the patient is high.
- 1 Reasons for the development of the pathology
- 2 Types and symptoms of the disease
- 3 Diagnosis, treatment and prognosis
There is a classification according to which each disease is assigned an international code. So, according to the ICD-10, the gastrointestinal bleeding received code K92.Abbreviation ICD-10 means that the classification of all diseases is revised for the tenth time.
Gastrointestinal bleeding( HCC) is a complication of various diseases and represents the appearance of blood in the cavity of the digestive tract. This pathology is one of the most frequent causes of emergency hospitalization in the department of surgery. The main thing in this case is stopping bleeding, stabilizing the patient's condition and preventing the development of repetitions.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;