Diabetes is classified as a group of diseases characterized by an increased concentration of glucose in the blood plasma, leading to premature aging of the human body and affecting almost all systems of its vital activity.
Acute complications of diabetes are considered to be life threatening:
- Hypoglycemia - glucose drops to 2.8 mmol / l. If the indices become even lower, then a hypoglycemic coma may occur;
- Hyperglycemia - increased serum glucose;
- Ketoacidosis is a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, resulting in excessive production and poisoning with ketone bodies and acetone.
Depression of consciousness in hypoglycemia rarely leads to death. What can not be said about ketoacidosis and severe hyperglycemia, which can cause a deadly state of coma in diabetes mellitus.
Diabetic coma

Diabetic coma is a life-threatening complication of the course of diabetes, which is caused by insufficient insulin production. Such a malfunction causes a state of hyperglycemia, too much increased production of glucagon, somato- and corticotropin. Violated the balance of electrolytes and acid-base blood, protein and water metabolism. Depending on which of these disorders becomes predominant, there are three variants of diabetic coma:
- ketoacidotic;
- is hypersmolar;
- is hyperlactacidemic.
Ketoacidotic coma( DKA)
This is a common coma in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Most often, DKA is called hyperglycemic or hyperketonemic. It develops quite quickly - in a few hours or days.
This form of coma occurs due to poisoning with ketone bodies and acetone. Because of the lack of sugars, the body cells begin to produce energy from proteins and fats, and not from glucose. It is because of this that acetone acetic acid and ketones are formed.
DKA occurs with the following indices:
- Glucose in the plasma exceeds 13.9 mmol / l( 2.8-5.5 norm).The indicators are purely individual, but, as a rule, it is from 30 to 40 mmol / l( limit 50).
- Ketone bodies in the blood - above 5, to 8-17 mmol / l( norm 0.08-0.43).
- Residual nitrogen in the blood - increases to 10-12 mmol / l.
- Ketone bodies in urine( ketonuria) -( ≥ ++).
- Acid-base balance of arterial blood - below 7.3.
- The leukocyte blood formula is shifted to the left.
- Increases the content of acetone and glucose in the urine.
The severity of DKA( light, medium or heavy) is determined by the level of bicarbonate of the serum of ketone bodies in the blood and urine.
For DKA, the following symptoms are typical:
- From the mouth it smells of apple, acetone.
- Due to strong intoxication of the body, hyperventilation of the lungs occurs and Kussmaul's breathing appears - the patient breathes often, deeply and noisily;
- nausea and bouts of vomiting.
- Dehydration of the body. A weight loss of up to 10% is possible. Dryness of the skin. The face is pale( less often, but there may be severe redness of the entire face and neck).The skin on the palms and soles is icteric. Over the entire surface of the body, the skin can peel off, itch. Quickly develops furunculosis.
- Muscles of limbs are flaccid, there are no reflexes. Hands and feet are cold to the touch. Body temperature decreased. Sometimes a symptom of Kernig is observed.
- The tone of the eyeballs is reduced, so the eyes are very soft when palpated. The pupils become narrower or become different in size. Sometimes there is a squint, a descent of the upper eyelid.
- Frequent urge to urinate. Which in a deep coma becomes spontaneous. Urine acquires a fruiting odor.
- The abdomen is bulging and sore, the front wall is tense, the intestinal peristalsis is weakened, diarrhea.
- Degree of impaired consciousness - from drowsiness and lethargy to coma.
- Blood pressure lowered;
- Intoxication of the brain leads to bouts of epilepsy, confusion, delusions and hallucinations.
Delay in assisting or misconduct leads to disastrous consequences: heart attack, pneumonia, cerebral edema, sepsis.
Hypersmolar coma
This type of coma, although it occurs 6-10 times less often than DKA, but in 50% of cases leads to the death of the patient. Hypermolar coma is a diabetic coma, in which the increase in sugar in the blood is not accompanied by the production of ketone bodies and acetone, and the coma is caused by a sharp and severe dehydration.
During the hypersmolar syndrome, the electrolyte content in the blood increases, the osmolality rises, the glucose content rises sharply - above 30, usually from 40 to 50( limit) mmol / l, but the blood pH remains normal.
With signs of hypersmolar syndrome, elderly diabetics with a "long history" of type 2 diabetes mellitus are most often hospitalized. However, all non-insulin dependent diabetics need to be on guard - in 10% of cases the diabetic coma of the hypersmolar type ends with a ketoacidosis coma.
Hypersolar coma develops for several days or even weeks. The first days are characterized by a sign of frequent urination, which is practically absent by the time of hospitalization. Symptoms and signs of this form are no different from ketoacidosis, with the exception of vomiting, Kussmaul breath and acetone odor from the mouth. This form is also characterized by cramps, paralysis of certain muscle groups and nystagmus - convulsive frequent movements of the eyeballs.
Hyperlactacidemic coma
This is a rare complication of diabetes mellitus, which is common in elderly diabetics with severe chronic heart, kidney and liver diseases. The primary cause of the occurrence is increased formation and reduced utilization of lactate and hypoxia. Poisoning of the body develops due to excessive accumulation in the body of lactic acid - more than 4 mmol / l, according to some definitions - more than 2 mmol / l, a violation of the balance of lactate-pyruvate and the development of metabolic acidosis with a large anionic difference( ≥ 10 mmol / l).
Assistance for diabetic coma
Despite the fact that diabetic coma is a deadly complication of diabetes mellitus, they still have a reversible character - if the first urgent and subsequent medical qualified care is provided correctly, a lethal outcome can be avoided.
Diabetic coma are common first signs:
- severe thirst;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- strong weakness;
- paroxysmal headaches;
- lethargy and drowsiness, followed by nervous excitement;
- lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting.
Emergency care for diabetic coma
In the case of DKA, the following symptoms are added to the general symptoms:
- a diabetic suffers from a hunger attack;
- the body periodically shudders and sweats;
- there is a feeling of anxiety and fear.
At the very beginning of an attack and before its arrest it is necessary to call an ambulance, and then to perform a number of simple procedures. With diabetic coma, you need to put the patient on his side, wrap him and warm his feet. After that, measure the glucometer concentration of glucose, analyze the ketone test strip of any portion of urine and wait for the arrival of physicians. Do not inject insulin.
Ideally, if an ambulance doctor immediately injects 20 short-acting insulin( ICD) units and starts administering a 0.9% NaCl solution at a rate of 1 l / h. If the mind of the diabetic is preserved, such actions can be performed upon arrival in the intensive care unit.
Intensive therapy
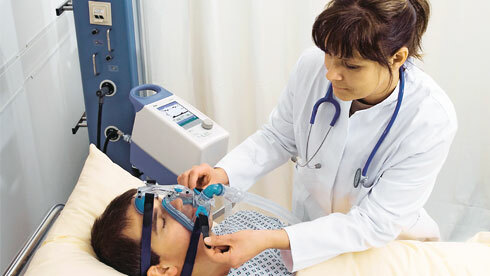
When hospitalized, the patient is equipped with an artificial lung ventilation device, followed by an infusion treatment with furosemide, mannitol and insulin therapy. For hypersmolar syndrome, insulin doses are halved. When the glucose level reaches 15-20 mmol / l, insulin is injected according to the algorithm - 2 units of insulin at 6 mmol / L of glucose.
Before providing medical care for hypersmolar coma, it is extremely important to conduct a differential diagnosis with cerebral edema in order to avoid erroneous diuretic appointment instead of rehydration.
Emergency care for hypoglycemic coma
At what lower sugar index do you need to start emergency activities? In patients receiving soshorosnizhayuschee therapy, to prevent coma, you need to proceed with a plasma glucose level = & lt;3.9 mmol / l. Emergency aid for diabetic coma( hypoglycemic variety) is performed according to the following scheme:
- Easy form ( self-help possible):
- Take 1-2 XE fast carbohydrates - 3-5 pieces of sugar for 5 grams or 1 tablespoon of jam( honey).It is possible to replace 100-200 ml of fruit juice( sugar lemonade) or 4-5 tablets of glucose( 3-4 g).
- If hypoglycemia is caused by prolonged action of insulin( especially at night) - then it is mandatory to take 1-2 XE slow carbohydrates( bread, porridge, pasta).
- Severe form ( unconsciousness, need help from a relative):
- Patient lying on one side. Check that the oral cavity is not occupied with food.
- Initiate a jet injection of 40% glucose solution( maximum 100 ml) or 1 mg glucagon before reconstitution. For children, the dosage is halved.
- If consciousness is not restored - call an ambulance and begin a dropwise injection of a 5-10% solution of glucose.
In the treatment of diabetic coma adhere to the general scheme:
- intensive rehydration - elimination of symptoms of dehydration;
- recovery of insulin deficiency and glucose level;
- normalization of acid-base balance, intracellular electrolyte composition and carbohydrate metabolism;
- diagnosis of the underlying causes of coma and complex therapy to restore normal life.
Consequences of
In case of onset of diabetic coma, timely measures to stabilize the condition, competent treatment and rehabilitation will avoid serious consequences: paralysis, cerebral edema, sepsis, heart attack, stroke, true coma, lethal outcome.
Diagnosed "Diabetes mellitus" in no case should lead to panic and suicidal thoughts. Proper treatment tactics, strict self-discipline and control, a fashionable low-carbohydrate diet, regular exercise and weight normalization, categorical refusal of self-treatment, will not only help to avoid severe chronic complications, but also to live a full life.