 Tumors of bones take a special place in oncology, as they are accompanied by great difficulties in the process of diagnosis and treatment.
Tumors of bones take a special place in oncology, as they are accompanied by great difficulties in the process of diagnosis and treatment.
Ewing's sarcoma is an exclusively malignant tumor.
Its frequency is about 9% of all malignant bone tumors, which is 3 times more likely than osteogenic sarcoma.
Mainly observed in children and adolescents. Females are sick less than 2 times that of males.
Article Contents
- Historical background
- Etiology
- clinical picture
- Features of clinical protocols examination and treatment
- Radiology
- Morphological study
- Differential diagnosis
- Stages flow
- disease possibilities of modern medicine
- forecast
Historical background
as an independent nosological form of sarcoma was allocated Ewing in 1921.Stressing the origin of the tumor from the endothelium of the vessels, the author called it endothelioma. At present, discussions about the nature of education are continuing.
This type of sarcoma develops from the reticuloendothelial tissue and consists of cells that in the course of their development did not differentiate and did not acquire characteristic properties.
Depending on which tissue( bone, cartilaginous, connective) predominates in the tumor, the following are distinguished:
- osteoblastic;
- chondroblastic;
- fibroplastic sarcomas.
The first of these is called the Ewing tumor.
A characteristic localization of osteogenic sarcoma is the diaphysis of long tubular bones. The femur and tibia are most often affected. The wings of the iliac bones, scapula, and vertebral bodies suffer considerably less.
Basically, only one bone is involved in the pathological process. Foci of tumor cancellation can be found in the liver, lungs, lymph nodes.
Etiology
The causes and mechanisms of bone tumors have not been fully understood to date. Most scientists adhere to the theory of multistage stage carcinogenesis.
According to this view, the tumor occurs during the sequential accumulation of various lesions of the genetic 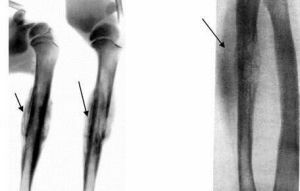 cell apparatus.
cell apparatus.
These changes can occur under the influence of physical( radioactive and ultraviolet radiation), chemical( nitrosocompounds, polycyclic carbohydrates, cytostatics, heavy metals, benzene and its derivatives), bolographic( human papillomaviruses, Epstein-Barr, hepatitis B, HIV)
picture
Ewing's sarcoma can often have symptoms that vary greatly in different cases.
Often, the disease can simulate chronic osteomyelitis. In most cases, the onset of the disease is erased. The main complaint that leads a patient to a doctor is pain.
The pain is wavy. The tumor is characterized by rapid growth. With an increase in the size of the pathological focus increases pain, there is swelling of surrounding tissues.
As a result of arisen venous stasis, the superficial veins widen, and the skin becomes thinner, acquires a cyanotic color.
After 4-5 months from the onset of the disease, the movements in the nearest joint gradually decrease, up to the development of pain contracture.
The limb loses its support function. This symptom is also characteristic of osteogenic sarcoma. In the case of Ewing's tumor, the whole clinical picture develops much more slowly.
When palpation of the tumor, you can determine its dense consistency, in some cases softening foci can be determined. This sign appears as a result of the decomposition of the affected tissues. In the late stages of the disease, with palpation of the formation, a crunch may appear.
In most cases, an increase in lymph nodes is not observed. At the initial stages, the general well-being of the patient does not change. Only after 3-4 months, when the tumor reaches significant dimensions, the body temperature rises to 39 0С.
Some authors identify two variants of the course of the disease.
- In one case, the tumor remains undetected for a long time, metastases appear late.
- In another case, the disease progresses rapidly, causes bone destruction, the tumor early metastasizes.
Features of clinical protocols for examination and treatment
Before the appointment of treatment, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination:
- general clinical analysis of blood, urine;
- biochemical blood test;
- definition of group affiliation of blood, Rh-factor;
- blood test for syphilis;
- electrocardiography;
- chest radiography;
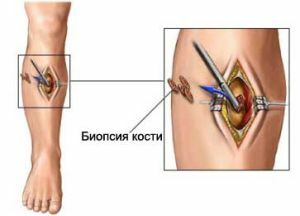
- X-ray of the affected limb segment;
- ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- tumor biopsy with further morphological examination( if available);
- computed tomography of pathological education;
- consultation of narrow specialists( for correction of possible special therapy).
Only after a comprehensive examination of the conclusion of a consultation, the patient is referred for specific or symptomatic treatment.
A laboratory blood test can reveal an increase in the number of leukocytes, acceleration of the ESR.In the late stages of the disease, anemia develops. In the biochemical study of blood and urine, there is an increase in alkaline phosphatase, which is characteristic of the malignant process.
X-ray diagnostics
At the beginning of its development on the roentgenogram, the tumor has blurred and fuzzy outlines. Characteristic of osteoporosis in the form of scattered spots, the destruction of the cortical layer of the tubular bone.
When a lesion of the periosteum( accompanied by a sharp increase in pain) appears characteristic radiographic signs - "visor".
During the progression of the disease, the "visor" increases, an onion-like pattern appears, and the medullary canal narrows.
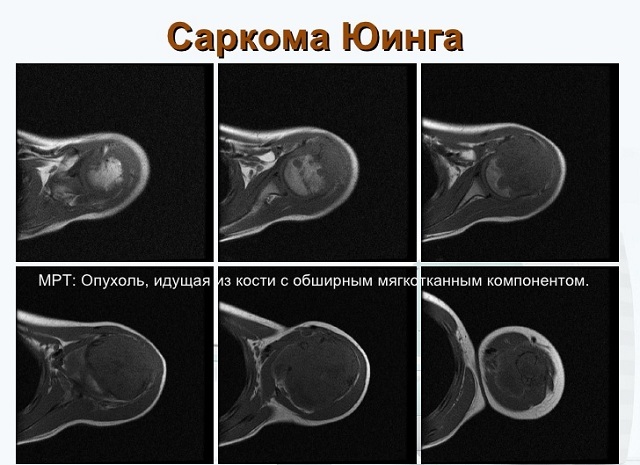
On the photo of Ewing's sarcoma and the stage of its development
X-ray varieties of Ewing's sarcoma:
- small-focal, scattered bone or oval bone fracture;
- longitudinal defibration and stratification of the cortical layer with the formation of lamellar destruction;
- large foci of bone destruction.
Morphological examination of
Microscopically, the tumor tissue is represented by monotonous small cells with a rounded nucleus and an indistinctly delineated cytoplasm.
The nucleus of the cell is brightly colored, occupying the entire cell. Intercellular substance is not determined. Cell division is not numerous.
Differential diagnosis of
Ewing sarcoma must be differentiated with chronic osteomyelitis, periostitis, osteosarcoma, bone metastases and lymphoma.
The stages of
sarcoma Ejin's disease course develops in 4 stages:
- I stage .Patients complain of pain. Visually, the limb is not changed. On the roentgenogram, the tumor looks like an indistinct focal osteoporosis with sclerotic inclusions, the surrounding bone tissue is not changed.
- II stage .The pain intensifies. The limb in the tumor region becomes edematous, cyanotic. On the roentgenogram there is a symptom of a "peak".
- III - IV stage. The pain becomes intolerable. Pathological education can be palpated, it can be determined visually. The skin over the tumor starts to shine. The function of the limb is severely impaired.
The possibilities of modern medicine
The treatment of Ewing's sarcoma is the combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy , which is determined by the high sensitivity of the tumor to these factors.
The most effective radiation is in a total dose of 4000-5000 R. Surgical treatment due to its biological characteristics is receding into the background.
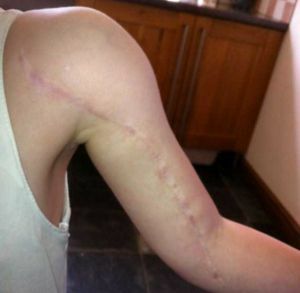
The girl was removed and then stitched back
The operation is most often performed in the amputation of the limb.
This type of treatment is possible only in conditions of compliance with the rules of ablastics and antiloblastics.
However, surgical treatment can not prevent the occurrence of metastases.
At the present stage of development of medicine, new chemotherapeutic agents are being developed, which make it possible to avoid surgical intervention.
Forecast
The course of the pathological process is quite fast. Metastases are observed during the first year of the disease. Even with the conditions of timely treatment of the disease, a prognosis for life should be given cautiously.